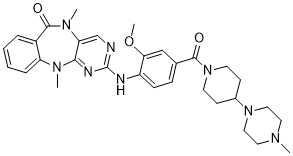
LRRK2-IN-1 (LRRK2-IN 1; LRRK2 IN-1) is a novel, highly potent and selective inhibitor of leucine-rich repeat kinase 2 (LRRK2) with anti-PD (Parkinson's disease) activity. It inhibits LRRK2 (G2019S) and LRRK2 (WT) with IC50s of 6 nM and 13 nM, respectively. Mutations in LRRK2 are closely related to late-onset autosomal dominant Parkinson's disease.
Physicochemical Properties
| Molecular Formula | C31H38N8O3 | |
| Molecular Weight | 570.69 | |
| Exact Mass | 570.306 | |
| CAS # | 1234480-84-2 | |
| Related CAS # |
|
|
| PubChem CID | 46843906 | |
| Appearance | Light yellow to yellow solid powder | |
| Density | 1.3±0.1 g/cm3 | |
| Boiling Point | 787.8±70.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Flash Point | 430.3±35.7 °C | |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±2.7 mmHg at 25°C | |
| Index of Refraction | 1.641 | |
| LogP | 0.36 | |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 1 | |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 9 | |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 5 | |
| Heavy Atom Count | 42 | |
| Complexity | 939 | |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 | |
| InChi Key | IWMCPJZTADUIFX-UHFFFAOYSA-N | |
| InChi Code | InChI=1S/C31H38N8O3/c1-35-15-17-38(18-16-35)22-11-13-39(14-12-22)29(40)21-9-10-24(27(19-21)42-4)33-31-32-20-26-28(34-31)36(2)25-8-6-5-7-23(25)30(41)37(26)3/h5-10,19-20,22H,11-18H2,1-4H3,(H,32,33,34) | |
| Chemical Name | 2-((2-methoxy-4-(4-(4-methylpiperazin-1-yl)piperidine-1-carbonyl)phenyl)amino)-5,11-dimethyl-5,11-dihydro-6H-benzo[e]pyrimido[5,4-b][1,4]diazepin-6-one | |
| Synonyms | LRRK2-IN 1; LRRK2-IN1; LRRK2-IN-1; | |
| HS Tariff Code | 2934.99.9001 | |
| Storage |
Powder-20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
|
| Shipping Condition | Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs) |
Biological Activity
| ln Vitro | The TR-FRET signal is 2.5 times higher in the wild-type and G2019S transduction, and this signal can be dose-dependently inhibited by LRRK2-IN-1, with IC50 values of 0.08 µM and 0.03 µM, respectively[1]. In DCLK2 inhibition, LRRK2-IN-1 had an IC50 of 45 nM. In biochemical assays for AURKB, CHEK2, MKNK2, MYLK, NUAK1, and PLK1, it has an IC50 of more than 1 µM. It has been verified that LRRK2-IN-1 inhibits MAPK7, with an EC50 of 160 nM. When LRRK2-IN-1 is stably transfected into HEK293 cells, it causes a dose-dependent inhibition of Ser910 and Ser935 phosphorylation along with the loss of 14-3-3 binding. IC50 of 49.3 µM indicates that LRRK2-IN-1 is moderately cytotoxic to HepG2 cells. In both the presence and absence of S9, LRRK2-IN-1 exhibits genotoxicity at 15.6 and 3.9 µM, respectively[3]. LRRK2-IN-1 prevents HCT116 and AsPC-1 cells from proliferating, migrating, and causing cell death with characteristics of apoptosis[4]. | ||
| ln Vivo | LRRK2-IN-1 (100 mg/kg, ip) causes LRRK2 to be dephosphorylated in the mice's kidney[2]. AsPC-1 tumor xenografts' tumor volume and weight significantly decrease after intraperitoneal injection of LRRK2-IN-1 (100 mg/kg)[4]. | ||
| Animal Protocol |
|
||
| References |
[1]. Screening for Novel LRRK2 Inhibitors Using a High-Throughput TR-FRET Cellular Assay for LRRK2 Ser935 Phosphorylation.PLoS One. 2012;7(8):e43580. Epub 2012 Aug 28. [2]. Characterization of a selective inhibitor of the Parkinson's disease kinase LRRK2. Nature Chemical Biology (2011), 7(4), 203-205. [3]. Alternative to LRRK2-IN-1 for Pharmacological Studies of Parkinson's Disease. Pharmacology. 2015;96(5-6):240-7. [4]. Small molecule kinase inhibitor LRRK2-IN-1 demonstrates potent activity against colorectal and pancreatic cancer through inhibition of doublecortin-like kinase 1. Mol Cancer. 2014 May 6;13:103. |
||
| Additional Infomation | LRRK2-IN-1 is a member of the class of pyrimidobenzodiazepines that is 5,11-dimethylpyrimido[4,5-b][1,4]benzodiazepin-6-one carrying at C-2 on the pyrimidine ring a 4-[(4-methylpiperazin-1-yl)piperidine-1-carbonyl]-2-methoxyanilino substituent. It is an inhibitor of the Parkinson's disease kinase LRRK2. It has a role as an EC 2.7.11.1 (non-specific serine/threonine protein kinase) inhibitor and an antineoplastic agent. It is a N-acylpiperidine, a N-alkylpiperazine, an aromatic ether, a pyrimidobenzodiazepine, an aromatic amine, a secondary amino compound and a tertiary amino compound. |
Solubility Data
| Solubility (In Vitro) |
|
|||
| Solubility (In Vivo) |
Solubility in Formulation 1: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (4.38 mM) (saturation unknown) in 10% DMSO + 40% PEG300 + 5% Tween80 + 45% Saline (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), clear solution. For example, if 1 mL of working solution is to be prepared, you can add 100 μL of 25.0 mg/mL clear DMSO stock solution to 400 μL PEG300 and mix evenly; then add 50 μL Tween-80 to the above solution and mix evenly; then add 450 μL normal saline to adjust the volume to 1 mL. Preparation of saline: Dissolve 0.9 g of sodium chloride in 100 mL ddH₂ O to obtain a clear solution. Solubility in Formulation 2: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (4.38 mM) (saturation unknown) in 10% DMSO + 90% (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline) (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), clear solution. For example, if 1 mL of working solution is to be prepared, you can add 100 μL of 25.0 mg/mL clear DMSO stock solution to 900 μL of 20% SBE-β-CD physiological saline solution and mix evenly. Preparation of 20% SBE-β-CD in Saline (4°C,1 week): Dissolve 2 g SBE-β-CD in 10 mL saline to obtain a clear solution. Solubility in Formulation 3: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (4.38 mM) (saturation unknown) in 10% DMSO + 90% Corn Oil (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), clear solution. For example, if 1 mL of working solution is to be prepared, you can add 100 μL of 25.0 mg/mL clear DMSO stock solution to 900 μL of corn oil and mix evenly. Solubility in Formulation 4: Captisol: 17mg/mL (Please use freshly prepared in vivo formulations for optimal results.) |
| Preparing Stock Solutions | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 1.7523 mL | 8.7613 mL | 17.5226 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.3505 mL | 1.7523 mL | 3.5045 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.1752 mL | 0.8761 mL | 1.7523 mL |