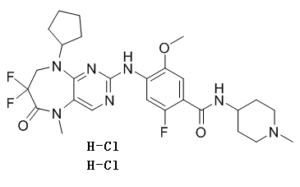
TAK-960 DiHCl, the dihydrochloride salt of TAK960, is an orally bioavailable, potent, and selective PLK1 polo-like kinase 1 (PLK1) inhibitor with an IC50 of 0.8 nM at 10 μM ATP.
Physicochemical Properties
| Molecular Formula | C27H36CL2F3N7O3 |
| Molecular Weight | 561.59916 |
| Exact Mass | 561.267 |
| Elemental Analysis | C, 57.74; H, 6.10; F, 10.15; N, 17.46; O, 8.55 |
| CAS # | 1137868-52-0 |
| Related CAS # | TAK-960 dihydrochloride;TAK-960 hydrochloride;1137868-96-2;TAK-960 monohydrochloride;2108449-45-0 |
| PubChem CID | 53357478 |
| Appearance | White to beige solid powder |
| Density | 1.4±0.1 g/cm3 |
| Index of Refraction | 1.615 |
| LogP | 1.33 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 2 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 11 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 6 |
| Heavy Atom Count | 40 |
| Complexity | 903 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| SMILES | 0 |
| InChi Key | GWRSATNRNFYMDI-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| InChi Code | InChI=1S/C27H34F3N7O3/c1-35-10-8-16(9-11-35)32-24(38)18-12-22(40-3)20(13-19(18)28)33-26-31-14-21-23(34-26)37(17-6-4-5-7-17)15-27(29,30)25(39)36(21)2/h12-14,16-17H,4-11,15H2,1-3H3,(H,32,38)(H,31,33,34) |
| Chemical Name | 4-[(9-cyclopentyl-7,7-difluoro-5-methyl-6-oxo-8H-pyrimido[4,5-b][1,4]diazepin-2-yl)amino]-2-fluoro-5-methoxy-N-(1-methylpiperidin-4-yl)benzamide |
| Synonyms | TAK-960; TAK960 dihydrochloride; TAK 960 dihydrochloride |
| HS Tariff Code | 2934.99.9001 |
| Storage |
Powder-20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
| Shipping Condition | Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs) |
Biological Activity
| Targets | PLK1 (IC50 = 0.8 nM); PLK2 (IC50 = 16.9 nM); PLK3 (IC50 = 50.2 nM); FAK/PTK2 (IC50 = 19.6 nM); MLCK/MYLK (IC50 = 25.6 nM); FES/FPS (IC50 = 58.2 nM); |
| ln Vitro |
TAK-960 dihydrochloride treatment results in increased phosphorylation of histone H3 (pHH3), aberrant polo mitosis morphology, and accumulation of G2-M cells. With mean EC50 values ranging from 8.4 to 46.9 nM, TAK-960 dihydrochloride (2-1000 nM; 72 hours) inhibits the proliferation of multiple cancer cell lines, but not nondividing normal cells[1]. TAK-960 dihydrochloride (8 nM) causes G2/M cell cycle arrest without causing appreciable cytotoxicity in HeLa cells[2]. |
| ln Vivo |
TAK-960 dihydrochloride shows notable efficacy against multiple tumor xenografts (10 mg/kg; p.o.; once daily for 2 weeks)[1]. TAK-960 dihydrochloride (p.o.) in animal models significantly inhibits the growth of HT-29 colorectal cancer xenografts and raises pHH3 in a dose-dependent manner[1]. |
| Cell Assay | After adding 10% fetal calf serum to the suitable medium, 3,000–30,000 cells are seeded into each well of 96-well plates. The CellTiter-Glo Assay is used to determine the number of viable cells after treating the cells with TAK-960 serial dilutions for 24 hours. A 72-hour analysis is conducted. With GraphPad Prism, EC50 values are calculated and statistical analysis is performed. |
| Animal Protocol |
nude mice or SCID mice (bearing HCT116, PC-3, BT474, A549, NCI-H1299, NCI-H1975, A2780, and MV4-11 cells)[1] 10 mg/kg P.o.; once daily for 2 weeks |
| References |
[1]. TAK-960, a novel, orally available, selective inhibitor of polo-like kinase 1, shows broad-spectrum preclinical antitumor activity in multiple dosing regimens. Mol Cancer Ther. 2012 Mar;11(3):700-9. [2]. PLK1 blockade enhances therapeutic effects of radiation by inducing cell cycle arrest at the mitotic phase. Sci Rep. 2015 Oct 27;5:15666. |
| Additional Infomation | PLK1 Inhibitor TAK-960 is an orally available, Polo-like kinase 1 (PLK1) inhibitor with potential antineoplastic activity. Polo-like kinase 1 inhibitor TAK-960 selectively inhibits PLK1, inducing selective G2/M cell-cycle arrest followed by apoptosis in a variety of tumor cells while causing reversible cell-cycle arrest at the G1 and G2 stages without apoptosis in normal cells. PLK1 inhibition may result in the inhibition of proliferation in PLK1-overexpressed tumor cells. PLK1, named after the polo gene of Drosophila melanogaster, is a serine/threonine kinase crucial in the regulation of mitosis. |
