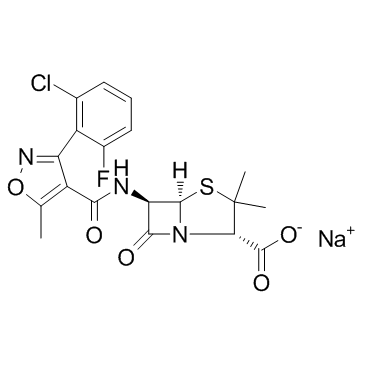
Flucloxacillin sodium (Floxacillin, Floxapen) is a potent narrow-spectrum beta-lactam antibiotic used to treat infections caused by susceptible Gram-positive bacteria. Unlike other penicillins, flucloxacillin is beta-lactamase stable and thus has activity against beta-lactamase-producing organisms such as Staphylococcus aureus as it is. However, it is ineffective against methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA). It is very similar to dicloxacillin and they are considered to be interchangeable.
Physicochemical Properties
| Molecular Formula | C19H16CLFN3NAO5S |
| Molecular Weight | 475.8512 |
| Exact Mass | 475.038 |
| Elemental Analysis | C, 47.96; H, 3.39; Cl, 7.45; F, 3.99; N, 8.83; Na, 4.83; O, 16.81; S, 6.74 |
| CAS # | 1847-24-1 |
| Related CAS # | Flucloxacillin;5250-39-5 |
| PubChem CID | 21319 |
| Appearance | Solid powder |
| Boiling Point | 677.3ºC at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 176-178ºC |
| Flash Point | 363.4ºC |
| Vapour Pressure | 2.86E-19mmHg at 25°C |
| LogP | 1.681 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 2 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 8 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 4 |
| Heavy Atom Count | 30 |
| Complexity | 758 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 3 |
| SMILES | ClC1=C([H])C([H])=C([H])C(=C1C1C(=C(C([H])([H])[H])ON=1)C(N([H])[C@]1([H])C(N2[C@@]([H])(C(=O)[O-])C(C([H])([H])[H])(C([H])([H])[H])S[C@@]21[H])=O)=O)F.[Na+] |
| InChi Key | OTEANHMVDHZOPB-SLINCCQESA-M |
| InChi Code | InChI=1S/C19H17ClFN3O5S.Na/c1-7-10(12(23-29-7)11-8(20)5-4-6-9(11)21)15(25)22-13-16(26)24-14(18(27)28)19(2,3)30-17(13)24/h4-6,13-14,17H,1-3H3,(H,22,25)(H,27,28)/q+1/p-1/t13-,14+,17-/m1./s1 |
| Chemical Name | Sodium (2S-(2alpha,5alpha,6beta))-6-(((3-(2-chloro-6-fluorophenyl)-5-methylisoxazol-4-yl)carbonyl)amino)-3,3-dimethyl-7-oxo-4-thia-1-azabicyclo(3.2.0)heptane-2-carboxylate |
| Synonyms | Floxapen;Floxacillin;Flucloxacillin; Fluorochloroxacillin |
| HS Tariff Code | 2934.99.9001 |
| Storage |
Powder-20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month Note: Please store this product in a sealed and protected environment, avoid exposure to moisture. |
| Shipping Condition | Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs) |
Biological Activity
| ln Vivo |
|
|
| Animal Protocol |
|
|
| ADME/Pharmacokinetics |
Absorption, Distribution and Excretion Bioavailability is 50–70% following oral administration. Metabolism / Metabolites Hepatic. Flucloxacillin has known human metabolites that include 6-[[3-(2-Chloro-6-fluorophenyl)-5-(hydroxymethyl)-1,2-oxazole-4-carbonyl]amino]-3,3-dimethyl-7-oxo-4-thia-1-azabicyclo[3.2.0]heptane-2-carboxylic acid. Biological Half-Life 0.75–1 hour |
|
| Toxicity/Toxicokinetics |
Effects During Pregnancy and Lactation ◉ Summary of Use during Lactation Floxacillin (flucloxacillin) is not approved for marketing in the United States by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration. It is acceptable to use during breastfeeding and is frequently used abroad to treat mastitis in nursing mothers. Limited information indicates that floxacillin levels in milk are low and are not expected to cause adverse effects in breastfed infants. Occasionally disruption of the infant's gastrointestinal flora, resulting in diarrhea or thrush have been reported with penicillins, but these effects have not been adequately evaluated. Floxacillin is acceptable in nursing mothers. ◉ Effects in Breastfed Infants Relevant published information was not found as of the revision date. ◉ Effects on Lactation and Breastmilk Relevant published information was not found as of the revision date. |
|
| References |
