Physicochemical Properties
| Molecular Formula | C8H14N4O7 |
| Molecular Weight | 278.22 |
| Exact Mass | 278.086 |
| CAS # | 78491-02-8 |
| PubChem CID | 62277 |
| Appearance | White to off-white solid powder |
| Density | 1.8±0.1 g/cm3 |
| Boiling Point | 421.04°C (rough estimate) |
| Index of Refraction | 1.703 |
| LogP | -3.69 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 5 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 7 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 5 |
| Heavy Atom Count | 19 |
| Complexity | 376 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
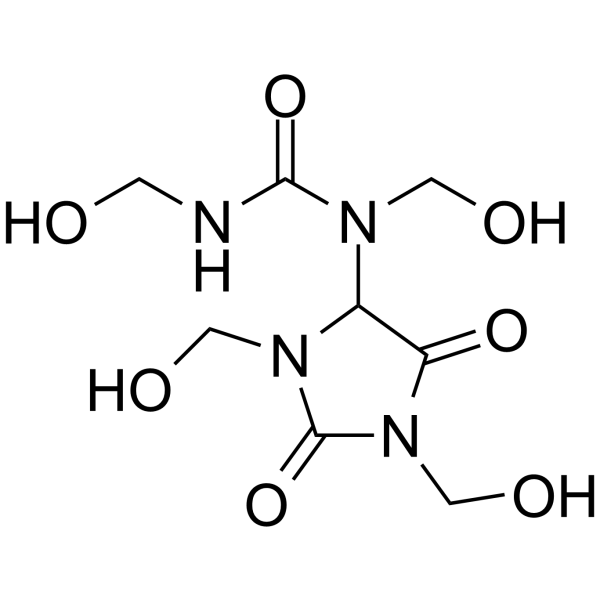
| SMILES | O=C1C([H])(N(C(N([H])C([H])([H])O[H])=O)C([H])([H])O[H])N(C([H])([H])O[H])C(N1C([H])([H])O[H])=O |
| InChi Key | SOROIESOUPGGFO-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| InChi Code | InChI=1S/C8H14N4O7/c13-1-9-7(18)10(2-14)5-6(17)12(4-16)8(19)11(5)3-15/h5,13-16H,1-4H2,(H,9,18) |
| Chemical Name | 1-[1,3-bis(hydroxymethyl)-2,5-dioxoimidazolidin-4-yl]-1,3-bis(hydroxymethyl)urea |
| HS Tariff Code | 2934.99.9001 |
| Storage |
Powder-20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month Note: This product requires protection from light (avoid light exposure) during transportation and storage. |
| Shipping Condition | Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs) |
Biological Activity
| ADME/Pharmacokinetics |
Metabolism / Metabolites Formaldehyde may be absorbed following inhalation, oral, or dermal exposure. It is an essential metabolic intermediate in all cells and is produced during the normal metabolism of serine, glycine, methionine, and choline and also by the demethylation of N-, S-, and O-methyl compounds. Exogenous formaldehyde is metabolized to formate by the enzyme formaldehyde dehydrogenase at the initial site of contact. After oxidation of formaldehyde to formate, the carbon atom is further oxidized to carbon dioxide or incorporated into purines, thymidine, and amino acids via tetrahydrofolatedependent one-carbon biosynthetic pathways. Formaldehyde is not stored in the body and is excreted in the urine (primarily as formic acid), incorporated into other cellular molecules, or exhaled as carbon dioxide. (L962) |
| References |
[1]. Kantor GR, et al. Acute allergic contact dermatitis from diazolidinyl urea (Germall II) in a hair gel. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1985;13(1):116-119. [2]. Doi T, et al. The different decomposition properties of diazolidinyl urea in cosmetics and patch test materials. Contact Dermatitis. 2011;65(2):81-91. [3]. Perret CM, et al. Contact sensitivity to diazolidinyl urea (Germall II). Arch Dermatol Res. 1989;281(1):57-59. |
| Additional Infomation |
Diazolidinylurea is an imidazolidine-2,4-dione. Diazolidinyl urea is an antimicrobial preservative that acts as a formaldehyde releaser. It is used in many cosmetics, skin care products, shampoos and conditioners, as well as a wide range of products including bubble baths, baby wipes and household detergents. Diazolidinyl urea is found in the commercially available preservative Germaben. Diazolidinyl urea may cause contact dermatitis. Its toxicity is also due to it's ability to release formaldehyde, which is believed to be carcinogenic. (L1895) |
Solubility Data
| Solubility (In Vitro) |
DMSO : 250 mg/mL (898.57 mM) H2O : 166.67 mg/mL (599.06 mM) |
| Solubility (In Vivo) |
Solubility in Formulation 1: ≥ 4.17 mg/mL (14.99 mM) (saturation unknown) in 10% DMSO + 40% PEG300 + 5% Tween80 + 45% Saline (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), clear solution. For example, if 1 mL of working solution is to be prepared, you can add 100 μL of 41.7 mg/mL clear DMSO stock solution to 400 μL PEG300 and mix evenly; then add 50 μL Tween-80 to the above solution and mix evenly; then add 450 μL normal saline to adjust the volume to 1 mL. Preparation of saline: Dissolve 0.9 g of sodium chloride in 100 mL ddH₂ O to obtain a clear solution. Solubility in Formulation 2: ≥ 4.17 mg/mL (14.99 mM) (saturation unknown) in 10% DMSO + 90% (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline) (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), clear solution. For example, if 1 mL of working solution is to be prepared, you can add 100 μL of 41.7 mg/mL clear DMSO stock solution to 900 μL of 20% SBE-β-CD physiological saline solution and mix evenly. Preparation of 20% SBE-β-CD in Saline (4°C,1 week): Dissolve 2 g SBE-β-CD in 10 mL saline to obtain a clear solution. Solubility in Formulation 3: ≥ 4.17 mg/mL (14.99 mM) (saturation unknown) in 10% DMSO + 90% Corn Oil (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), clear solution. For example, if 1 mL of working solution is to be prepared, you can add 100 μL of 41.7 mg/mL clear DMSO stock solution to 900 μL of corn oil and mix evenly. Solubility in Formulation 4: 110 mg/mL (395.37 mM) in PBS (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), clear solution; with ultrasonication. (Please use freshly prepared in vivo formulations for optimal results.) |
| Preparing Stock Solutions | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 3.5943 mL | 17.9714 mL | 35.9428 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.7189 mL | 3.5943 mL | 7.1886 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.3594 mL | 1.7971 mL | 3.5943 mL |