Physicochemical Properties
| Molecular Formula | C17H18BR2N2O |
| Molecular Weight | 426.15 |
| Exact Mass | 423.978 |
| Elemental Analysis | C, 47.91; H, 4.26; Br, 37.50; N, 6.57; O, 3.75 |
| CAS # | 253449-04-6 |
| PubChem CID | 2775510 |
| Appearance | White to off-white solid powder |
| Density | 1.6±0.1 g/cm3 |
| Boiling Point | 320.2±22.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 153-155ºC |
| Flash Point | 147.4±22.3 °C |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±0.7 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.657 |
| LogP | 5.65 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 1 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 2 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 4 |
| Heavy Atom Count | 22 |
| Complexity | 356 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| InChi Key | XUBJEDZHBUPBKL-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| InChi Code | InChI=1S/C17H18Br2N2O/c1-20(2)9-13(22)10-21-16-5-3-11(18)7-14(16)15-8-12(19)4-6-17(15)21/h3-8,13,22H,9-10H2,1-2H3 |
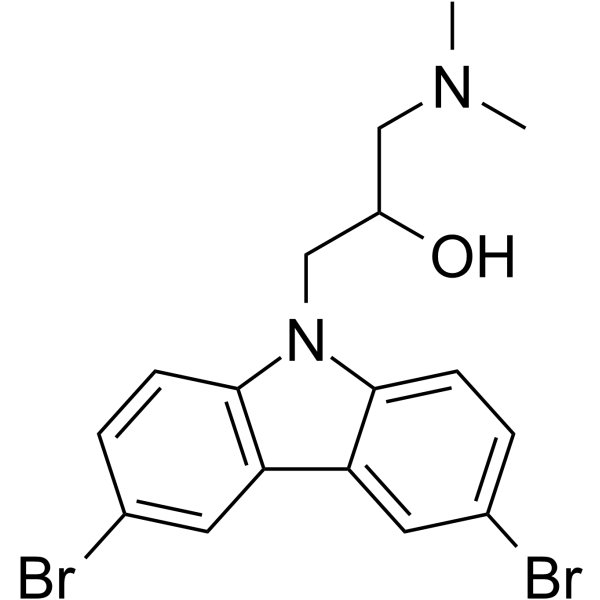
| Chemical Name | 1-(3,6-dibromocarbazol-9-yl)-3-(dimethylamino)propan-2-ol |
| Synonyms | Wiskostatin; 253449-04-6; 1-(3,6-dibromo-9H-carbazol-9-yl)-3-(dimethylamino)propan-2-ol; 1-(3,6-dibromocarbazol-9-yl)-3-(dimethylamino)propan-2-ol; CHEBI:78012; C17H18Br2N2O; MFCD00218393; Maybridge1_002006; |
| HS Tariff Code | 2934.99.9001 |
| Storage |
Powder-20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
| Shipping Condition | Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs) |
Biological Activity
| Targets | Neuronal Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome protein (N-WASP)-mediated actin polymerization |
| ln Vitro | Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome protein (WASP) and WAVE stimulate actin-related protein (Arp)2/3-mediated actin polymerization, leading to diverse downstream effects, including the formation and remodeling of cell surface protrusions, modulation of cell migration, and intracytoplasmic propulsion of organelles and pathogens. Selective inhibitors of individual Arp2/3 activators would enable more exact dissection of WASP- and WAVE-dependent cellular pathways and are potential therapeutic targets for viral pathogenesis. Wiskostatin is a recently described chemical inhibitor that selectively inhibits neuronal WASP (N-WASP)-mediated actin polymerization in vitro. A growing number of recent studies have utilized this drug in vivo to uncover novel cellular functions for N-WASP; however, the selectivity of wiskostatin in intact cells has not been carefully explored. In the current studies with this drug, researchers observed rapid and dose-dependent inhibition of N-WASP-dependent membrane trafficking steps. Additionally, however, researchers found that addition of wiskostatin inhibited numerous other cellular functions that are not believed to be N-WASP dependent. Further studies revealed that wiskostatin treatment caused a rapid, profound, and irreversible decrease in cellular ATP levels, consistent with its global effects on cell function. The above data caution against the use of this drug as a selective perturbant of N-WASP-dependent actin dynamics in vivo[1]. |
