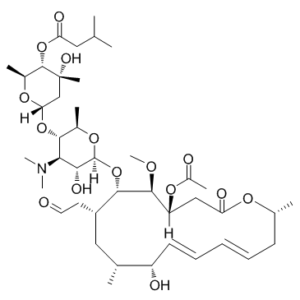
Josamycin (BRN-1677122; CCRIS 8511; EN-141) is a macrolide antibiotic that exhibits antimicrobial activity against a wide spectrum of pathogens, such as bacteria. The dissociation constant Kd from ribosome for Josamycin is 5.5 nM. It is synthesized from strains of Streptomyces narbonensis var.
Physicochemical Properties
| Molecular Formula | C42H69NO15 |
| Molecular Weight | 827.99496 |
| Exact Mass | 827.466 |
| Elemental Analysis | C, 60.92; H, 8.40; N, 1.69; O, 28.98 |
| CAS # | 16846-24-5 |
| Related CAS # | 31674-19-8 (Josamycin propionate); 11033-19-5 (Josamycin HCl); 4564-87-8 (Carbomycin); 35775-82-7 (Maridomycin); 20283-69-6 (niddamycin); 1404-48-4 (relomycin);35834-26-5 (rosaramicin); 497-72-3 (methymycin); 30042-37-6 (lankamycin ) |
| PubChem CID | 5282165 |
| Appearance | Solid powder |
| Density | 1.2±0.1 g/cm3 |
| Boiling Point | 877.8±65.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 131.5℃ |
| Flash Point | 484.7±34.3 °C |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±0.6 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.535 |
| LogP | 3.88 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 3 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 16 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 14 |
| Heavy Atom Count | 58 |
| Complexity | 1390 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 16 |
| SMILES | O[C@H]1[C@](O[C@H](C)[C@@H](O[C@@](O[C@@H](C)[C@@H]2OC(CC(C)C)=O)([H])C[C@]2(O)C)[C@@H]1N(C)C)([H])O[C@@H]([C@H](C[C@H]([C@H](/C=C/C=C/C3)O)C)CC=O)[C@H]([C@](CC(O[C@@H]3C)=O)([H])OC(C)=O)OC |
| InChi Key | XJSFLOJWULLJQS-DJBGMQKKSA-N |
| InChi Code | InChI=1S/C42H69NO15/c1-23(2)19-32(47)56-40-27(6)53-34(22-42(40,8)50)57-37-26(5)54-41(36(49)35(37)43(9)10)58-38-29(17-18-44)20-24(3)30(46)16-14-12-13-15-25(4)52-33(48)21-31(39(38)51-11)55-28(7)45/h12-14,16,18,23-27,29-31,34-41,46,49-50H,15,17,19-22H2,1-11H3/b13-12-,16-14+/t24-,25-,26-,27+,29+,30+,31-,34+,35-,36-,37-,38+,39+,40+,41+,42-/m1/s1 |
| Chemical Name | Leucomycin V, 3-acetate 4(sup B)-(3-methylbutanoate) |
| Synonyms | Josamycin; BRN-1677122; CCRIS 8511; BRN 1677122; BRN1677122; Josamycin hydrochloride; Leucomycin A3 hydrochloride; |
| HS Tariff Code | 2934.99.9001 |
| Storage |
Powder-20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month Note: Please store this product in a sealed and protected environment, avoid exposure to moisture. |
| Shipping Condition | Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs) |
Biological Activity
| Targets | Macrolide |
| ln Vitro | According to studies, josamycin has an average lifetime of 3 hours on the ribosome and a dissociation constant of 5.5 nM when it binds to the ribosome. Josamycin completely prevents the synthesis of full-length proteins at saturating drug concentrations by completely inhibiting the formation of the second or third peptide bond, depending on the peptide sequence. Josamycin also slows down the formation of the first peptide bond of a nascent peptide in an amino acid-dependent manner. Josamycin completely inhibits the synthesis of full-length proteins at a saturating drug concentration[1]. |
| ln Vivo | After giving rabbits 200 mg/kg of josamycin orally, the drug is present in their blood and tissues. In general, tissue levels are significantly higher than blood levels, and they are also somewhat higher three hours after the dose than they are one hour later, when the blood level is at its lowest. The level in the lungs is the highest of all tissue levels one hour after the medication[2]. |
| Enzyme Assay | 0.5 mM calcium chloride, 5 mM magnesium acetate, 5 mM ammonium chloride, 95 mM potassium chloride, 8 mM putrescine, 1 mM spermidine, 5 mM potassium phosphate, and 1 mM dithioerythritol are the ingredients used to prepare josamycin in polymix buffer. Preinitiated ribosomes are treated with varying concentrations of josamycin (2, 3, 4, and 6 μM) to initiate the incubation process. At each incubation period, one volume of the reaction mix is mixed with one volume of the elongation mix. The reaction is then quenched with formic acid after ten seconds. The fraction of ribosomes that form tripeptides is used to estimate the association rates[1]. |
