Z-LEHD-FMK is a caspase-9 enzyme inhibitor that is cell-permeable, specific, competitive, and irreversible. It promotes cell survival, guards against lethal reperfusion injury, and reduces apoptosis. In a rat model of spinal cord injury, Z-LEHD-FMK exhibits the neuroprotective effect. Z-LEHD-FMK prevented apoptosis caused by tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL) in the human colon cancer cell line HCT116 and the human embryonic kidney cell line 293. These findings suggested that TRAIL caused some human cell death by way of the mitochondrial pathway. Z-LEHD-FMK prevented the decrease in colony growth of HCT116 caused by TRAIL in a colony assay. Z-LEHD-FMK prevented TRAIL-induced apoptosis in healthy human hepatocytes. According to these findings, Z-LEHD-FMK and TRAIL together selectively killed cancer cells while safeguarding healthy liver cells.
Physicochemical Properties
| Molecular Formula | C32H43FN6O10 | |
| Molecular Weight | 690.72 | |
| Exact Mass | 690.302 | |
| Elemental Analysis | C, 55.64; H, 6.28; F, 2.75; N, 12.17; O, 23.16 | |
| CAS # | 210345-04-3 | |
| Related CAS # | Z-LEHD-FMK TFA;524746-03-0 | |
| PubChem CID | 10032582 | |
| Appearance | White to yellow solid powder | |
| LogP | 2.366 | |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 5 | |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 12 | |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 23 | |
| Heavy Atom Count | 49 | |
| Complexity | 1140 | |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 4 | |
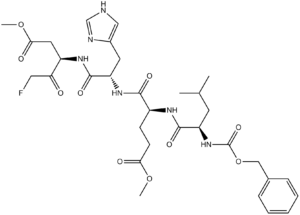
| SMILES | FCC([C@H](CC(=O)OC)NC([C@H](CC1=CN=CN1)NC([C@H](CCC(=O)OC)NC([C@H](CC(C)C)NC(=O)OCC1C=CC=CC=1)=O)=O)=O)=O |
|
| InChi Key | YXRKBEPGVHOXSV-QORCZRPOSA-N | |
| InChi Code | InChI=1S/C32H43FN6O10/c1-19(2)12-24(39-32(46)49-17-20-8-6-5-7-9-20)30(44)36-22(10-11-27(41)47-3)29(43)38-25(13-21-16-34-18-35-21)31(45)37-23(26(40)15-33)14-28(42)48-4/h5-9,16,18-19,22-25H,10-15,17H2,1-4H3,(H,34,35)(H,36,44)(H,37,45)(H,38,43)(H,39,46)/t22-,23-,24-,25-/m0/s1 | |
| Chemical Name | methyl (4S)-5-[[(2S)-1-[[(3S)-5-fluoro-1-methoxy-1,4-dioxopentan-3-yl]amino]-3-(1H-imidazol-5-yl)-1-oxopropan-2-yl]amino]-4-[[(2S)-4-methyl-2-(phenylmethoxycarbonylamino)pentanoyl]amino]-5-oxopentanoate | |
| Synonyms |
|
|
| HS Tariff Code | 2934.99.9001 | |
| Storage |
Powder-20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month Note: Please store this product in a sealed and protected environment, avoid exposure to moisture. |
|
| Shipping Condition | Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs) |
Biological Activity
| Targets |
|
|
| ln Vitro | Z-LEHD-FMK (20 μM; pretreated for 30 min) completely protects HCT116 and 293 cells from TRAIL-induced toxicity[1]. Z-LEHD-FMK (20 μM ; 6 h) guards against TRAIL-induced apoptosis in healthy human hepatocytes[1]. | |
| ln Vivo | In rats with spinal cord injury (SCI), Z-LEHD-FMK (0.8 μmol/kg; i.v. for 7 days) protects neurons, glia, myelin, axons, and intracellular organelles[2]. | |
| Cell Assay | Z-IETD-FMK (caspase 8 inhibitor), Z-LEHD-FMK (caspase 9 inhibitor), Z-VDAVD-FMK (caspase 2 inhibitor), and Z-AEVD-FMK (caspase 10 inhibitor; 20 m each) were pretreated for 2 hours before TRAIL (50 ng/ml) was added to HCT116 and SW480 cells (as indicated). Extracts were gathered and checked for the expression of various proteins using Western blotting after 4 hours (or 16 hours for caspase 3 activation) of TRAIL exposure. | |
| References |
[1]. The caspase 9 inhibitor Z-LEHD-FMK protects human liver cells while permitting death of cancer cells exposed to tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand. Cancer Res. 2000 Nov 15; 60(22): 6259-65. [2]. Neuroprotection and functional recovery after application of the caspase-9 inhibitor z-LEHD-fmk in a rat model of traumatic spinal cord injury. J Neurosurg Spine. 2005 Mar; 2(3): 327-34. [3]. Caspase inhibition and limitation of myocardial infarct size: protection against lethal reperfusion injury. Br J Pharmacol. 2000 May; 130(2): 197-200. |
