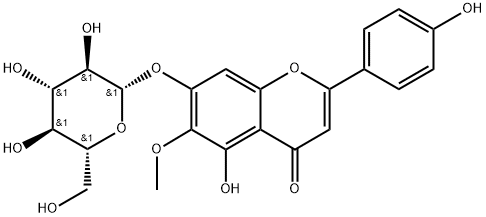
Homoplantaginin is a naturally occurring flavonoid isolated from Salvia plebeia (a traditional Chinese medicine), has anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties by suppressing the expression of TNF-α, IL-6, and the activation of IKKβ and NF-κB.
Physicochemical Properties
| Molecular Formula | C22H22O11 |
| Molecular Weight | 462.4035 |
| Exact Mass | 462.116 |
| CAS # | 17680-84-1 |
| Related CAS # | 17680-84-1 |
| PubChem CID | 5318083 |
| Appearance | Light yellow to yellow solid |
| Density | 1.6±0.1 g/cm3 |
| Boiling Point | 798.1±60.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 256-258℃ |
| Flash Point | 279.7±26.4 °C |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±3.0 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.695 |
| LogP | -0.97 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 6 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 11 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 5 |
| Heavy Atom Count | 33 |
| Complexity | 721 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 5 |
| SMILES | O1[C@]([H])([C@@]([H])([C@]([H])([C@@]([H])([C@@]1([H])C([H])([H])O[H])O[H])O[H])O[H])OC1C([H])=C2C(C(C([H])=C(C3C([H])=C([H])C(=C([H])C=3[H])O[H])O2)=O)=C(C=1OC([H])([H])[H])O[H] |
| InChi Key | GCLAFEGUXXHIFT-IWLDQSELSA-N |
| InChi Code | InChI=1S/C22H22O11/c1-30-21-14(32-22-20(29)19(28)17(26)15(8-23)33-22)7-13-16(18(21)27)11(25)6-12(31-13)9-2-4-10(24)5-3-9/h2-7,15,17,19-20,22-24,26- |
| Chemical Name | 5-hydroxy-2-(4-hydroxyphenyl)-6-methoxy-7-[(2S,3R,4S,5S,6R)-3,4,5-trihydroxy-6-(hydroxymethyl)oxan-2-yl]oxychromen-4-one |
| Synonyms | Homoplantaginin |
| HS Tariff Code | 2934.99.9001 |
| Storage |
Powder-20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
| Shipping Condition | Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs) |
Biological Activity
| Targets | NF-κB; TNF-α; IKKβ; IL-6 |
| ln Vitro | Homoplantaginin exhibits an IC50 of 0.35 μg/mL for DPPH radical reduction. In addition to increasing glutathione, glutathione peroxidase, and superoxide dismutase in the supernatant of human hepatocyte HL-7702 cells exposed to H2O2, homoplantaginin (0.1-100μg/mL) significantly reduces lactate dehydrogenase leakage[1]. Toll-like receptor-4 expression induced by palmitic acid (100 μM) is reduced by homoplantaginin (0.1, 1, 10 μM) dose-dependently. By inhibiting the NLRP3 and caspase-1 proteins, which are reactive oxygen species-sensitive thioredoxin-interacting proteins, homoplantaginin tightly regulates palmitic acid-induced reactive oxygen species to prevent NLRP3 inflammasome activation[2]. Homoplantaginin pre-treatment significantly reduces palmitic acid-induced mRNA expression of TNF-α and IL-6 as well as IKKβ and NF-κB p65 phosphorylation in human umbilical vein endothelial cells. Homoplantaginin significantly alters IRS-1's Ser/Thr phosphorylation, enhances Akt and endothelial nitric oxide synthase phosphorylation, and boosts NO production in the presence of insulin[3]. |
| ln Vivo | Homoplantaginin (25-100mg/kg) significantly lowers the rise in serum alanine and aspartate aminotransferase levels and lowers TNF-α and IL-1 levels. The same procedure also increases the levels of GSH, GSH-Px, and SOD in hepatic homogenate and decreases the content of thiobarbituric acid-reactive substances[1]. Homoplantaginin absorbs quickly (Tmax=16.00±8.94min), and its mean Cmax ranges between 0.77 and 1.27 nmol/mL. It is estimated that only 0.75% percent of the oral bioavailability is absolute. |
| Cell Assay | The MTT assay is used to assess the viability of cultured cells. Homoplantaginin is applied to human umbilical vein endothelial cells for 48 hours at varying concentrations (0.1, 1, 3, 10, 30, 100 M). Then, each well receives 20 μL of MTT (5 mg/mL) for an additional 4 hours at 37°C. After removing the supernatant, DMSO is added to help dissolve the formazan crystals. At 540 nm[3], the optical absorbance is measured. |
