Physicochemical Properties
| Molecular Formula | C28H46CLN7 |
| Molecular Weight | 516.16 |
| Exact Mass | 587.3 |
| CAS # | 2253744-59-9 |
| PubChem CID | 137919856 |
| Appearance | Typically exists as solid at room temperature |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 4 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 5 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 17 |
| Heavy Atom Count | 38 |
| Complexity | 533 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| InChi Key | KLPOLRXJKIOFIQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| InChi Code | InChI=1S/C28H45N7.3ClH/c1-5-16-34(17-6-2)19-8-7-18-32(3)21-25-9-11-26(12-10-25)22-35(23-27-29-13-14-30-27)24-28-31-15-20-33(28)4;;;/h9-15,20H,5-8,16-19,21-24H2,1-4H3,(H,29,30);3*1H |
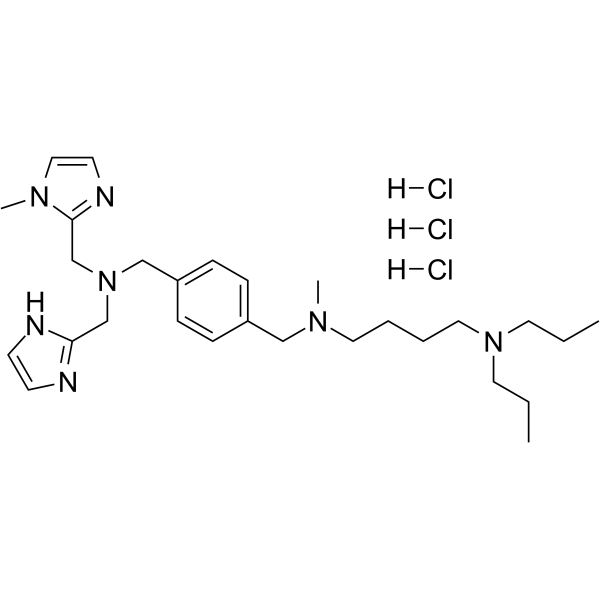
| Chemical Name | N-[[4-[[1H-imidazol-2-ylmethyl-[(1-methylimidazol-2-yl)methyl]amino]methyl]phenyl]methyl]-N-methyl-N',N'-dipropylbutane-1,4-diamine;trihydrochloride |
| Synonyms | KRH-3955 hydrochloride |
| HS Tariff Code | 2934.99.9001 |
| Storage |
Powder-20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
| Shipping Condition | Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs) |
Biological Activity
| Targets | X4 HIV-1NL4-3 ( EC50 = 0.3-1.0 nM ); SDF-1α-CXCR4 ( EC50 = 0.61 nM ) |
| ln Vitro |
KRH-3955 inhibits the replication of NL4-3 in activated peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) from eight different donors with the EC50 ranging from 0.23 to 1.3 nM[1]. KRH-3955, whose IC50 ranges from 0.4 to 0.8 nM, prevents these recombinant drug-resistant viruses from infecting CD4/CXCR4 cells. These viruses include those resistant to PIs, NRTIs, or NNRTIs, multidrug-resistant viruses, and T20-resistant viruses[1]. KRH-3955 (10-100 nM) precludes the increase in intracellular Ca2+ concentration induced by SDF-1α in a dose-dependent manner[1]. KRH-3955 (0.1-1000 nM) binding sites are found in an area that is made up of CXCR4's three extracellular loops (ECLs)[1]. KRH-3955 (10 nM) has a strong binding affinity for CXCR4 and a slow dissociation rate[1]. KRH-3955 MAb 12G5 binding to CXCR4 mutants with the IC50 ranging from 0.5 to 14.1 nM[1]. |
| ln Vivo |
KRH-3955 (10 mg/kg; a single p.o.) effectively suppresses X4 HIV-1 infection in hu-PBL-SCID mice[1]. KRH-3955 (10 mg/kg; one oral dose) has a Cmax of 86.3 ng/mL and a moderate oral bioavailability of 25.6%[1]. KRH-3955 (10 mg/kg; a single i.v.) demonstrates terminal elimination half-lives of 99 hours as a result of large distribution volumes (374 liters/kg) and high plasma clearance (3.9 liters/h/kg)[1]. |
| Animal Protocol |
C.B-17 SCID mice engrafted with human PBMCs and injected with infectious X4 HIV-1 (NL4-3) 10 mg/kg A single p.o. administration |
| References |
[1]. The Novel CXCR4 Antagonist KRH-3955 Is an Orally Bioavailable and Extremely Potent Inhibitor of Human Immunodeficiency Virus Type 1 Infection: Comparative Studies With AMD3100. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2009 Jul; 53(7): 2940-8. |
Solubility Data
| Solubility (In Vitro) | May dissolve in DMSO (in most cases), if not, try other solvents such as H2O, Ethanol, or DMF with a minute amount of products to avoid loss of samples |
| Solubility (In Vivo) |
