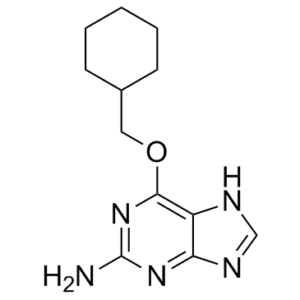
NU2058 (also known as NU 2058; NU-2058; O6-(Cyclohexylmethyl)guanine) is a novel and potent O(6)-Cyclohexylmethylguanine-based CDK2 (cyclin-dependent kinases 2) inhibitor with IC50 of 17 μM in an enzymatic assay. It can increase the cytotoxicity of cisplatin in vitro and may have anticancer properties. Additionally, it has the ability to increase the potency of melphalan (DMF 2.3) and monohydroxymelphalan (1.7), but not temozolomide or ionizing radiation. Using a dose modification factor (DMF) of 3.1, NU2058 enhanced the cytotoxicity of cisplatin in the clonogenic assay. Both the total intracellular platinum levels and the levels of platinum-DNA adduct were increased twofold by NU2058. Moreover, the presence of NU2058 increased the toxicity of the cisplatin-DNA adducts that formed. Cancer is characterized by dysregulation of this intricately regulated process, which is fueled by the periodic association of cyclin-dependent kinases (CDKs) and their partner cyclins and regulated by kinase inhibitors, such as p27.
Physicochemical Properties
| Molecular Formula | C12H17N5O | |
| Molecular Weight | 247.3 | |
| Exact Mass | 247.143 | |
| Elemental Analysis | C, 58.28; H, 6.93; N, 28.32; O, 6.47 | |
| CAS # | 161058-83-9 | |
| Related CAS # |
|
|
| PubChem CID | 4564 | |
| Appearance | White to off-white solid powder | |
| Density | 1.3±0.1 g/cm3 | |
| Boiling Point | 580.8±53.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Melting Point | 199 °C | |
| Flash Point | 305.0±30.9 °C | |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±1.6 mmHg at 25°C | |
| Index of Refraction | 1.650 | |
| LogP | 2.89 | |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 2 | |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 5 | |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 3 | |
| Heavy Atom Count | 18 | |
| Complexity | 271 | |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 | |
| SMILES | O(C1C2=C(N=C([H])N2[H])N=C(N([H])[H])N=1)C([H])([H])C1([H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])C1([H])[H] |
|
| InChi Key | MWGXGTJJAOZBNW-UHFFFAOYSA-N | |
| InChi Code | InChI=1S/C12H17N5O/c13-12-16-10-9(14-7-15-10)11(17-12)18-6-8-4-2-1-3-5-8/h7-8H,1-6H2,(H3,13,14,15,16,17) | |
| Chemical Name | 6-(cyclohexylmethoxy)-7H-purin-2-amine | |
| Synonyms |
|
|
| HS Tariff Code | 2934.99.9001 | |
| Storage |
Powder-20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
|
| Shipping Condition | Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs) |
Biological Activity
| Targets | CDK1 (IC50 = 26 μM); CDK2 (IC50 = 17 μM); CDK2 (Ki = 12 μM) | ||
| ln Vitro | Nu2058 modifies cisplatin transport, increasing Pt-DNA adducts and making cells more susceptible to DNA damage brought on by melphalans and cisplatin. Nevertheless, CDK2 inhibition has no bearing on NU2058's effects[1]. The growth inhibition caused by NU2058 in LNCaP cells and their Casodex-resistant derivative, LNCaP-cdxR, is accompanied by concentration-dependent increases in p27 levels, a decrease in early gene expression, phosphorylation of pRb and CDK2 activity, and G1 cell cycle phase arrest in both cell lines. In S phase, NU2058 reduces the cell cycle and prevents pRb from being phosphorylated. In LNCaP cells, it causes a G1 arrest and boosts the expression of the p27 protein while having no discernible impact on p21 levels[2]. | ||
| ln Vivo |
|
||
| Enzyme Assay | NU2058 is a CDK2 (cyclin-dependent kinases 2) inhibitor based on O(6)-Cyclohexylmethylguanine that, in an enzymatic assay, has an IC50 of 17 μM. For one hour, Casodex or NU2058 were applied to exponentially growing parental and derivative LNCaP cells (8–10 × 105). After being cleaned with PBS, the cells were taken out and lysed in reaction lysis buffer (50 mM Tris, pH 7.5, 150 mM NaCl, 0.2 mM Na3VO4, 0.5% NP40, 1 mM PMSF, 1 mM dithiothreitol, 25 μg/ml leupeptin, 25 μg/ml aprotinin, and 25 μg/ml pepstatin) for 30 minutes on ice. The lysates underwent a 3-minute, 14,000-g centrifugation. After three washes in reaction lysis buffer, the supernatants were precleared with 20 μl protein G sepharose (PGS) and rotated at 4°C for 4 hours. By centrifuging at 14,000 g for five minutes, PGS and nonspecific-bound protein were eliminated. Using 2 μg of polyclonal anti-CDK2 antibody (Santa Cruz Biotechnology), immunoprecipitation was carried out on the samples, and they were incubated at 4°C with rotation for an entire night. Following incubation, immunoprecipitated samples were incubated again for one hour at 4°C while being rotated, and 20 μl of PGS were added. After centrifuging PGS containing bound protein complexes for 5 minutes at 14,000 g, the beads were twice washed in PBS and once in wash buffer (PBS, 0.2% Triton X-100). The amount of phosphorylation on histone H1 was determined by soaking the beads in γ[32P]ATP, 1 mM ATP, CDK buffer (50 mM Tris, pH 7.5, 5 mM MgCl2), and histone H1 (5 mg/ml) for 10 minutes at 30°C. To stop the reaction, 50 μl of Laemmli buffer was added. After samples were analyzed using 12% SDS-PAGE, the gel was dried and autoradiographically examined. | ||