| Animal Protocol |
Rats: Homoplantaginin is dissolved in a solution of DMSO, PEG 400, ethanol, and normal saline (2:2:3:3, v/v/v/v) in rats at a concentration of 10 mg/mL. To administer oral administration (150 mg/kg), tail vein injection (15 mg/kg), and peritoneal injection (15 mg/kg) to the rats, the groups are randomly divided into three. At 5, 10, 20, 30, 45, 60, 90, 120, and 180 minutes after administration, blood samples (roughly 0.5 mL) are drawn from the retro-orbital plexus into heparinized microfugetubes. The plasma samples were extracted from the blood samples by centrifuging them at 10,000 rpm[4]. Mice: Homoplantaginin is dissolved in 5% amylum. Homoplantaginin is administered orally by gastric intubation during the experimental period at doses of 25, 50, 100 mg/kg/d, respectively. The mice are put to sleep with ether and blood samples are drawn by exsanguination from the inferior vein eight hours after LPS injection. To facilitate histological examination, the liver is taken out and fixed in formalin[1]. |
| References |
[1]. Protective effects of Salvia plebeia compound homoplantaginin on hepatocyte injury. Food Chem Toxicol. 2009 Jul;47(7):1710-5. [2]. Homoplantaginin Inhibits Palmitic Acid-induced Endothelial Cells Inflammation by Suppressing TLR4 and NLRP3 Inflammasome. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 2016 Jan;67(1):93-101. [3]. Homoplantaginin modulates insulin sensitivity in endothelial cells by inhibiting inflammation. Biol Pharm Bull. 2012;35(7):1171-7. [4]. Pharmacokinetics of homoplantaginin in rats following intravenous, peritoneal injection and oral administration. J Pharm Biomed Anal. 2016 Sep 10;129:405-9. |
| Additional Infomation |
Homoplantaginin is a glycoside and a member of flavonoids. Homoplantaginin has been reported in Salvia plebeia, Salvia officinalis, and other organisms with data available. |
Solubility Data
| Solubility (In Vitro) | DMSO: 50~92 mg/mL (108.1~199.0 mM) |
| Solubility (In Vivo) |
Solubility in Formulation 1: ≥ 2.08 mg/mL (4.50 mM) (saturation unknown) in 10% DMSO + 40% PEG300 + 5% Tween80 + 45% Saline (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), clear solution. For example, if 1 mL of working solution is to be prepared, you can add 100 μL of 20.8 mg/mL clear DMSO stock solution to 400 μL PEG300 and mix evenly; then add 50 μL Tween-80 to the above solution and mix evenly; then add 450 μL normal saline to adjust the volume to 1 mL. Preparation of saline: Dissolve 0.9 g of sodium chloride in 100 mL ddH₂ O to obtain a clear solution. Solubility in Formulation 2: 2.08 mg/mL (4.50 mM) in 10% DMSO + 90% (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline) (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), suspension solution; with ultrasonication. For example, if 1 mL of working solution is to be prepared, you can add 100 μL of 20.8 mg/mL clear DMSO stock solution to 900 μL of 20% SBE-β-CD physiological saline solution and mix evenly. Preparation of 20% SBE-β-CD in Saline (4°C,1 week): Dissolve 2 g SBE-β-CD in 10 mL saline to obtain a clear solution. Solubility in Formulation 3: ≥ 2.08 mg/mL (4.50 mM) (saturation unknown) in 10% DMSO + 90% Corn Oil (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), clear solution. For example, if 1 mL of working solution is to be prepared, you can add 100 μL of 20.8 mg/mL clear DMSO stock solution to 900 μL of corn oil and mix evenly. (Please use freshly prepared in vivo formulations for optimal results.) |
| Preparing Stock Solutions | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.1626 mL | 10.8131 mL | 21.6263 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.4325 mL | 2.1626 mL | 4.3253 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.2163 mL | 1.0813 mL | 2.1626 mL |