Physicochemical Properties
| Molecular Formula | C25H27N3O3S |
| Molecular Weight | 449.57 |
| Exact Mass | 449.177 |
| CAS # | 228544-65-8 |
| PubChem CID | 9933427 |
| Appearance | Light yellow to yellow solid powder |
| LogP | 8.306 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 2 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 4 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 6 |
| Heavy Atom Count | 32 |
| Complexity | 592 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| InChi Key | XFFITGBWVLQNCD-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| InChi Code | InChI=1S/C25H27N3O3S/c1-16(2)22-6-5-7-23(17(3)4)24(22)27-25(29)26-18-8-12-20(13-9-18)32-21-14-10-19(11-15-21)28(30)31/h5-17H,1-4H3,(H2,26,27,29) |
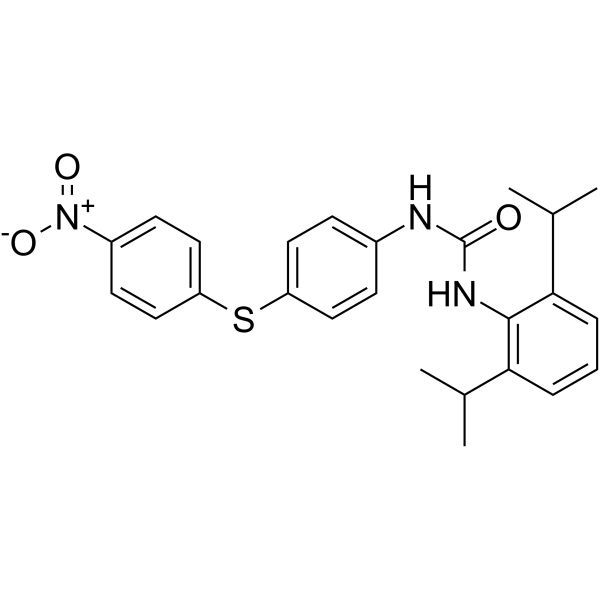
| Chemical Name | 1-[2,6-di(propan-2-yl)phenyl]-3-[4-(4-nitrophenyl)sulfanylphenyl]urea |
| HS Tariff Code | 2934.99.9001 |
| Storage |
Powder-20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
| Shipping Condition | Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs) |
Biological Activity
| Targets | ACAT |
| ln Vitro | When HepG2 cells are subjected to hypoxia, VULM1457 (0.03 and 0.1 µM) dramatically down-regulates particular AM receptors on the cells, resulting in decreased AM secretion[1]. Cell growth brought on by AM is negatively regulated by VULM1457[1]. When HepG2 cells are preincubated with VULM1457 (0.1 µM), the overall number of particular [125I]AM bindings found on the cells at unaffected affinity is greatly decreased. HepG2 cells' properties of AM binding are considerably altered when high doses of VULM1457 (1.0 and 10.0 µM) are preincubated with them[1]. HepG2 cells that are hypoxic (BmaxHypox = 127±10, KD = 0.06±0.11 nM) exhibit a considerable reduction in specific [125I]AM binding upon preincubation with VULM1457 (0.1 µM). Higher doses of VULM1457 (1.0 and 10.0 µM) result in a reduction in the total number of cells, while preincubation with VULM1457 (0.1 µM) considerably increases the number of cells (24.2±6%). The decreases in [125I]AM specific binding to HepG2 cells are significantly reduced at high concentrations of VULM1457 (1.0 and 10.0 µM)[1]. |
| ln Vivo | In animal models of experimental atherosclerosis, VULM 1457 dramatically lowers atherogenic activity[1]. In vivo ischaemia/reperfusion damage to the hearts of diabetic-hypercholesterolemic rats is prevented by VULM 1457[2]. Plasma total cholesterol levels are dramatically reduced by VULM 1457 (50 mg/kg/day; added as an admixture to the fat-cholesterol diet for 5 days) (1.7±0.1 mM vs. 2.9±0.5 mM in diabetic–hypercholesterolaemic animals). In the liver of DM-HCH rats, VULM 1457 similarly has a hypolipidaemic impact (3.9±0.2 mg/g vs. 7.4±1.0 mg/g)[2]. |
| Animal Protocol |
Animal/Disease Models: Male Wistar rats (250-300 g body weight), fed a standard diet and tap water ad libitum[2] Doses: 50 mg/kg/day Route of Administration: Administered as an admixture to the fat-cholesterol diet for 5 days Experimental Results: Improved the overall myocardial ischaemia-reperfusion injury outcomes in the diabetic-hypercholesterolaemic rats by suppressing arrhythmogenesis as well as by reducing myocardial necrosis, aside from remarkable hypolipidaemic activity. |
| References |
[1]. The ACAT inhibitor VULM1457 significantly reduced production and secretion of adrenomedullin (AM) and down-regulated AM receptors on human hepatoblastic cells. Gen Physiol Biophys. 2005 Dec;24(4):397-409. [2]. The myocardial infarct size-limiting and antiarrhythmic effects of acyl-CoA:cholesterol acyltransferase inhibitor VULM 1457 protect the hearts of diabetic-hypercholesterolaemic rats against ischaemia/reperfusion injury both in vitro and. |
