Physicochemical Properties
| Molecular Formula | C22H21F2N3O |
| Molecular Weight | 381.42 |
| Exact Mass | 381.165 |
| Elemental Analysis | C, 69.28; H, 5.55; F, 9.96; N, 11.02; O, 4.19 |
| CAS # | 1627710-50-2 |
| Related CAS # | 1627710-50-2 |
| PubChem CID | 73010393 |
| Appearance | White to off-white solid powder |
| Density | 1.3±0.1 g/cm3 |
| Boiling Point | 481.1±45.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Flash Point | 244.7±28.7 °C |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±1.3 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.601 |
| LogP | 3.31 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 1 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 6 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 3 |
| Heavy Atom Count | 28 |
| Complexity | 482 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
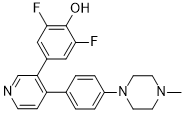
| SMILES | C1=C(C2C(C3C=CC(N4CCN(CC4)C)=CC=3)=CC=NC=2)C=C(C(O)=C1F)F |
| InChi Key | IKUFKDGKRLMXEX-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| InChi Code | InChI=1S/C22H21F2N3O/c1-26-8-10-27(11-9-26)17-4-2-15(3-5-17)18-6-7-25-14-19(18)16-12-20(23)22(28)21(24)13-16/h2-7,12-14,28H,8-11H2,1H3 |
| Chemical Name | 2,6-difluoro-4-[4-[4-(4-methylpiperazin-1-yl)phenyl]pyridin-3-yl]phenol |
| Synonyms | LJH685; LJH685; LJH685; NVP LJH685; NVP-LJH685;NVPLJH685; NVP LJH 685; 2,6-difluoro-4-[4-[4-(4-methylpiperazin-1-yl)phenyl]pyridin-3-yl]phenol; 2,6-Difluoro-4-{4-[4-(4-Methylpiperazin-1-Yl)phenyl]pyridin-3-Yl}phenol; CHEMBL3604793; 27CZQ807C1; NVP-LJH-685 |
| HS Tariff Code | 2934.99.9001 |
| Storage |
Powder-20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
| Shipping Condition | Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs) |
Biological Activity
| Targets | RSK1/Ribosomal S6 Kinase (IC50 = 6 nM); RSK1 (IC50 = 5 nM); RSK1 (IC50 = 4 nM) |
| ln Vitro |
LJH685 (0.01-100 μM; 72 hours) has effective EC50 values of 0.73 and 0.79 μM, respectively, for inhibiting the growth of MDA-MB-231 and H358 cells in soft agar. LJH685 (0.1-10 μM; 4 hours) efficient at submicromolar concentrations and nearly completely inhibits YB1 phosphorylation at higher concentrations[1]. |
| ln Vivo |
The RSK inhibitor, LJH685, suppressed BLBC cell tumourigenesis in vivo by disturbing YB-1-KLF5 axis. Our data suggest that YB-1 positively regulates KLF5 at multiple levels to promote BLBC progression. The novel RSK2-YB-1-KLF5-KRT16/Ly6D axis provides candidate diagnostic markers and therapeutic targets for BLBC.[2] To test this, we evaluated the anti-tumour effect of LJH685 in an HCC1806 orthotopic xenograft mouse model. As expected, we observed significant suppression of tumour growth following LJH685 administration (Fig. 7H, I), although this compound showed low solubility in water and a short half-life in blood. There was no marked weight loss in the LJH685-treated mice, suggesting its toxicity was acceptable (Supplementary Fig. S8E). Furthermore, we demonstrated that LJH685 decreased the expression of YB-1 pS102, KLF5, KRT16, Ly6D, and Cyclin D1, but increased cleaved-PARP1 in the xenograft tumour tissues (Supplementary Fig. S8F). Taken together, LJH685 efficiently inhibits HCC1806 cell growth in vivo and therefore represents a potential drug for the treatment of BLBC.[2] |
| Enzyme Assay | Recombinant full-length RSK protein is used to measure the enzymatic activity of RSK isoforms 1, 2, and 3 (PV4049, PV4051, and PV3846). RSK1 (1 nmol/L), RSK2 (0.1 nmol/L), or RSK3 (1 nmol/L) is allowed to phosphorylate 200 nmol/L peptide substrate (biotin-AGAGRSRHSSYPAGT-OH) in the presence of ATP at concentration equal to the Km for ATP for each enzyme (RSK1, 5 μmol/L; RSK2, 20 μmol/L; and RSK3, 10 μmol/L) and appropriate dilutions of RSK inhibitors. |
| Cell Assay | By seeding 1000 cells per well on 96-well tissue culture-treated plates with cell growth medium, it is possible to measure cell growth under the attached conditions. After 72 hours, cell growth is evaluated by adding CellTiter Glo reagent in accordance with manufacturer's instructions. Appropriate dilutions of the compound are added to the medium above the cells. |
| Animal Protocol |
Administration of LJH685 in tumour burden mice[2] HCC1806 cells (6 × 105) were injected subcutaneously into both the left and right mammary fat pads of twelve female nude mice (6–7-week-old). After seven days, the tumour volume and weight of mice were measured, and mice were randomly distributed into two groups. The mice were then treated with LJH685 or NC by intraperitoneal injection daily. The tumour volume and mouse weight were measured every other day. The mice were sacrificed on day 21, and the tumours were harvested and weighed. LJH685 was prepared by adding each of the following solvents in sequential order; 10% DMSO, 40% PEG300, 5% Tween-80, and 45% saline. The drug solution was freshly prepared to avoid freeze thawing that could cause drug precipitation. |