| Animal Protocol |
Rat: Rats are given 200 mg/kg of oral Josamycin labeled with tritium. Bioassay is used to determine the blood and tissue levels at one hour and three hours[2]. Mouse: Mice are given 200 mg/kg of josamycin labeled with tritium orally. Bioassay is used to determine the blood and tissue levels at one hour and three hours[2]. |
| References |
[1]. Kinetics of macrolide action: the Josamycin and erythromycin cases. J Biol Chem. 2004 Dec 17;279(51):53506-15. [2]. Pharmacokinetics of macrolides, lincosamides and streptogramins. J Antimicrob Chemother. 1985 Jul;16 Suppl A:151-66. |
| Additional Infomation |
Josamycin is a macrolide antibiotic produced by certain strains of Streptomyces narbonensis var. josamyceticus. It has a role as an antibacterial drug and a metabolite. It is a macrolide antibiotic, an aldehyde, a tertiary amino compound, a tertiary alcohol, an acetate ester, a disaccharide derivative and a glycoside. A macrolide antibiotic from Streptomyces narbonensis. The drug has antimicrobial activity against a wide spectrum of pathogens. A macrolide antibiotic from Streptomyces narbonensis. The drug has antimicrobial activity against a wide spectrum of pathogens. Drug Indication For the treatment of bacterial infections. Mechanism of Action The mechanism of action of macrolides such as Josamycin is via inhibition of bacterial protein biosynthesis by binding reversibly to the subunit 50S of the bacterial ribosome, thereby inhibiting translocation of peptidyl tRNA. This action is mainly bacteriostatic, but can also be bactericidal in high concentrations. Macrolides tend to accumulate within leukocytes, and are therefore actually transported into the site of infection. Pharmacodynamics Josamycin is a macrolide antibiotic from Streptomyces narbonensis. The drug has antimicrobial activity against a wide spectrum of pathogens. |
Solubility Data
| Solubility (In Vitro) |
DMSO : 41.67~100 mg/mL (50.33~120.77 mM) H2O : 8.33 mg/mL (10.06 mM) Ethanol : ~100 mg/mL |
| Solubility (In Vivo) |
Solubility in Formulation 1: 2.5 mg/mL (3.02 mM) in 10% DMSO + 40% PEG300 + 5% Tween80 + 45% Saline (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), suspension solution; with sonication. For example, if 1 mL of working solution is to be prepared, you can add 100 μL of 25.0 mg/mL clear DMSO stock solution to 400 μL PEG300 and mix evenly; then add 50 μL Tween-80 to the above solution and mix evenly; then add 450 μL normal saline to adjust the volume to 1 mL. Preparation of saline: Dissolve 0.9 g of sodium chloride in 100 mL ddH₂ O to obtain a clear solution. Solubility in Formulation 2: 2.5 mg/mL (3.02 mM) in 10% DMSO + 90% (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline) (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), suspension solution; with ultrasonication. For example, if 1 mL of working solution is to be prepared, you can add 100 μL of 25.0 mg/mL clear DMSO stock solution to 900 μL of 20% SBE-β-CD physiological saline solution and mix evenly. Preparation of 20% SBE-β-CD in Saline (4°C,1 week): Dissolve 2 g SBE-β-CD in 10 mL saline to obtain a clear solution. Solubility in Formulation 3: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (3.02 mM) (saturation unknown) in 10% DMSO + 90% Corn Oil (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), clear solution. For example, if 1 mL of working solution is to be prepared, you can add 100 μL of 25.0 mg/mL clear DMSO stock solution to 900 μL of corn oil and mix evenly. Solubility in Formulation 4: 10% DMSO+40% PEG300+5% Tween-80+45% Saline: 2.5 mg/mL (3.02 mM) (Please use freshly prepared in vivo formulations for optimal results.) |
| Preparing Stock Solutions | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 1.2077 mL | 6.0387 mL | 12.0774 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.2415 mL | 1.2077 mL | 2.4155 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.1208 mL | 0.6039 mL | 1.2077 mL |