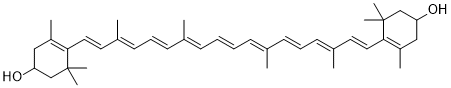
Zeaxanthin is a naturally occurring carotenoid and one of the most common carotenoid alcohols found in nature. It is crucial to the xanthophyll cycle. It is the pigment that gives paprika (made from bell peppers), corn, saffron, wolfberries, and many other plants and microbes their distinctive color.
Physicochemical Properties
| Molecular Formula | C40H56O2 |
| Molecular Weight | 568.8715 |
| Exact Mass | 568.428 |
| Elemental Analysis | C, 84.45; H, 9.92; O, 5.62 |
| CAS # | 144-68-3 |
| Related CAS # | 144-68-3 |
| PubChem CID | 5280899 |
| Appearance | Solid powder |
| Density | 1.0±0.1 g/cm3 |
| Boiling Point | 711.4±55.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 203-2050C |
| Flash Point | 273.4±26.1 °C |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±5.2 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.585 |
| LogP | 11.84 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 2 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 2 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 10 |
| Heavy Atom Count | 42 |
| Complexity | 1190 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 2 |
| SMILES | O([H])[C@]1([H])C([H])([H])C(C([H])([H])[H])=C(/C(/[H])=C(\[H])/C(=C(\[H])/C(/[H])=C(\[H])/C(=C(\[H])/C(/[H])=C(\[H])/C(/[H])=C(\C([H])([H])[H])/C(/[H])=C(\[H])/C(/[H])=C(\C([H])([H])[H])/C(/[H])=C(\[H])/C2=C(C([H])([H])[H])C([H])([H])[C@]([H])(C([H])([H])C2(C([H])([H])[H])C([H])([H])[H])O[H])/C([H])([H])[H])/C([H])([H])[H])C(C([H])([H])[H])(C([H])([H])[H])C1([H])[H] |
| InChi Key | JKQXZKUSFCKOGQ-QAYBQHTQSA-N |
| InChi Code | InChI=1S/C40H56O2/c1-29(17-13-19-31(3)21-23-37-33(5)25-35(41)27-39(37,7)8)15-11-12-16-30(2)18-14-20-32(4)22-24-38-34(6)26-36(42)28-40(38,9)10/h11-24,35-36,41-42H,25-28H2,1-10H3/b12-11+,17-13+,18-14+,23-21+,24-22+,29-15+,30-16+,31-19+,32-20+/t35-,36-/m1/s1 |
| Chemical Name | (1R)-4-[(1E,3E,5E,7E,9E,11E,13E,15E,17E)-18-[(4R)-4-hydroxy-2,6,6-trimethylcyclohexen-1-yl]-3,7,12,16-tetramethyloctadeca-1,3,5,7,9,11,13,15,17-nonaenyl]-3,5,5-trimethylcyclohex-3-en-1-ol |
| Synonyms | beta-Carotene-3,3'-diol; Xanthophyll 3; Zeaxanthin; Zeaxanthol; Anchovyxanthin |
| HS Tariff Code | 2934.99.9001 |
| Storage |
Powder-20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month Note: (1). This product requires protection from light (avoid light exposure) during transportation and storage.(2). This product is not stable in solution, please use freshly prepared working solution for optimal results. |
| Shipping Condition | Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs) |
Biological Activity
| Targets | Microbial Metabolite; Human Endogenous Metabolite |
| ln Vitro | Plant leaves contain lutein and zeaxanthin that are primarily attached to proteins. The xanthophylls are condensed and purified into chromoplasts, which are found dissolved in membranes, in fruits and flower petals. In humans and other higher animals, lipophilic tissues like adipose tissue are where lutein and zeaxanthin accumulate. Lipoproteins formulate these pigments in the blood, most likely in a way that is deeply non-phospholipid-based. While hydrocarbon carotenoids are preferentially concentrated in the LDL fraction, up to 75% of them, lutein and zeaxanthin are equally distributed in the blood's LDL and HDL fractions [3]. |
| References |
[1]. Distribution of lutein and zeaxanthin stereoisomers in the human retina. Exp Eye Res. 1997 Feb;64(2):211-8. [2]. Evaluation of antioxidant treatments for the modulation of macrophage function in the context of retinal degeneration. Mol Vis. 2019 Sep 5;25:479-488. [3]. Biologic mechanisms of the protective role of lutein and zeaxanthin in the eye.Annu Rev Nutr. 2003;23:171-201. |
| Additional Infomation |