Note: Listed below are some common formulations that may be used to formulate products with low water solubility (e.g. < 1 mg/mL), you may test these formulations using a minute amount of products to avoid loss of samples. Injection Formulations (e.g. IP/IV/IM/SC) Injection Formulation 1: DMSO : Tween 80: Saline = 10 : 5 : 85 (i.e. 100 μL DMSO stock solution → 50 μL Tween 80 → 850 μL Saline) *Preparation of saline: Dissolve 0.9 g of sodium chloride in 100 mL ddH ₂ O to obtain a clear solution. Injection Formulation 2: DMSO : PEG300 :Tween 80 : Saline = 10 : 40 : 5 : 45 (i.e. 100 μL DMSO → 400 μLPEG300 → 50 μL Tween 80 → 450 μL Saline) Injection Formulation 3: DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90 (i.e. 100 μL DMSO → 900 μL Corn oil) Example: Take the Injection Formulation 3 (DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90) as an example, if 1 mL of 2.5 mg/mL working solution is to be prepared, you can take 100 μL 25 mg/mL DMSO stock solution and add to 900 μL corn oil, mix well to obtain a clear or suspension solution (2.5 mg/mL, ready for use in animals). Injection Formulation 4: DMSO : 20% SBE-β-CD in saline = 10 : 90 [i.e. 100 μL DMSO → 900 μL (20% SBE-β-CD in saline)] *Preparation of 20% SBE-β-CD in Saline (4°C,1 week): Dissolve 2 g SBE-β-CD in 10 mL saline to obtain a clear solution. Injection Formulation 5: 2-Hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin : Saline = 50 : 50 (i.e. 500 μL 2-Hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin → 500 μL Saline) Injection Formulation 6: DMSO : PEG300 : castor oil : Saline = 5 : 10 : 20 : 65 (i.e. 50 μL DMSO → 100 μLPEG300 → 200 μL castor oil → 650 μL Saline) Injection Formulation 7: Ethanol : Cremophor : Saline = 10: 10 : 80 (i.e. 100 μL Ethanol → 100 μL Cremophor → 800 μL Saline) Injection Formulation 8: Dissolve in Cremophor/Ethanol (50 : 50), then diluted by Saline Injection Formulation 9: EtOH : Corn oil = 10 : 90 (i.e. 100 μL EtOH → 900 μL Corn oil) Injection Formulation 10: EtOH : PEG300:Tween 80 : Saline = 10 : 40 : 5 : 45 (i.e. 100 μL EtOH → 400 μLPEG300 → 50 μL Tween 80 → 450 μL Saline) Oral Formulations Oral Formulation 1: Suspend in 0.5% CMC Na (carboxymethylcellulose sodium) Oral Formulation 2: Suspend in 0.5% Carboxymethyl cellulose Example: Take the Oral Formulation 1 (Suspend in 0.5% CMC Na) as an example, if 100 mL of 2.5 mg/mL working solution is to be prepared, you can first prepare 0.5% CMC Na solution by measuring 0.5 g CMC Na and dissolve it in 100 mL ddH2O to obtain a clear solution; then add 250 mg of the product to 100 mL 0.5% CMC Na solution, to make the suspension solution (2.5 mg/mL, ready for use in animals). Oral Formulation 3: Dissolved in PEG400 Oral Formulation 4: Suspend in 0.2% Carboxymethyl cellulose Oral Formulation 5: Dissolve in 0.25% Tween 80 and 0.5% Carboxymethyl cellulose Oral Formulation 6: Mixing with food powders Note: Please be aware that the above formulations are for reference only. InvivoChem strongly recommends customers to read literature methods/protocols carefully before determining which formulation you should use for in vivo studies, as different compounds have different solubility properties and have to be formulated differently. (Please use freshly prepared in vivo formulations for optimal results.) |
| Preparing Stock Solutions | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 1.9374 mL | 9.6869 mL | 19.3738 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.3875 mL | 1.9374 mL | 3.8748 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.1937 mL | 0.9687 mL | 1.9374 mL |