[1].Paton DM, et al. Bioavailability and half-life of two preparations of flucloxacillin. N Z Med J. 1982 Nov 10;95(719):766-8. [2].Williams J, et al.Sweat tests and flucloxacillin. Arch Dis Child. 1988 Jul;63(7):847-8. [3].Everett JR, et al. 19F NMR spectroscopy study of the metabolites of flucloxacillin in rat urine. J Pharm Pharmacol. 1985 Dec;37(12):869-73. |
|
| Additional Infomation |
Flucloxacillin is a penicillin compound having a 6beta-[3-(2-chloro-6-fluorophenyl)-5-methyl-1,2-oxazole-4-carboxamido] side-chain. It has a role as an antibacterial drug. It is a penicillin and a penicillin allergen. It is a conjugate acid of a flucloxacillin(1-). Antibiotic analog of [cloxacillin]. Flucloxacillin is a narrow-spectrum, semisynthetic isoxazolyl penicillin with antibacterial activity. Floxacillin binds to and inactivates penicillin-binding proteins (PBPs) located on the inner membrane of the bacterial cell wall. Inactivation of PBPs interferes with the cross-linkage of peptidoglycan chains necessary for bacterial cell wall strength and rigidity. This interrupts bacterial cell wall synthesis and results in the weakening of the bacterial cell wall, eventually causing cell lysis. Antibiotic analog of CLOXACILLIN. Drug Indication Used to treat bacterial infection by susceptible microorganisms. Mechanism of Action By binding to specific penicillin-binding proteins (PBPs) located inside the bacterial cell wall, flucloxacillin inhibits the third and last stage of bacterial cell wall synthesis. Cell lysis is then mediated by bacterial cell wall autolytic enzymes such as autolysins; it is possible that flucloxacillin interferes with an autolysin inhibitor. |
Solubility Data
| Solubility (In Vitro) |
H2O : ~100 mg/mL (~210.15 mM ) DMSO : ≥ 100 mg/mL (~210.15 mM) |
| Solubility (In Vivo) |
Solubility in Formulation 1: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (5.25 mM) (saturation unknown) in 10% DMSO + 40% PEG300 + 5% Tween80 + 45% Saline (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), clear solution. For example, if 1 mL of working solution is to be prepared, you can add 100 μL of 25.0 mg/mL clear DMSO stock solution to 400 μL PEG300 and mix evenly; then add 50 μL Tween-80 to the above solution and mix evenly; then add 450 μL normal saline to adjust the volume to 1 mL. Preparation of saline: Dissolve 0.9 g of sodium chloride in 100 mL ddH₂ O to obtain a clear solution. Solubility in Formulation 2: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (5.25 mM) (saturation unknown) in 10% DMSO + 90% (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline) (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), clear solution. For example, if 1 mL of working solution is to be prepared, you can add 100 μL of 25.0 mg/mL clear DMSO stock solution to 900 μL of 20% SBE-β-CD physiological saline solution and mix evenly. Preparation of 20% SBE-β-CD in Saline (4°C,1 week): Dissolve 2 g SBE-β-CD in 10 mL saline to obtain a clear solution. Solubility in Formulation 3: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (5.25 mM) (saturation unknown) in 10% DMSO + 90% Corn Oil (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), clear solution. For example, if 1 mL of working solution is to be prepared, you can add 100 μL of 25.0 mg/mL clear DMSO stock solution to 900 μL of corn oil and mix evenly. Solubility in Formulation 4: 10% DMSO+40% PEG300+5% Tween-80+45% Saline: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (5.25 mM) Solubility in Formulation 5: 100 mg/mL (210.15 mM) in PBS (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), clear solution; with ultrasonication. (Please use freshly prepared in vivo formulations for optimal results.) |
| Preparing Stock Solutions | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.1015 mL | 10.5075 mL | 21.0150 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.4203 mL | 2.1015 mL | 4.2030 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.2102 mL | 1.0508 mL | 2.1015 mL |