Temocapril (CS-622; CS622; temocaprilum; Aceco) is a potent and long-acting angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitor, approved for use (not in the USA) in the treatment of hypertension. Temocapril is a prodrug-type of ACE inhibitor not approved for use in the United States, but was approved in Japan and South Korea. Temocapril can also be used in hemodialysis patients without risk of serious accumulation.
Physicochemical Properties
| Molecular Formula | C23H28N2O5S2 | |
| Molecular Weight | 476.61 | |
| Exact Mass | 476.144 | |
| CAS # | 111902-57-9 | |
| Related CAS # | Temocapril hydrochloride;110221-44-8;Temocapril-d5;1356840-03-3 | |
| PubChem CID | 443874 | |
| Appearance | Off-white to yellow solid powder | |
| Density | 1.33 g/cm3 | |
| Boiling Point | 717.4ºC at 760 mmHg | |
| Melting Point | >230ºC (dec) | |
| Flash Point | 387.7ºC | |
| LogP | 3.3 | |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 2 | |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 8 | |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 11 | |
| Heavy Atom Count | 32 | |
| Complexity | 644 | |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 3 | |
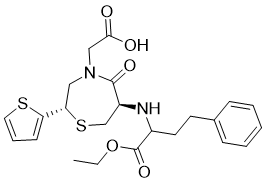
| SMILES | CCOC(=O)[C@H](CCC1=CC=CC=C1)N[C@H]2CS[C@@H](CN(C2=O)CC(=O)O)C3=CC=CS3 |
|
| InChi Key | FIQOFIRCTOWDOW-BJLQDIEVSA-N | |
| InChi Code | InChI=1S/C23H28N2O5S2/c1-2-30-23(29)17(11-10-16-7-4-3-5-8-16)24-18-15-32-20(19-9-6-12-31-19)13-25(22(18)28)14-21(26)27/h3-9,12,17-18,20,24H,2,10-11,13-15H2,1H3,(H,26,27)/t17-,18-,20-/m0/s1 | |
| Chemical Name | 2-[(2S,6R)-6-[[(2S)-1-ethoxy-1-oxo-4-phenylbutan-2-yl]amino]-5-oxo-2-thiophen-2-yl-1,4-thiazepan-4-yl]acetic acid | |
| Synonyms |
|
|
| HS Tariff Code | 2934.99.9001 | |
| Storage |
Powder-20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
|
| Shipping Condition | Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs) |
Biological Activity
| ln Vitro | The prodrug of Temocaprilat, an ACE inhibitor, is Temocapril hydrochloride. Temoprilat hydrochloride is easily absorbed by the small intestine and then processed by CES1 (human carboxylesterase 1) in the liver to produce its active metabolite, temoprilat [1]. In spontaneously hypertensive rats (SHR), temocapril hydrochloride (500 nM) lessens the inhibitory effects of RS (N-acetyltetradecane renin substrate) and AngI (angiotensin) on neurogenic vasodilation [2]. The redox protein thioredoxin (TRX) is stimulated by temocapril hydrochloride (0.1–10 μM; 24 h), although the expression of the antioxidant enzymes Cu/ZnSOD and Mn-SOD is unaffected [3]. |
| ln Vivo | In addition to improving autoimmune myocarditis, temocapril (10 mg/kg; oral; 21 days) increases the expression of thioredoxin in cardiomyocytes [3]. Temocapril (30 mg/kg; oral; once daily; for 4 weeks) did not lower renal Ang II levels but does suppress angiotensin I-induced hypertension, plasma, and renal ACE activity [4]. |
| Cell Assay |
Western Blot analysis [3] Cell Types: Cultured neonatal rat cardiomyocytes Tested Concentrations: 0.1 μM, 1 μM, 10 μM Incubation Duration: 24 hrs (hours) Experimental Results: The expression of redox protein thioredoxin (TRX) was enhanced by 1.9 times at 10 μM , and does not affect TRX2, Cu/Zn-SOD or Mn-SOD protein expression. |
| Animal Protocol |
Animal/Disease Models: Experimental autoimmune myocarditis (EAM) rat model [3] Doses: 10 mg/kg Route of Administration: po (oral gavage); water management; 21-day Experimental Results: Improve EAM and prevent cellular protein oxidation. The expression of redox regulatory protein TRX in cardiomyocytes is enhanced. Animal/Disease Models: Male Sprague Dawley rat [4] Doses: 30 mg/kg Route of Administration: po (oral gavage), one time/day for 4 weeks. Experimental Results: Inhibited the increase in blood pressure caused by Ang I. |
| ADME/Pharmacokinetics |
Absorption, Distribution and Excretion Temocapril is rapidly absorbed in the gastrointestinal tract and converted into the diacid (active) metabolite, which inhibits ACE in plasma. Temocapril is eliminated primarily through the liver and kidneys. 19.4% urinary recovery. Biological Half-Life 13.1 hours in patients with normal liver function. |
| Toxicity/Toxicokinetics |
Protein Binding 99.5%, including those with renal impairment. |
| References |
[1]. In vitro evaluation of inhibitory effects of antidiabetic and antihyperlipidemic drugs on human carboxylesterase activities. Drug Metab Dispos. 2010 Dec;38(12):2173-8. [2]. Angiotensin inhibits neurotransmission of calcitonin gene-related peptide-containing vasodilator nerves in mesenteric artery of spontaneously hypertensive rats. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1998 Feb;284(2):508-15. [3]. Temocapril treatment ameliorates autoimmune myocarditis associated with enhanced cardiomyocyte thioredoxin expression. Cardiovasc Res. 2002 Aug 1;55(2):320-8. [4]. Angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor does not suppress renal angiotensin II levels in angiotensin I-infused rats. J Pharmacol Sci. 2013;122(2):103-8. |
| Additional Infomation |
Temocapril is a dipeptide. Temocapril is a prodrug-type angiotensin-I converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitor not approved for use in the United States, but is approved in Japan and South Korea. Temocapril can also be used in hemodialysis patients without risk of serious accumulation. Drug Indication Temocapril is an ACE inhibitor primarily indicated in the treatment of hypertension and congestive heart failure, diabetic nephropathy, and improvement of prognosis for coronary artery diseases (including acute myocardial infarction). Pharmacodynamics Temocapril is a prodrug of its active metabolite (and diacid form) temocaprilat which contains a thiazepine ring. Temocaprilat has slightly higher potency than enalaprilat in ACE inhibition isolated from rabbit lung. ACE inhibitors exert their hemodynamic effect mainly by inhibiting the renin-angiotensin system. They also modulate sympathetic nervous system activity and increase prostaglandin synthesis. They cause mainly vasodilation and mild natriuresis without affecting heart rate and contractility.). When compared with other Angiotensin-converting Enzyme Inhibitors, temocapril's advantages include a rapid onset of action and what research suggests is tighter vascular ACE binding than enalaprilat. |
Solubility Data
| Solubility (In Vitro) |
|
|||
| Solubility (In Vivo) |
|
| Preparing Stock Solutions | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.0982 mL | 10.4908 mL | 20.9815 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.4196 mL | 2.0982 mL | 4.1963 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.2098 mL | 1.0491 mL | 2.0982 mL |