| Enzyme Assay | Wiskostatin (1-(3,6-dibromo-9H-carbazol-9-yl)-3-(dimethylamino)propan-2-ol) (1) is a carbazole-based compound reported as a specific and relatively potent inhibitor of the N-WASP actin remodelling complex (S-isomer EC50 = 4.35 μM; R-isomer EC50 = 3.44 μM). An NMR solution structure showed that wiskostatin interacts with a cleft in the regulatory GTPase binding domain of N-WASP. However, numerous studies have reported wiskostatin's actions on membrane transport and cytokinesis that are independent of the N-WASP-Arp2/3 complex pathway, but offer limited alternative explanation. The large GTPase, dynamin has established functional roles in these pathways. This study reveals that wiskostatin and its analogues, as well as other carbazole-based compounds, are inhibitors of helical dynamin GTPase activity and endocytosis. We characterise the effects of wiskostatin on in vitro dynamin GTPase activity, in-cell endocytosis, and determine the importance of wiskostatin functional groups on these activities through design and synthesis of libraries of wiskostatin analogues. We also examine whether other carbazole-based scaffolds frequently used in research or the clinic also modulate dynamin and endocytosis. Understanding off-targets for compounds used as research tools is important to be able to confidently interpret their action on biological systems, particularly when the target and off-targets affect overlapping mechanisms (e.g. cytokinesis and endocytosis). Herein we demonstrate that wiskostatin is a dynamin inhibitor (IC50 20.7 ± 1.2 μM) and a potent inhibitor of clathrin mediated endocytosis (IC50 = 6.9 ± 0.3 μM). Synthesis of wiskostatin analogues gave rise to 1-(9H-carbazol-9-yl)-3-((4-methylbenzyl)amino)propan-2-ol (35) and 1-(9H-carbazol-9-yl)-3-((4-chlorobenzyl)amino)propan-2-ol (43) as potent dynamin inhibitors (IC50 = 1.0 ± 0.2 μM), and (S)-1-(3,6-dibromo-9H-carbazol-9-yl)-3-(dimethylamino)propan-2-ol (8a) and (R)-1-(3,6-dibromo-9H-carbazol-9-yl)-3-(dimethylamino)propan-2-ol (8b) that are amongst the most potent inhibitors of clathrin mediated endocytosis yet reported (IC50 = 2.3 ± 3.3 and 2.1 ± 1.7 μM, respectively).https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/36577213/ |
| References |
[1]. N-WASP inhibitor wiskostatin nonselectively perturbs membrane transport by decreasing cellular ATP levels. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2007;292(4):C1562-C1566. |
| Additional Infomation | 1-(3,6-dibromocarbazol-9-yl)-3-(dimethylamino)propan-2-ol is a member of the class of carbazoles that is 1-(carbazol-9-yl)-3-(dimethylamino)propan-2-ol bearing two additional bromo substituents at positions 3 and 6 on the carbazole ring system. It is a member of carbazoles, an organobromine compound, a secondary alcohol and a tertiary amino compound. |
Solubility Data
| Solubility (In Vitro) | DMSO : ~25 mg/mL (~58.66 mM) |
| Solubility (In Vivo) |
Solubility in Formulation 1: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (5.87 mM) (saturation unknown) in 10% DMSO + 90% Corn Oil (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), clear solution. For example, if 1 mL of working solution is to be prepared, you can add 100 μL of 25.0 mg/mL clear DMSO stock solution to 900 μL of corn oil and mix evenly. (Please use freshly prepared in vivo formulations for optimal results.) |
| Preparing Stock Solutions | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.3466 mL | 11.7330 mL | 23.4659 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.4693 mL | 2.3466 mL | 4.6932 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.2347 mL | 1.1733 mL | 2.3466 mL |