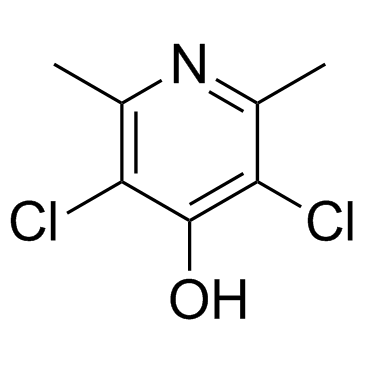
Clopidol (BRN 1527826; HSDB7907; Lerbek; WR-61112) is a potent coccidiostat agent used veterinary medicine to treat parasite infections. As an anticoccidial agent, it is often used as feed additive to control coccidiosis in chickens. Clopidol inhibits the sporulation of Eimeria tenella oocysts.
Physicochemical Properties
| Molecular Formula | C7H7CL2NO |
| Molecular Weight | 192.03 |
| Exact Mass | 190.99 |
| Elemental Analysis | C, 43.78; H, 3.67; Cl, 36.92; N, 7.29; O, 8.33 |
| CAS # | 2971-90-6 |
| PubChem CID | 18087 |
| Appearance | White to off-white solid powder |
| Density | 1.4±0.1 g/cm3 |
| Boiling Point | 318.4±37.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | >320℃ |
| Flash Point | 146.4±26.5 °C |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±0.7 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.578 |
| LogP | 1.24 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 1 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 2 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 0 |
| Heavy Atom Count | 11 |
| Complexity | 252 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| SMILES | ClC1C(C(=C(C([H])([H])[H])N([H])C=1C([H])([H])[H])Cl)=O |
| InChi Key | ZDPIZLCVJAAHHR-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| InChi Code | InChI=1S/C7H7Cl2NO/c1-3-5(8)7(11)6(9)4(2)10-3/h1-2H3,(H,10,11) |
| Chemical Name | 3,5-dichloro-2,6-dimethylpyridin-4-ol |
| Synonyms | BRN 1527826; BRN-1527826; Clopidol; 2971-90-6; 3,5-dichloro-2,6-dimethylpyridin-4-ol; Meticlorpindol; Coyden; Lerbek; Coccidiostat C; Metichlorpindol; BRN1527826; Clopidolo; HSDB 7907; HSDB-7907; HSDB7907; Lerbek; Methylchloropindol |
| HS Tariff Code | 2934.99.9001 |
| Storage |
Powder-20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
| Shipping Condition | Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs) |
Biological Activity
| Targets | Plasmodium;Coccidia |
| ln Vitro | In the low micromolar range, clopidol is effective against strains of Plasmodium falciparum that are resistant to atovaquone (FCR3) and chloroquine (W2)[3]. |
| ln Vivo | Clopidol (31.25-93.75 mg/kg feed; p.o. for 10 d) reduces the rate at which Eimeria tenella oocysts sporulate[2]. |
| Cell Assay | Feed additive anticoccidials currently used in Japan were examined for possible effects on oocyst sporulation of Eimeria tenella. Monensin, salinomycin, lasalocid, amprolium plus ethpabate, amporolium plus ethopabate plus sulfaquinoxaline, clopidol, or nicarbazin were given to chickens continuously via the feed at the recommended use level or one-half of that level. Oocysts discharged in feces 7-8 days post inoculation (PI) were collected and aerated for sporulation. Low sporulation rate was noted, when clopidol at 62.5 mg kg-1 was given from 4 to 7 days PI. These oocysts were as infective as oocysts from controls, based on weight gain, feed efficiency, gross lesion score of cecae, and oocyst count 7 days PI. The results of the study indicated that the second schizogony and gametogony are vulnerable to clopidol, as evidenced by oocyst sporulation, but infectivity of these sporulated oocysts was not affected[2]. |
| Animal Protocol | A high-performance liquid chromatographic-mass spectrometric (HPLC-MS) method has been developed for determination of clopidol residues in chicken tissues. Samples are extracted with acetonitrile. The extracts are cleaned up on an alumina column followed by an anion-exchange column. The clopidol is separated on a column (150 cmx4.6 mm) of Intertsil by using acetonitrile-water (20:80) as mobile phase. The clopidol was qualitatively identified by molecule mass and determined quantitatively by selected ion monitoring mode at 190 m/z. The recoveries with RSDs ranged from 91.6+/-10.1 to 97.3+/-5.7 at 0.010 to 10.0 mg/kg by spiking three matrices (chicken muscle, liver, and kidney). The limit of detection was 0.005 mg/kg, and the limit of quantification was 0.010 mg/kg.[1] |
| Toxicity/Toxicokinetics |
rat LD50 oral 18 gm/kg Merck Index; an Encyclopedia of Chemicals, Drugs, and Biologicals, 11th ed., Rahway, NJ 07065, Merck & Co., Inc. 1989, 11(375), 1989 rabbit LD50 oral >8 gm/kg Documentation of the Threshold Limit Values and Biological Exposure Indices, 5th ed., Cincinnati, OH, American Conference of Governmental Industrial Hygienists, Inc., 1986, 6(324), 1991 guinea pig LD50 oral >8 gm/kg Documentation of the Threshold Limit Values and Biological Exposure Indices, 5th ed., Cincinnati, OH, American Conference of Governmental Industrial Hygienists, Inc., 1986, 6(324), 1991 Non-Human Toxicity Values LD50 Rat oral 18 g/kg /SRP: 18,000 mg/kg/ |
| References |
[1]. Determination of clopidol residues in chicken tissues by high-performance liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry. J Chromatogr A. 2000 Jun 16;882(1-2):85-8. [2]. Effects of clopidol on sporulation and infectivity of Eimeria tenella oocysts. Vet Parasitol. 1991 Jan;38(1):55-60. [3]. Design, synthesis and structure-activity relationships of (1H-pyridin-4-ylidene)amines as potential antimalarials. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2009 Jul 1;19(13):3476-80. |