Solubility Data
| Solubility (In Vitro) | DMSO: 250 mg/mL (556.09 mM) |
| Solubility (In Vivo) |
Note: Listed below are some common formulations that may be used to formulate products with low water solubility (e.g. < 1 mg/mL), you may test these formulations using a minute amount of products to avoid loss of samples. Injection Formulations (e.g. IP/IV/IM/SC) Injection Formulation 1: DMSO : Tween 80: Saline = 10 : 5 : 85 (i.e. 100 μL DMSO stock solution → 50 μL Tween 80 → 850 μL Saline) *Preparation of saline: Dissolve 0.9 g of sodium chloride in 100 mL ddH ₂ O to obtain a clear solution. Injection Formulation 2: DMSO : PEG300 :Tween 80 : Saline = 10 : 40 : 5 : 45 (i.e. 100 μL DMSO → 400 μLPEG300 → 50 μL Tween 80 → 450 μL Saline) Injection Formulation 3: DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90 (i.e. 100 μL DMSO → 900 μL Corn oil) Example: Take the Injection Formulation 3 (DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90) as an example, if 1 mL of 2.5 mg/mL working solution is to be prepared, you can take 100 μL 25 mg/mL DMSO stock solution and add to 900 μL corn oil, mix well to obtain a clear or suspension solution (2.5 mg/mL, ready for use in animals). Injection Formulation 4: DMSO : 20% SBE-β-CD in saline = 10 : 90 [i.e. 100 μL DMSO → 900 μL (20% SBE-β-CD in saline)] *Preparation of 20% SBE-β-CD in Saline (4°C,1 week): Dissolve 2 g SBE-β-CD in 10 mL saline to obtain a clear solution. Injection Formulation 5: 2-Hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin : Saline = 50 : 50 (i.e. 500 μL 2-Hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin → 500 μL Saline) Injection Formulation 6: DMSO : PEG300 : castor oil : Saline = 5 : 10 : 20 : 65 (i.e. 50 μL DMSO → 100 μLPEG300 → 200 μL castor oil → 650 μL Saline) Injection Formulation 7: Ethanol : Cremophor : Saline = 10: 10 : 80 (i.e. 100 μL Ethanol → 100 μL Cremophor → 800 μL Saline) Injection Formulation 8: Dissolve in Cremophor/Ethanol (50 : 50), then diluted by Saline Injection Formulation 9: EtOH : Corn oil = 10 : 90 (i.e. 100 μL EtOH → 900 μL Corn oil) Injection Formulation 10: EtOH : PEG300:Tween 80 : Saline = 10 : 40 : 5 : 45 (i.e. 100 μL EtOH → 400 μLPEG300 → 50 μL Tween 80 → 450 μL Saline) Oral Formulations Oral Formulation 1: Suspend in 0.5% CMC Na (carboxymethylcellulose sodium) Oral Formulation 2: Suspend in 0.5% Carboxymethyl cellulose Example: Take the Oral Formulation 1 (Suspend in 0.5% CMC Na) as an example, if 100 mL of 2.5 mg/mL working solution is to be prepared, you can first prepare 0.5% CMC Na solution by measuring 0.5 g CMC Na and dissolve it in 100 mL ddH2O to obtain a clear solution; then add 250 mg of the product to 100 mL 0.5% CMC Na solution, to make the suspension solution (2.5 mg/mL, ready for use in animals). Oral Formulation 3: Dissolved in PEG400 Oral Formulation 4: Suspend in 0.2% Carboxymethyl cellulose Oral Formulation 5: Dissolve in 0.25% Tween 80 and 0.5% Carboxymethyl cellulose Oral Formulation 6: Mixing with food powders Note: Please be aware that the above formulations are for reference only. InvivoChem strongly recommends customers to read literature methods/protocols carefully before determining which formulation you should use for in vivo studies, as different compounds have different solubility properties and have to be formulated differently. (Please use freshly prepared in vivo formulations for optimal results.) |
| Preparing Stock Solutions | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.2243 mL | 11.1217 mL | 22.2435 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.4449 mL | 2.2243 mL | 4.4487 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.2224 mL | 1.1122 mL | 2.2243 mL |