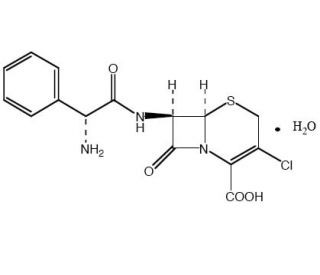
Cefaclor monohydrate, the monohydrated form of Cefaclor (Ceclor; Distaclor, Keflor, Biocef, Medacef, Raniclor), is a cephalosporin / beta-lactam antibiotic used as a generic drug in the treatment of certain bacterial infections such as pneumonia and infections of the ear, skin, throat, lung, and urinary tract.
Physicochemical Properties
| Molecular Formula | C15H16CLN3O5S |
| Molecular Weight | 385.8226 |
| Exact Mass | 385.05 |
| Elemental Analysis | C, 46.70; H, 4.18; Cl, 9.19; N, 10.89; O, 20.73; S, 8.31 |
| CAS # | 70356-03-5 |
| Related CAS # | Cefaclor;53994-73-3 |
| PubChem CID | 51038 |
| Appearance | Off-white to light yellow solid powder |
| Boiling Point | 713.4ºC at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | >180ºC (dec.) |
| Flash Point | 385.2ºC |
| LogP | 1.586 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 4 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 7 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 4 |
| Heavy Atom Count | 25 |
| Complexity | 606 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 3 |
| SMILES | ClC1C([H])([H])S[C@]2([H])[C@@]([H])(C(N2C=1C(=O)O[H])=O)N([H])C([C@@]([H])(C1C([H])=C([H])C([H])=C([H])C=1[H])N([H])[H])=O.O([H])[H] |
| InChi Key | WKJGTOYAEQDNIA-IOOZKYRYSA-N |
| InChi Code | InChI=1S/C15H14ClN3O4S.H2O/c16-8-6-24-14-10(13(21)19(14)11(8)15(22)23)18-12(20)9(17)7-4-2-1-3-5-7;/h1-5,9-10,14H,6,17H2,(H,18,20)(H,22,23);1H2/t9-,10-,14-;/m1./s1 |
| Chemical Name | (6R,7R)-7-((R)-2-amino-2-phenylacetamido)-3-chloro-8-oxo-5-thia-1-azabicyclo[4.2.0]oct-2-ene-2-carboxylic acid hydrate |
| Synonyms | Ceclor; Keclor; S6472; S-6472; S 6472; LS-149967; LS149967; LS 149967; |
| HS Tariff Code | 2934.99.9001 |
| Storage |
Powder-20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
| Shipping Condition | Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs) |
Biological Activity
| Targets | β-lactam |
| Toxicity/Toxicokinetics |
Effects During Pregnancy and Lactation ◉ Summary of Use during Lactation Cefaclor is no longer marketed in the United States. Limited information indicates that maternal cefaclor produces low levels in milk which are not expected to cause adverse effects in breastfed infants. Occasionally disruption of the infant's gastrointestinal flora, resulting in diarrhea or thrush have been reported with cephalosporins, but these effects have not been adequately evaluated. Cefaclor is acceptable in nursing mothers. ◉ Effects in Breastfed Infants In a telephone follow-up study, 5 nursing mothers reported taking cefaclor (dosage unspecified). One mother reported diarrhea in her infant. No rashes or candidiasis were reported among the exposed infants. ◉ Effects on Lactation and Breastmilk Relevant published information was not found as of the revision date. |
| References |
[1]. Characterization of penicillin-binding protein 2 of Staphylococcus aureus: deacylation reaction and identification of two penicillin-binding peptides. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1992 Mar;36(3):656-61. [2]. Cefaclor revisited. Clin Ther. 2000 Feb;22(2):154-66. [3]. Pharmacokinetic profile of cefaclor. Int J Clin Pharmacol Ther. |
| Additional Infomation |
Cefaclor is a beta-lactam, second-generation cephalosporin antibiotic with bactericidal activity. Cefaclor binds to and inactivates penicillin-binding proteins (PBP) located in bacterial cytoplasmic membranes. PBPs are enzymes involved in the terminal stages of assembling the bacterial cell wall and in reshaping the cell wall during growth and division. Inactivation of PBPs interferes with the cross-linkage of peptidoglycan chains necessary for bacterial cell wall strength and rigidity. This results in the weakening of the bacterial cell wall and causes cell lysis. Semisynthetic, broad-spectrum antibiotic derivative of CEPHALEXIN. See also: Cefaclor (annotation moved to). |