| References |
[1]. Mol Cancer Res. 2014 May;12(5):803-12. [2]. YB-1 is a positive regulator of KLF5 transcription factor in basal-like breast cancer. Cell Death & Differentiation volume 29, pages1283–1295 (2022) |
| Additional Infomation |
The p90 ribosomal S6 kinase (RSK) family of serine/threonine kinases is expressed in a variety of cancers and its substrate phosphorylation has been implicated in direct regulation of cell survival, proliferation, and cell polarity. This study characterizes and presents the most selective and potent RSK inhibitors known to date, LJH685 and LJI308. Structural analysis confirms binding of LJH685 to the RSK2 N-terminal kinase ATP-binding site and reveals that the inhibitor adopts an unusual nonplanar conformation that explains its excellent selectivity for RSK family kinases. LJH685 and LJI308 efficiently inhibit RSK activity in vitro and in cells. Furthermore, cellular inhibition of RSK and its phosphorylation of YB1 on Ser102 correlate closely with inhibition of cell growth, but only in an anchorage-independent growth setting, and in a subset of examined cell lines. Thus, RSK inhibition reveals dynamic functional responses among the inhibitor-sensitive cell lines, underscoring the heterogeneous nature of RSK dependence in cancer.[1] Y-box binding protein 1 (YB-1) is a well-known oncogene highly expressed in various cancers, including basal-like breast cancer (BLBC). Beyond its role as a transcription factor, YB-1 is newly defined as an epigenetic regulator involving RNA 5-methylcytosine. However, its specific targets and pro-cancer functions are poorly defined. Here, based on clinical database, we demonstrate a positive correlation between Kruppel-like factor 5 (KLF5) and YB-1 expression in breast cancer patients, but a negative correlation with that of Dachshund homolog 1 (DACH1). Mechanistically, YB-1 enhances KLF5 expression not only through transcriptional activation that can be inhibited by DACH1, but also by stabilizing KLF5 mRNA in a RNA 5-methylcytosine modification-dependent manner. Additionally, ribosomal S6 kinase 2 (RSK2) mediated YB-1 phosphorylation at Ser102 promotes YB-1/KLF5 transcriptional complex formation, which co-regulates the expression of BLBC specific genes, Keratin 16 (KRT16) and lymphocyte antigen 6 family member D (Ly6D), to promote cancer cell proliferation. The RSK inhibitor, LJH685, suppressed BLBC cell tumourigenesis in vivo by disturbing YB-1-KLF5 axis. Our data suggest that YB-1 positively regulates KLF5 at multiple levels to promote BLBC progression. The novel RSK2-YB-1-KLF5-KRT16/Ly6D axis provides candidate diagnostic markers and therapeutic targets for BLBC.[2] |
Solubility Data
| Solubility (In Vitro) |
DMSO: ~20 mg/mL (~52.4 mM) Ethanol: ~10mg/mL (~26.2 mM) |
| Solubility (In Vivo) |
Solubility in Formulation 1: ≥ 1 mg/mL (2.62 mM) (saturation unknown) in 10% DMSO + 40% PEG300 + 5% Tween80 + 45% Saline (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), clear solution. For example, if 1 mL of working solution is to be prepared, you can add 100 μL of 10.0 mg/mL clear DMSO stock solution to 400 μL of PEG300 and mix evenly; then add 50 μL of Tween-80 to the above solution and mix evenly; then add 450 μL of normal saline to adjust the volume to 1 mL. Preparation of saline: Dissolve 0.9 g of sodium chloride in 100 mL ddH₂ O to obtain a clear solution. Solubility in Formulation 2: ≥ 1 mg/mL (2.62 mM) (saturation unknown) in 10% DMSO + 90% (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline) (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), clear solution. For example, if 1 mL of working solution is to be prepared, you can add 100 μL of 10.0 mg/mL clear DMSO stock solution to 900 μL of 20% SBE-β-CD physiological saline solution and mix evenly. Preparation of 20% SBE-β-CD in Saline (4°C,1 week): Dissolve 2 g SBE-β-CD in 10 mL saline to obtain a clear solution. Solubility in Formulation 3: ≥ 1 mg/mL (2.62 mM) (saturation unknown) in 10% DMSO + 90% Corn Oil (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), clear solution. For example, if 1 mL of working solution is to be prepared, you can add 100 μL of 10.0 mg/mL clear DMSO stock solution to 900 μL of corn oil and mix evenly. (Please use freshly prepared in vivo formulations for optimal results.) |
| Preparing Stock Solutions | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.6218 mL | 13.1089 mL | 26.2178 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.5244 mL | 2.6218 mL | 5.2436 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.2622 mL | 1.3109 mL | 2.6218 mL |