RO-9187 is a novel and potent inhibitor of HCV virus replication with IC50 of 171 nM. RO-0622 and RO-9187 were excellent substrates for deoxycytidine kinase and were phosphorylated with efficiencies up to 3-fold higher than deoxycytidine. As compared with previous reports on ribonucleosides, higher levels of triphosphate were formed from RO-9187 in primary human hepatocytes, and both compounds were potent inhibitors of HCV virus replication in the replicon system (IC(50) = 171 +/- 12 nM and 24 +/- 3 nM for RO-9187 and RO-0622, respectively; CC(50) >1 mM for both). Both compounds inhibited RNA synthesis by HCV polymerases from either HCV genotypes 1a and 1b or containing S96T or S282T point mutations with similar potencies, suggesting no cross-resistance with either R1479 (4'-azidocytidine) or 2'-C-methyl nucleosides. Pharmacokinetic studies with RO-9187 in rats and dogs showed that plasma concentrations exceeding HCV replicon IC(50) values 8-150-fold could be achieved by low dose (10 mg/kg) oral administration. Therefore, 2'-alpha-deoxy-4'-azido nucleosides are a new class of antiviral nucleosides with promising preclinical properties as potential medicines for the treatment of HCV infection.
Physicochemical Properties
| Molecular Formula | C9H12N6O5 |
| Molecular Weight | 284.22878 |
| Exact Mass | 284.087 |
| Elemental Analysis | C, 38.03; H, 4.26; N, 29.57; O, 28.14 |
| CAS # | 876708-03-1 |
| PubChem CID | 11514721 |
| Appearance | Light yellow to yellow solid powder |
| LogP | -1.8 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 4 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 7 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 3 |
| Heavy Atom Count | 20 |
| Complexity | 529 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 4 |
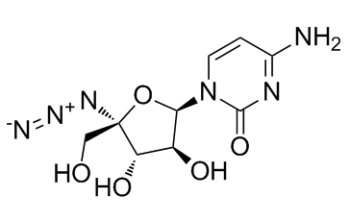
| SMILES | N([C@]1([C@@H](O)[C@H](O)[C@H](N2C=CC(N)=NC2=O)O1)CO)=[N+]=[N-] |
| InChi Key | ODLGMSQBFONGNG-XZMZPDFPSA-N |
| InChi Code | InChI=1S/C9H12N6O5/c10-4-1-2-15(8(19)12-4)7-5(17)6(18)9(3-16,20-7)13-14-11/h1-2,5-7,16-18H,3H2,(H2,10,12,19)/t5-,6-,7+,9+/m0/s1 |
| Chemical Name | 4-amino-1-[(2R,3S,4S,5R)-5-azido-3,4-dihydroxy-5-(hydroxymethyl)oxolan-2-yl]pyrimidin-2-one |
| Synonyms | RO-9187; RO 9187; RO9187. |
| HS Tariff Code | 2934.99.9001 |
| Storage |
Powder-20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
| Shipping Condition | Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs) |
Biological Activity
| Targets | HCV(IC50=171 nM) |
| ln Vitro | RO-9187 is phosphorylated with efficiencies up to three times higher than deoxycytidine, making it a great substrate for deoxycytidine kinase. Inhibiting RNA synthesis by HCV polymerases from HCV genotypes 1a and 1b or with S96T or S282T point mutations with comparable potencies, RO-9187 suggests that there is no cross-resistance with 2′-C-methyl nucleosides or R1479 (4′-azidocytidine). RO-9187-TP production rose in a dose- and time-dependent fashion. Half-maximum triphosphate formation is reached at 12 μM, and the maximum triphosphate concentration at 24 hours is 87 pmol/106 cells. RO-9187 [1]. |
| ln Vivo | Following oral dosing, rats' plasma exposures to RO-9187 rise between 10 and 2000 mg/kg in a dose-dependent manner. At a dose level of 10 mg/kg, rats and dogs exhibit plasma concentrations of 1.4 and 26 μM (390 and 7454 ng/mL), respectively. Rats given 2000 mg/kg/day can achieve plasma concentrations of up to 57 μM[1]. |
| Animal Protocol | Rats: Hanover-Wistar rats are used in a 2-week oral range finding toxicity study with RO-9187 and ribavirin. For 14 days, five male and five female rats in each of the five treatment groups receive once-daily oral gavage doses of 200, 600, or 2000 mg/kg RO-9187 or 200 mg/kg ribavirin[1]. |
| References |
[1]. 2'-deoxy-4'-azido nucleoside analogs are highly potent inhibitors of hepatitis C virus replication despite the lack of 2'-alpha-hydroxyl groups. J Biol Chem. 2008 Jan 25;283(4):2167-75. |
Solubility Data
| Solubility (In Vitro) |
DMSO : ~100 mg/mL (~351.83 mM) H2O : ~5 mg/mL (~17.59 mM) |
| Solubility (In Vivo) |
Solubility in Formulation 1: 2.5 mg/mL (8.80 mM) in 10% DMSO + 40% PEG300 + 5% Tween80 + 45% Saline (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), clear solution; with sonication. For example, if 1 mL of working solution is to be prepared, you can add 100 μL of 25.0 mg/mL clear DMSO stock solution to 400 μL PEG300 and mix evenly; then add 50 μL Tween-80 to the above solution and mix evenly; then add 450 μL normal saline to adjust the volume to 1 mL. Preparation of saline: Dissolve 0.9 g of sodium chloride in 100 mL ddH₂ O to obtain a clear solution. Solubility in Formulation 2: 2.5 mg/mL (8.80 mM) in 10% DMSO + 90% (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline) (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), clear solution; with ultrasonication. For example, if 1 mL of working solution is to be prepared, you can add 100 μL of 25.0 mg/mL clear DMSO stock solution to 900 μL of 20% SBE-β-CD physiological saline solution and mix evenly. Preparation of 20% SBE-β-CD in Saline (4°C,1 week): Dissolve 2 g SBE-β-CD in 10 mL saline to obtain a clear solution. Solubility in Formulation 3: 2.5 mg/mL (8.80 mM) in 10% DMSO + 90% Corn Oil (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), clear solution; with ultrasonication. For example, if 1 mL of working solution is to be prepared, you can add 100 μL of 25.0 mg/mL clear DMSO stock solution to 900 μL of corn oil and mix evenly. Solubility in Formulation 4: 10% DMSO+40% PEG300+5% Tween-80+45% Saline: 2.5 mg/mL (8.80 mM) Solubility in Formulation 5: 5.88 mg/mL (20.69 mM) in PBS (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), clear solution; with ultrasonication (<60°C). (Please use freshly prepared in vivo formulations for optimal results.) |
| Preparing Stock Solutions | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 3.5183 mL | 17.5914 mL | 35.1828 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.7037 mL | 3.5183 mL | 7.0366 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.3518 mL | 1.7591 mL | 3.5183 mL |