Solubility Data
| Solubility (In Vitro) | DMSO : ~11 mg/mL ( ~28.51 mM ) |
| Solubility (In Vivo) |
Note: Listed below are some common formulations that may be used to formulate products with low water solubility (e.g. < 1 mg/mL), you may test these formulations using a minute amount of products to avoid loss of samples. Injection Formulations (e.g. IP/IV/IM/SC) Injection Formulation 1: DMSO : Tween 80: Saline = 10 : 5 : 85 (i.e. 100 μL DMSO stock solution → 50 μL Tween 80 → 850 μL Saline) *Preparation of saline: Dissolve 0.9 g of sodium chloride in 100 mL ddH ₂ O to obtain a clear solution. Injection Formulation 2: DMSO : PEG300 :Tween 80 : Saline = 10 : 40 : 5 : 45 (i.e. 100 μL DMSO → 400 μLPEG300 → 50 μL Tween 80 → 450 μL Saline) Injection Formulation 3: DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90 (i.e. 100 μL DMSO → 900 μL Corn oil) Example: Take the Injection Formulation 3 (DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90) as an example, if 1 mL of 2.5 mg/mL working solution is to be prepared, you can take 100 μL 25 mg/mL DMSO stock solution and add to 900 μL corn oil, mix well to obtain a clear or suspension solution (2.5 mg/mL, ready for use in animals). Injection Formulation 4: DMSO : 20% SBE-β-CD in saline = 10 : 90 [i.e. 100 μL DMSO → 900 μL (20% SBE-β-CD in saline)] *Preparation of 20% SBE-β-CD in Saline (4°C,1 week): Dissolve 2 g SBE-β-CD in 10 mL saline to obtain a clear solution. Injection Formulation 5: 2-Hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin : Saline = 50 : 50 (i.e. 500 μL 2-Hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin → 500 μL Saline) Injection Formulation 6: DMSO : PEG300 : castor oil : Saline = 5 : 10 : 20 : 65 (i.e. 50 μL DMSO → 100 μLPEG300 → 200 μL castor oil → 650 μL Saline) Injection Formulation 7: Ethanol : Cremophor : Saline = 10: 10 : 80 (i.e. 100 μL Ethanol → 100 μL Cremophor → 800 μL Saline) Injection Formulation 8: Dissolve in Cremophor/Ethanol (50 : 50), then diluted by Saline Injection Formulation 9: EtOH : Corn oil = 10 : 90 (i.e. 100 μL EtOH → 900 μL Corn oil) Injection Formulation 10: EtOH : PEG300:Tween 80 : Saline = 10 : 40 : 5 : 45 (i.e. 100 μL EtOH → 400 μLPEG300 → 50 μL Tween 80 → 450 μL Saline) Oral Formulations Oral Formulation 1: Suspend in 0.5% CMC Na (carboxymethylcellulose sodium) Oral Formulation 2: Suspend in 0.5% Carboxymethyl cellulose Example: Take the Oral Formulation 1 (Suspend in 0.5% CMC Na) as an example, if 100 mL of 2.5 mg/mL working solution is to be prepared, you can first prepare 0.5% CMC Na solution by measuring 0.5 g CMC Na and dissolve it in 100 mL ddH2O to obtain a clear solution; then add 250 mg of the product to 100 mL 0.5% CMC Na solution, to make the suspension solution (2.5 mg/mL, ready for use in animals). Oral Formulation 3: Dissolved in PEG400 Oral Formulation 4: Suspend in 0.2% Carboxymethyl cellulose Oral Formulation 5: Dissolve in 0.25% Tween 80 and 0.5% Carboxymethyl cellulose Oral Formulation 6: Mixing with food powders Note: Please be aware that the above formulations are for reference only. InvivoChem strongly recommends customers to read literature methods/protocols carefully before determining which formulation you should use for in vivo studies, as different compounds have different solubility properties and have to be formulated differently. (Please use freshly prepared in vivo formulations for optimal results.) |
| Preparing Stock Solutions | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.5919 mL | 12.9594 mL | 25.9188 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.5184 mL | 2.5919 mL | 5.1838 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.2592 mL | 1.2959 mL | 2.5919 mL |