Solubility Data
| Solubility (In Vitro) |
|
|||
| Solubility (In Vivo) |
Note: Listed below are some common formulations that may be used to formulate products with low water solubility (e.g. < 1 mg/mL), you may test these formulations using a minute amount of products to avoid loss of samples. Injection Formulations (e.g. IP/IV/IM/SC) Injection Formulation 1: DMSO : Tween 80: Saline = 10 : 5 : 85 (i.e. 100 μL DMSO stock solution → 50 μL Tween 80 → 850 μL Saline) *Preparation of saline: Dissolve 0.9 g of sodium chloride in 100 mL ddH ₂ O to obtain a clear solution. Injection Formulation 2: DMSO : PEG300 :Tween 80 : Saline = 10 : 40 : 5 : 45 (i.e. 100 μL DMSO → 400 μLPEG300 → 50 μL Tween 80 → 450 μL Saline) Injection Formulation 3: DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90 (i.e. 100 μL DMSO → 900 μL Corn oil) Example: Take the Injection Formulation 3 (DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90) as an example, if 1 mL of 2.5 mg/mL working solution is to be prepared, you can take 100 μL 25 mg/mL DMSO stock solution and add to 900 μL corn oil, mix well to obtain a clear or suspension solution (2.5 mg/mL, ready for use in animals). Injection Formulation 4: DMSO : 20% SBE-β-CD in saline = 10 : 90 [i.e. 100 μL DMSO → 900 μL (20% SBE-β-CD in saline)] *Preparation of 20% SBE-β-CD in Saline (4°C,1 week): Dissolve 2 g SBE-β-CD in 10 mL saline to obtain a clear solution. Injection Formulation 5: 2-Hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin : Saline = 50 : 50 (i.e. 500 μL 2-Hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin → 500 μL Saline) Injection Formulation 6: DMSO : PEG300 : castor oil : Saline = 5 : 10 : 20 : 65 (i.e. 50 μL DMSO → 100 μLPEG300 → 200 μL castor oil → 650 μL Saline) Injection Formulation 7: Ethanol : Cremophor : Saline = 10: 10 : 80 (i.e. 100 μL Ethanol → 100 μL Cremophor → 800 μL Saline) Injection Formulation 8: Dissolve in Cremophor/Ethanol (50 : 50), then diluted by Saline Injection Formulation 9: EtOH : Corn oil = 10 : 90 (i.e. 100 μL EtOH → 900 μL Corn oil) Injection Formulation 10: EtOH : PEG300:Tween 80 : Saline = 10 : 40 : 5 : 45 (i.e. 100 μL EtOH → 400 μLPEG300 → 50 μL Tween 80 → 450 μL Saline) Oral Formulations Oral Formulation 1: Suspend in 0.5% CMC Na (carboxymethylcellulose sodium) Oral Formulation 2: Suspend in 0.5% Carboxymethyl cellulose Example: Take the Oral Formulation 1 (Suspend in 0.5% CMC Na) as an example, if 100 mL of 2.5 mg/mL working solution is to be prepared, you can first prepare 0.5% CMC Na solution by measuring 0.5 g CMC Na and dissolve it in 100 mL ddH2O to obtain a clear solution; then add 250 mg of the product to 100 mL 0.5% CMC Na solution, to make the suspension solution (2.5 mg/mL, ready for use in animals). Oral Formulation 3: Dissolved in PEG400 Oral Formulation 4: Suspend in 0.2% Carboxymethyl cellulose Oral Formulation 5: Dissolve in 0.25% Tween 80 and 0.5% Carboxymethyl cellulose Oral Formulation 6: Mixing with food powders Note: Please be aware that the above formulations are for reference only. InvivoChem strongly recommends customers to read literature methods/protocols carefully before determining which formulation you should use for in vivo studies, as different compounds have different solubility properties and have to be formulated differently. (Please use freshly prepared in vivo formulations for optimal results.) |
| Preparing Stock Solutions | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 1.4478 mL | 7.2388 mL | 14.4776 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.2896 mL | 1.4478 mL | 2.8955 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.1448 mL | 0.7239 mL | 1.4478 mL |