Zeaxanthin is a carotenol. It has a role as a bacterial metabolite, a cofactor and an antioxidant. It derives from a hydride of a beta-carotene. Zeaxanthin is a most common carotenoid alcohols found in nature that is involved in the xanthophyll cycle. As a coexistent isomer of lutein, zeaxanthin is synthesized in plants and some micro-organisms. It gives the distinct yellow color to many vegetables and other plants including paprika, corn, saffron and wolfberries. Zeaxanthin is one of the two primary xanthophyll carotenoids contained within the retina of the eye and plays a predominant component in the central macula. It is available as a dietary supplement for eye health benefits and potential prevention of age-related macular degeneration. Zeaxanthin is also added as a food dye. Zeaxanthin has been reported in Planktothrix rubescens, Planktothrix agardhii, and other organisms with data available. Carotenoids found in fruits and vegetables. Zeaxanthin accumulates in the MACULA LUTEA. See also: Saffron (part of); Corn (part of); Lycium barbarum fruit (part of). |
Solubility Data
| Solubility (In Vitro) |
THF: ≥ 10 mg/mL (~17.6 mM) DMSO: < 1 mg/mL |
| Solubility (In Vivo) |
Note: Listed below are some common formulations that may be used to formulate products with low water solubility (e.g. < 1 mg/mL), you may test these formulations using a minute amount of products to avoid loss of samples. Injection Formulations (e.g. IP/IV/IM/SC) Injection Formulation 1: DMSO : Tween 80: Saline = 10 : 5 : 85 (i.e. 100 μL DMSO stock solution → 50 μL Tween 80 → 850 μL Saline) *Preparation of saline: Dissolve 0.9 g of sodium chloride in 100 mL ddH ₂ O to obtain a clear solution. Injection Formulation 2: DMSO : PEG300 :Tween 80 : Saline = 10 : 40 : 5 : 45 (i.e. 100 μL DMSO → 400 μLPEG300 → 50 μL Tween 80 → 450 μL Saline) Injection Formulation 3: DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90 (i.e. 100 μL DMSO → 900 μL Corn oil) Example: Take the Injection Formulation 3 (DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90) as an example, if 1 mL of 2.5 mg/mL working solution is to be prepared, you can take 100 μL 25 mg/mL DMSO stock solution and add to 900 μL corn oil, mix well to obtain a clear or suspension solution (2.5 mg/mL, ready for use in animals). Injection Formulation 4: DMSO : 20% SBE-β-CD in saline = 10 : 90 [i.e. 100 μL DMSO → 900 μL (20% SBE-β-CD in saline)] *Preparation of 20% SBE-β-CD in Saline (4°C,1 week): Dissolve 2 g SBE-β-CD in 10 mL saline to obtain a clear solution. Injection Formulation 5: 2-Hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin : Saline = 50 : 50 (i.e. 500 μL 2-Hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin → 500 μL Saline) Injection Formulation 6: DMSO : PEG300 : castor oil : Saline = 5 : 10 : 20 : 65 (i.e. 50 μL DMSO → 100 μLPEG300 → 200 μL castor oil → 650 μL Saline) Injection Formulation 7: Ethanol : Cremophor : Saline = 10: 10 : 80 (i.e. 100 μL Ethanol → 100 μL Cremophor → 800 μL Saline) Injection Formulation 8: Dissolve in Cremophor/Ethanol (50 : 50), then diluted by Saline Injection Formulation 9: EtOH : Corn oil = 10 : 90 (i.e. 100 μL EtOH → 900 μL Corn oil) Injection Formulation 10: EtOH : PEG300:Tween 80 : Saline = 10 : 40 : 5 : 45 (i.e. 100 μL EtOH → 400 μLPEG300 → 50 μL Tween 80 → 450 μL Saline) Oral Formulations Oral Formulation 1: Suspend in 0.5% CMC Na (carboxymethylcellulose sodium) Oral Formulation 2: Suspend in 0.5% Carboxymethyl cellulose Example: Take the Oral Formulation 1 (Suspend in 0.5% CMC Na) as an example, if 100 mL of 2.5 mg/mL working solution is to be prepared, you can first prepare 0.5% CMC Na solution by measuring 0.5 g CMC Na and dissolve it in 100 mL ddH2O to obtain a clear solution; then add 250 mg of the product to 100 mL 0.5% CMC Na solution, to make the suspension solution (2.5 mg/mL, ready for use in animals). Oral Formulation 3: Dissolved in PEG400 Oral Formulation 4: Suspend in 0.2% Carboxymethyl cellulose Oral Formulation 5: Dissolve in 0.25% Tween 80 and 0.5% Carboxymethyl cellulose Oral Formulation 6: Mixing with food powders Note: Please be aware that the above formulations are for reference only. InvivoChem strongly recommends customers to read literature methods/protocols carefully before determining which formulation you should use for in vivo studies, as different compounds have different solubility properties and have to be formulated differently. (Please use freshly prepared in vivo formulations for optimal results.) |
| Preparing Stock Solutions | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 1.7579 mL | 8.7894 mL | 17.5787 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.3516 mL | 1.7579 mL | 3.5157 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.1758 mL | 0.8789 mL | 1.7579 mL |