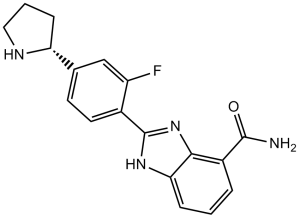
A-966492 is a selective and orally bioavailable PARP [poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase] inhibitor with potential anticancer activity. It inhibits PARP1 and PARP2 with Kis of 1 nM and 1.5 nM, respectively. In a B16-F10 melanoma model, it also showed exceptional in vivo antitumor efficacy when combined with temozolomide.
Physicochemical Properties
| Molecular Formula | C18H17FN4O | |
| Molecular Weight | 324.35 | |
| Exact Mass | 324.138 | |
| Elemental Analysis | C, 66.65; H, 5.28; F, 5.86; N, 17.27; O, 4.93 | |
| CAS # | 934162-61-5 | |
| Related CAS # |
|
|
| PubChem CID | 16666333 | |
| Appearance | White solid powder | |
| Density | 1.3±0.1 g/cm3 | |
| Boiling Point | 605.5±65.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Flash Point | 320.0±34.3 °C | |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±1.7 mmHg at 25°C | |
| Index of Refraction | 1.665 | |
| LogP | 0.96 | |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 3 | |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 4 | |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 3 | |
| Heavy Atom Count | 24 | |
| Complexity | 476 | |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 1 | |
| SMILES | C(C1C=CC=C2N=C(C3C=CC([C@H]4NCCC4)=CC=3F)NC=12)(=O)N |
|
| InChi Key | AHIVQGOUBLVTCB-AWEZNQCLSA-N | |
| InChi Code | InChI=1S/C18H17FN4O/c19-13-9-10(14-5-2-8-21-14)6-7-11(13)18-22-15-4-1-3-12(17(20)24)16(15)23-18/h1,3-4,6-7,9,14,21H,2,5,8H2,(H2,20,24)(H,22,23)/t14-/m0/s1 | |
| Chemical Name | 2-[2-fluoro-4-[(2S)-pyrrolidin-2-yl]phenyl]-1H-benzimidazole-4-carboxamide | |
| Synonyms |
|
|
| HS Tariff Code | 2934.99.9001 | |
| Storage |
Powder-20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
|
| Shipping Condition | Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs) |
Biological Activity
| Targets | PARP-1 ( Ki = 1 nM ); PARP-2 ( Ki = 1.5 nM ) | |
| ln Vitro |
|
|
| ln Vivo |
|
|
| Enzyme Assay | The buffer used for the enzyme assay contains 50 mM Tris, pH 8.0, 1 mM dithiothreitol (DTT), and 4 mM magnesium chloride. 1.5 μM [3H]-NAD+ (1.6 μCi/mmol), 200 nM biotinylated histone H1, 200 nM slDNA, and 1 nM or 4 nM PARP-2 enzyme are the ingredients of the PARP reaction. Autoreactions in 100 μL volumes in white 96-well plates are performed using SPA bead-based detection. 50 μL of the 2X NAD+ substrate mixture is added to 50 μL of the 2× enzyme mixture, which contains DNA and PARP, to start the reaction. The addition of 150 μL of 1.5 mM benzamide (approximately 1×103-fold over its IC50) stops these reactions. The stopped reaction mixtures are put in amounts of 170 μL to Flash Plates coated with streptavidin, incubated for an hour, and then counted using a TopCount microplate scintillation counter. Inhibition curves at varied substrate concentrations are used to calculate ki data. | |
| Cell Assay | In a 96-well plate, C41 cells are exposed to A-966492 for 30 minutes. DNA damage with 1 mM H2O2 for 10 minutes activates PARP. After one ice-cold wash in phosphate-buffered saline (PBS), cells are fixed for ten minutes at -20°C using prechilled methanol/acetone (7:3). Plates are allowed to air dry before being rehydrated with PBS and blocked for 30 minutes at room temperature using 5% nonfat dry milk in PBS-Tween (0.05%) as the blocking solution. Goat antimouse fluorescein 5(6)-isothiocyanate (FITC)-coupled antibody (1:50) and 1 μg/mL 40,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole (DAPI) are then added to the blocking solution and the cells are incubated for 60 minutes at room temperature. After washing the cells five times with PBS-Tween20, the cells are again incubated for 60 minutes with anti-PAR antibody 10H (1:50) in blocking solution. Following five PBS-Tween20 washes, the analysis is carried out using an fmax Fluorescence Microplate Reader that is configured to read at either the FITC or DAPI excitation and emission wavelengths. Cell numbers are used to normalize PARP activity (FITC signal) using DAPI. | |
| Animal Protocol |
|
|
| References |
[1]. Optimization of phenyl-substituted benzimidazole carboxamide poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase inhibitors: identification of (S)-2-(2-fluoro-4-(pyrrolidin-2-yl)phenyl)-1H-benzimidazole-4-carboxamide (A-966492), a highly potent and efficacious inhibitor. J Med Chem . 2010 Apr 22;53(8):3142-53. |
Solubility Data
| Solubility (In Vitro) |
|
|||
| Solubility (In Vivo) |
Solubility in Formulation 1: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (7.71 mM) (saturation unknown) in 10% DMSO + 40% PEG300 + 5% Tween80 + 45% Saline (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), clear solution. For example, if 1 mL of working solution is to be prepared, you can add 100 μL of 25.0 mg/mL clear DMSO stock solution to 400 μL PEG300 and mix evenly; then add 50 μL Tween-80 to the above solution and mix evenly; then add 450 μL normal saline to adjust the volume to 1 mL. Preparation of saline: Dissolve 0.9 g of sodium chloride in 100 mL ddH₂ O to obtain a clear solution. Solubility in Formulation 2: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (7.71 mM) (saturation unknown) in 10% DMSO + 90% (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline) (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), clear solution. For example, if 1 mL of working solution is to be prepared, you can add 100 μL of 25.0 mg/mL clear DMSO stock solution to 900 μL of 20% SBE-β-CD physiological saline solution and mix evenly. Preparation of 20% SBE-β-CD in Saline (4°C,1 week): Dissolve 2 g SBE-β-CD in 10 mL saline to obtain a clear solution. Solubility in Formulation 3: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (7.71 mM) (saturation unknown) in 10% DMSO + 90% Corn Oil (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), clear solution. For example, if 1 mL of working solution is to be prepared, you can add 100 μL of 25.0 mg/mL clear DMSO stock solution to 900 μL of corn oil and mix evenly. (Please use freshly prepared in vivo formulations for optimal results.) |
| Preparing Stock Solutions | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 3.0831 mL | 15.4154 mL | 30.8309 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.6166 mL | 3.0831 mL | 6.1662 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.3083 mL | 1.5415 mL | 3.0831 mL |