| Additional Infomation |
Clopidol is a white to light-brown, crystalline solid. Mp: 320 °C. Practically insoluble in water. Administered to poultry to prevent the growth of pathogenic parasites. Clopidol is a chloropyridine. A very effective anticoccidial agent used in poultry. See also: Clopidol; Lincomycin (component of); Bacitracin Zinc; Clopidol (component of); Bambermycins; Clopidol (component of) ... View More ... Therapeutic Uses THERAPEUTIC CATEGORY (VETERINARY): Coccidiostat Used as an anticoccidiostat in poultry. Clopidol is mainly coccidiostatic and is active only against the sporozoite stage of Eimeria. MEDICATION (VET): Turkeys grown for meat purposes only: As an aid in the prevention of leucocytozoonosis caused by Leucocytozoon smithi. MEDICATION (VET): Broiler and replacement chickens: As an aid in the prevention of coccidiosis in broilers and replacements for caged layers caused by E. tenella, Eimeria necatrix, Eimeria Acervulina, Eimeria maxima, Eimeria brunetti, Eimeria mivati. |
Solubility Data
| Solubility (In Vitro) |
4-Methylpyridine : ~3 mg/mL 0.1 M NaOH: ~26 mg/mL (~135.39 mM) DMSO : ~1 mg/mL ( ~5.2 mM ) |
| Solubility (In Vivo) |
Note: Listed below are some common formulations that may be used to formulate products with low water solubility (e.g. < 1 mg/mL), you may test these formulations using a minute amount of products to avoid loss of samples. Injection Formulations (e.g. IP/IV/IM/SC) Injection Formulation 1: DMSO : Tween 80: Saline = 10 : 5 : 85 (i.e. 100 μL DMSO stock solution → 50 μL Tween 80 → 850 μL Saline) *Preparation of saline: Dissolve 0.9 g of sodium chloride in 100 mL ddH ₂ O to obtain a clear solution. Injection Formulation 2: DMSO : PEG300 :Tween 80 : Saline = 10 : 40 : 5 : 45 (i.e. 100 μL DMSO → 400 μLPEG300 → 50 μL Tween 80 → 450 μL Saline) Injection Formulation 3: DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90 (i.e. 100 μL DMSO → 900 μL Corn oil) Example: Take the Injection Formulation 3 (DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90) as an example, if 1 mL of 2.5 mg/mL working solution is to be prepared, you can take 100 μL 25 mg/mL DMSO stock solution and add to 900 μL corn oil, mix well to obtain a clear or suspension solution (2.5 mg/mL, ready for use in animals). Injection Formulation 4: DMSO : 20% SBE-β-CD in saline = 10 : 90 [i.e. 100 μL DMSO → 900 μL (20% SBE-β-CD in saline)] *Preparation of 20% SBE-β-CD in Saline (4°C,1 week): Dissolve 2 g SBE-β-CD in 10 mL saline to obtain a clear solution. Injection Formulation 5: 2-Hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin : Saline = 50 : 50 (i.e. 500 μL 2-Hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin → 500 μL Saline) Injection Formulation 6: DMSO : PEG300 : castor oil : Saline = 5 : 10 : 20 : 65 (i.e. 50 μL DMSO → 100 μLPEG300 → 200 μL castor oil → 650 μL Saline) Injection Formulation 7: Ethanol : Cremophor : Saline = 10: 10 : 80 (i.e. 100 μL Ethanol → 100 μL Cremophor → 800 μL Saline) Injection Formulation 8: Dissolve in Cremophor/Ethanol (50 : 50), then diluted by Saline Injection Formulation 9: EtOH : Corn oil = 10 : 90 (i.e. 100 μL EtOH → 900 μL Corn oil) Injection Formulation 10: EtOH : PEG300:Tween 80 : Saline = 10 : 40 : 5 : 45 (i.e. 100 μL EtOH → 400 μLPEG300 → 50 μL Tween 80 → 450 μL Saline) Oral Formulations Oral Formulation 1: Suspend in 0.5% CMC Na (carboxymethylcellulose sodium) Oral Formulation 2: Suspend in 0.5% Carboxymethyl cellulose Example: Take the Oral Formulation 1 (Suspend in 0.5% CMC Na) as an example, if 100 mL of 2.5 mg/mL working solution is to be prepared, you can first prepare 0.5% CMC Na solution by measuring 0.5 g CMC Na and dissolve it in 100 mL ddH2O to obtain a clear solution; then add 250 mg of the product to 100 mL 0.5% CMC Na solution, to make the suspension solution (2.5 mg/mL, ready for use in animals). Oral Formulation 3: Dissolved in PEG400 Oral Formulation 4: Suspend in 0.2% Carboxymethyl cellulose Oral Formulation 5: Dissolve in 0.25% Tween 80 and 0.5% Carboxymethyl cellulose Oral Formulation 6: Mixing with food powders Note: Please be aware that the above formulations are for reference only. InvivoChem strongly recommends customers to read literature methods/protocols carefully before determining which formulation you should use for in vivo studies, as different compounds have different solubility properties and have to be formulated differently. (Please use freshly prepared in vivo formulations for optimal results.) |
| Preparing Stock Solutions | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 5.2075 mL | 26.0376 mL | 52.0752 mL | |
| 5 mM | 1.0415 mL | 5.2075 mL | 10.4150 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.5208 mL | 2.6038 mL | 5.2075 mL |