| Cell Assay | In six-well plates, 350,000 cells are seeded per well, and the cells are left to attach over night. Unless specified otherwise, growth media are swapped out on the day of the experiment for media containing 100 μM of either NU2058, NU6102, NU6230, or DMSO (0.1% (v/v) final concentration) for two hours, followed by an additional two hours in the presence of cytotoxic drugs. Cells are treated with NU2058 for a total of 4 hours in the radiation experiments; after the first 2 hours, the cells are exposed to radiation. Following therapy, the cells are trypsinized, cleaned twice in PBS, and replated at different densities (300–50,000 cells per plate) into 100 mm Petri dishes. The culture medium is removed after about 12 days, and the cells are fixed using Carnoy's reagent (75% (v/v) methanol, 25% (v/v) acetic acid), stained with crystal violet (0.4% (w/v) in water), and the colonies are counted during this process. | ||
| Animal Protocol |
|
||
| References |
[1]. Biochem Pharmacol . 2009 May 15;77(10):1586-92. [2]. Oncogene . 2007 Dec 6;26(55):7611-9. |
Solubility Data
| Solubility (In Vitro) |
|
|||
| Solubility (In Vivo) |
Note: Listed below are some common formulations that may be used to formulate products with low water solubility (e.g. < 1 mg/mL), you may test these formulations using a minute amount of products to avoid loss of samples. Injection Formulations (e.g. IP/IV/IM/SC) Injection Formulation 1: DMSO : Tween 80: Saline = 10 : 5 : 85 (i.e. 100 μL DMSO stock solution → 50 μL Tween 80 → 850 μL Saline) *Preparation of saline: Dissolve 0.9 g of sodium chloride in 100 mL ddH ₂ O to obtain a clear solution. Injection Formulation 2: DMSO : PEG300 :Tween 80 : Saline = 10 : 40 : 5 : 45 (i.e. 100 μL DMSO → 400 μLPEG300 → 50 μL Tween 80 → 450 μL Saline) Injection Formulation 3: DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90 (i.e. 100 μL DMSO → 900 μL Corn oil) Example: Take the Injection Formulation 3 (DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90) as an example, if 1 mL of 2.5 mg/mL working solution is to be prepared, you can take 100 μL 25 mg/mL DMSO stock solution and add to 900 μL corn oil, mix well to obtain a clear or suspension solution (2.5 mg/mL, ready for use in animals). Injection Formulation 4: DMSO : 20% SBE-β-CD in saline = 10 : 90 [i.e. 100 μL DMSO → 900 μL (20% SBE-β-CD in saline)] *Preparation of 20% SBE-β-CD in Saline (4°C,1 week): Dissolve 2 g SBE-β-CD in 10 mL saline to obtain a clear solution. Injection Formulation 5: 2-Hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin : Saline = 50 : 50 (i.e. 500 μL 2-Hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin → 500 μL Saline) Injection Formulation 6: DMSO : PEG300 : castor oil : Saline = 5 : 10 : 20 : 65 (i.e. 50 μL DMSO → 100 μLPEG300 → 200 μL castor oil → 650 μL Saline) Injection Formulation 7: Ethanol : Cremophor : Saline = 10: 10 : 80 (i.e. 100 μL Ethanol → 100 μL Cremophor → 800 μL Saline) Injection Formulation 8: Dissolve in Cremophor/Ethanol (50 : 50), then diluted by Saline Injection Formulation 9: EtOH : Corn oil = 10 : 90 (i.e. 100 μL EtOH → 900 μL Corn oil) Injection Formulation 10: EtOH : PEG300:Tween 80 : Saline = 10 : 40 : 5 : 45 (i.e. 100 μL EtOH → 400 μLPEG300 → 50 μL Tween 80 → 450 μL Saline) Oral Formulations Oral Formulation 1: Suspend in 0.5% CMC Na (carboxymethylcellulose sodium) Oral Formulation 2: Suspend in 0.5% Carboxymethyl cellulose Example: Take the Oral Formulation 1 (Suspend in 0.5% CMC Na) as an example, if 100 mL of 2.5 mg/mL working solution is to be prepared, you can first prepare 0.5% CMC Na solution by measuring 0.5 g CMC Na and dissolve it in 100 mL ddH2O to obtain a clear solution; then add 250 mg of the product to 100 mL 0.5% CMC Na solution, to make the suspension solution (2.5 mg/mL, ready for use in animals). Oral Formulation 3: Dissolved in PEG400 Oral Formulation 4: Suspend in 0.2% Carboxymethyl cellulose Oral Formulation 5: Dissolve in 0.25% Tween 80 and 0.5% Carboxymethyl cellulose Oral Formulation 6: Mixing with food powders Note: Please be aware that the above formulations are for reference only. InvivoChem strongly recommends customers to read literature methods/protocols carefully before determining which formulation you should use for in vivo studies, as different compounds have different solubility properties and have to be formulated differently. (Please use freshly prepared in vivo formulations for optimal results.) |
| Preparing Stock Solutions | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 4.0437 mL | 20.2184 mL | 40.4367 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.8087 mL | 4.0437 mL | 8.0873 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.4044 mL | 2.0218 mL | 4.0437 mL |