Solubility Data
| Solubility (In Vitro) |
H2O: ~10 mg/mL (~15.8 mM) DMSO: ~3.2 mg/mL (~5.1 mM) |
| Solubility (In Vivo) |
Note: Listed below are some common formulations that may be used to formulate products with low water solubility (e.g. < 1 mg/mL), you may test these formulations using a minute amount of products to avoid loss of samples. Injection Formulations (e.g. IP/IV/IM/SC) Injection Formulation 1: DMSO : Tween 80: Saline = 10 : 5 : 85 (i.e. 100 μL DMSO stock solution → 50 μL Tween 80 → 850 μL Saline) *Preparation of saline: Dissolve 0.9 g of sodium chloride in 100 mL ddH ₂ O to obtain a clear solution. Injection Formulation 2: DMSO : PEG300 :Tween 80 : Saline = 10 : 40 : 5 : 45 (i.e. 100 μL DMSO → 400 μLPEG300 → 50 μL Tween 80 → 450 μL Saline) Injection Formulation 3: DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90 (i.e. 100 μL DMSO → 900 μL Corn oil) Example: Take the Injection Formulation 3 (DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90) as an example, if 1 mL of 2.5 mg/mL working solution is to be prepared, you can take 100 μL 25 mg/mL DMSO stock solution and add to 900 μL corn oil, mix well to obtain a clear or suspension solution (2.5 mg/mL, ready for use in animals). Injection Formulation 4: DMSO : 20% SBE-β-CD in saline = 10 : 90 [i.e. 100 μL DMSO → 900 μL (20% SBE-β-CD in saline)] *Preparation of 20% SBE-β-CD in Saline (4°C,1 week): Dissolve 2 g SBE-β-CD in 10 mL saline to obtain a clear solution. Injection Formulation 5: 2-Hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin : Saline = 50 : 50 (i.e. 500 μL 2-Hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin → 500 μL Saline) Injection Formulation 6: DMSO : PEG300 : castor oil : Saline = 5 : 10 : 20 : 65 (i.e. 50 μL DMSO → 100 μLPEG300 → 200 μL castor oil → 650 μL Saline) Injection Formulation 7: Ethanol : Cremophor : Saline = 10: 10 : 80 (i.e. 100 μL Ethanol → 100 μL Cremophor → 800 μL Saline) Injection Formulation 8: Dissolve in Cremophor/Ethanol (50 : 50), then diluted by Saline Injection Formulation 9: EtOH : Corn oil = 10 : 90 (i.e. 100 μL EtOH → 900 μL Corn oil) Injection Formulation 10: EtOH : PEG300:Tween 80 : Saline = 10 : 40 : 5 : 45 (i.e. 100 μL EtOH → 400 μLPEG300 → 50 μL Tween 80 → 450 μL Saline) Oral Formulations Oral Formulation 1: Suspend in 0.5% CMC Na (carboxymethylcellulose sodium) Oral Formulation 2: Suspend in 0.5% Carboxymethyl cellulose Example: Take the Oral Formulation 1 (Suspend in 0.5% CMC Na) as an example, if 100 mL of 2.5 mg/mL working solution is to be prepared, you can first prepare 0.5% CMC Na solution by measuring 0.5 g CMC Na and dissolve it in 100 mL ddH2O to obtain a clear solution; then add 250 mg of the product to 100 mL 0.5% CMC Na solution, to make the suspension solution (2.5 mg/mL, ready for use in animals). Oral Formulation 3: Dissolved in PEG400 Oral Formulation 4: Suspend in 0.2% Carboxymethyl cellulose Oral Formulation 5: Dissolve in 0.25% Tween 80 and 0.5% Carboxymethyl cellulose Oral Formulation 6: Mixing with food powders Note: Please be aware that the above formulations are for reference only. InvivoChem strongly recommends customers to read literature methods/protocols carefully before determining which formulation you should use for in vivo studies, as different compounds have different solubility properties and have to be formulated differently. (Please use freshly prepared in vivo formulations for optimal results.) |
| Preparing Stock Solutions | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 1.7806 mL | 8.9031 mL | 17.8063 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.3561 mL | 1.7806 mL | 3.5613 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.1781 mL | 0.8903 mL | 1.7806 mL |