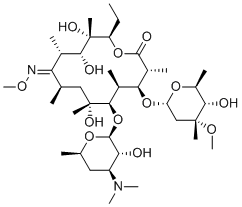
Lexithromycin (Erythromycin A 9-methoxime; Wy 48314) is a potent and semi-synthetic antibiotic derived from erythromycin A with antibacterial activity. It is prepared by reaction of the 9-keto moiety to methyl oxime. The structural change improves the pH stability profile and hydrophobicity of lexithromycin for better in vivo absorption. Thus lexithromycin has improved absorption in vivo over erythromycin due to increased hydrophopicity and pH stability. As with other macrolides, lexithromycin prevents protein synthesis by binding the ribosome at the polypeptide exit tunnel. Formulations containing lexithromycin were tested in clinical trials as treatment for HIV but were discontinued.
Physicochemical Properties
| Molecular Formula | C38H70N2O13 |
| Molecular Weight | 762.968 |
| Exact Mass | 762.488 |
| Elemental Analysis | C, 59.82; H, 9.25; N, 3.67; O, 27.26 |
| CAS # | 53066-26-5 |
| PubChem CID | 6532846 |
| Appearance | White to off-white solid powder |
| Density | 1.26g/cm3 |
| Boiling Point | 824.6ºC at 760mmHg |
| Flash Point | 452.5ºC |
| Index of Refraction | 1.543 |
| LogP | 2.218 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 5 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 15 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 8 |
| Heavy Atom Count | 53 |
| Complexity | 1230 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 18 |
| SMILES | CO[C@@](C)([C@@H](O)[C@H](C)O1)C[C@]1([H])O[C@@]([C@H]2C)([H])[C@@H]([C@H]([C@](O)(C[C@H](/C([C@H](C)[C@@H](O)[C@](C)(O)[C@@H](CC)OC2=O)=N\OC)C)C)O[C@@]3([H])[C@@H]([C@H](C[C@@H](C)O3)N(C)C)O)C |
| InChi Key | HPZGUSZNXKOMCQ-SQYJNGITSA-N |
| InChi Code | InChI=1S/C38H70N2O13/c1-15-26-38(10,46)31(42)21(4)28(39-48-14)19(2)17-36(8,45)33(53-35-29(41)25(40(11)12)16-20(3)49-35)22(5)30(23(6)34(44)51-26)52-27-18-37(9,47-13)32(43)24(7)50-27/h19-27,29-33,35,41-43,45-46H,15-18H2,1-14H3/b39-28+/t19-,20-,21+,22+,23-,24+,25+,26-,27+,29-,30+,31-,32+,33-,35+,36-,37-,38-/m1/s1 |
| Chemical Name | (3R,4S,5S,6R,7R,9R,11S,12R,13S,14R,E)-6-(((2S,3R,4S,6R)-4-(dimethylamino)-3-hydroxy-6-methyltetrahydro-2H-pyran-2-yl)oxy)-14-ethyl-7,12,13-trihydroxy-4-(((2R,4R,5S,6S)-5-hydroxy-4-methoxy-4,6-dimethyltetrahydro-2H-pyran-2-yl)oxy)-10-(methoxyimino)-3,5,7,9,11,13-hexamethyloxacyclotetradecan-2-one |
| Synonyms | Lexithromycin; Wy-48314; Wy 48314; Wy48314; |
| HS Tariff Code | 2934.99.03.00 |
| Storage |
Powder-20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month Note: Please store this product in a sealed and protected environment (e.g. under nitrogen), avoid exposure to moisture and light. |
| Shipping Condition | Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs) |
Biological Activity
| Targets | Bacterial |
| ln Vitro | A derivative of erythromycin A, lexithromycin has antibacterial properties. For S. pyogenes CN10A and Streptococcus sp. 64/848C, lexithromycin exhibits a minimal inhibitory concentration (MIC) of 0.06 μg/mL; for Staphylococcus aureus Oxford, it is 0.25 μg/mL; for S. aureus Russell and S. aureus T2, it is 0.5 μg/mL; and for S. pyogenes CN10A and Haemophilus influenzae Wy 21[1]. |
| References |
[1]. Erythromycin A 11,12-methylene acetal. J Antibiot (Tokyo). 1988 Nov;41(11):1644-8. [2]. A double-blind, randomised, placebo-controlled study of roxithromycin and doxycycline combination, roxithromycin alone, or matching placebo for 12 weeks in adults with frequent exacerbations of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. J Negat Results Biomed. 2015 Sep 7;14:15. |
Solubility Data
| Solubility (In Vitro) | DMSO : ~50 mg/mL (~65.53 mM) |
| Solubility (In Vivo) |
Solubility in Formulation 1: ≥ 5 mg/mL (6.55 mM) (saturation unknown) in 10% DMSO + 90% (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline) (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), clear solution. For example, if 1 mL of working solution is to be prepared, you can add 100 μL of 50.0 mg/mL clear DMSO stock solution to 900 μL of 20% SBE-β-CD physiological saline solution and mix evenly. Preparation of 20% SBE-β-CD in Saline (4°C,1 week): Dissolve 2 g SBE-β-CD in 10 mL saline to obtain a clear solution. Solubility in Formulation 2: ≥ 3.25 mg/mL (4.26 mM) (saturation unknown) in 10% DMSO + 40% PEG300 + 5% Tween80 + 45% Saline (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), clear solution. For example, if 1 mL of working solution is to be prepared, you can add 100 μL of 32.5 mg/mL clear DMSO stock solution to 400 μL of PEG300 and mix evenly; then add 50 μL of Tween-80 to the above solution and mix evenly; then add 450 μL of normal saline to adjust the volume to 1 mL. Preparation of saline: Dissolve 0.9 g of sodium chloride in 100 mL ddH₂ O to obtain a clear solution. Solubility in Formulation 3: ≥ 3.25 mg/mL (4.26 mM) (saturation unknown) in 10% DMSO + 90% Corn Oil (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), clear solution. For example, if 1 mL of working solution is to be prepared, you can add 100 μL of 32.5 mg/mL clear DMSO stock solution to 900 μL of corn oil and mix evenly. Solubility in Formulation 4: 10% DMSO+90% (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline): ≥ 5 mg/mL (6.55 mM) (Please use freshly prepared in vivo formulations for optimal results.) |
| Preparing Stock Solutions | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 1.3107 mL | 6.5533 mL | 13.1067 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.2621 mL | 1.3107 mL | 2.6213 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.1311 mL | 0.6553 mL | 1.3107 mL |