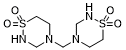
Taurolidine, synthetic taurine analog, is a potent and broad-spectrum antimicrobial agent with antimicrobial and anti-neoplastic activities and is used for the prevention of central venous catheter-related infections. Taurolidine has a direct and specific antineoplastic effect on brain tumor cells by the induction of apoptosis. Taurolidine and its metabolites mimic mannose by binding to the extracellular wall of bacteria, blocking adherence to epithelial and fibroblast cells. In addition to modulating immunoregulatory systems, taurolidine induces autophagy, apoptosis, and necrosis in human cancer cells. It produces cell death in malignant mesothelioma cells by oxidative stress in concert with inhibition of Akt signaling. Taurolidine, heparin (Defencath) was approved in 2023 by FDA for treating Incidence of catheter-related bloodstream infections, as a Thiadiazinane antimicrobial plus an anticoagulant.
Physicochemical Properties
| Molecular Formula | C7H16N4O4S2 |
| Molecular Weight | 284.3563 |
| Exact Mass | 284.061 |
| Elemental Analysis | C, 29.57; H, 5.67; N, 19.70; O, 22.51; S, 22.55 |
| CAS # | 19388-87-5 |
| PubChem CID | 29566 |
| Appearance | Solid powder |
| Density | 1.5±0.1 g/cm3 |
| Boiling Point | 471.2±55.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 156ºC |
| Flash Point | 238.8±31.5 °C |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±1.2 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.564 |
| LogP | -2.55 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 2 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 8 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 2 |
| Heavy Atom Count | 17 |
| Complexity | 419 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| SMILES | S1(C([H])([H])C([H])([H])N(C([H])([H])N1[H])C([H])([H])N1C([H])([H])N([H])S(C([H])([H])C1([H])[H])(=O)=O)(=O)=O |
| InChi Key | AJKIRUJIDFJUKJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| InChi Code | InChI=1S/C7H16N4O4S2/c12-16(13)3-1-10(5-8-16)7-11-2-4-17(14,15)9-6-11/h8-9H,1-7H2 |
| Chemical Name | 4,4'-methylenebis(1,2,4-thiadiazinane 1,1-dioxide) |
| Synonyms | Taurolidine, heparin (Defencath) |
| HS Tariff Code | 2934.99.9001 |
| Storage |
Powder-20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
| Shipping Condition | Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs) |
Biological Activity
| ADME/Pharmacokinetics |
Metabolism / Metabolites In an aqueous solution, taurolidine exists in an equilibrium with taurultam, which is subsequently metabolized to taurinamide. Both taurultam and taurinamide contribute to the antimicrobial activity of taurolidine. |
| References |
[1]. Taurolidine, an antiseptic for the prevention of central venous catheter-related infections. Rev Chilena Infectol. 2019 Aug;36(4):414-420. [2]. Treatment of glioblastoma with intravenous taurolidine. First clinical experience. Anticancer Res. 2004 Mar-Apr;24(2C):1143-7. |
| Additional Infomation |
Taurolidine is a member of the class of thiadiazinanes that is 1,2,4-thiadiazinane 1,1-dioxide substituted by a (1,1-dioxido-1,2,4-thiadiazinan-4-yl)methyl group at position 4. It is a broad-spectrum antiseptic used as lock therapy solution in patients with long term central venous catheters for the prevention of catheter related bloodstream infections. It has a role as an antibacterial agent, an anti-inflammatory agent, an antifungal agent, an antiseptic drug and an antineoplastic agent. It is a thiadiazinane and a sulfone. Taurolidine is an antimicrobial used for the prevention of catheter-related infections. It is a derivative of the amino acid [taurine]. It was first synthesized in the 1970s and was originally used as a prophylactic against intraperitoneal bacterial infections in patients with peritonitis. In November 2023, a catheter lock solution of taurolidine in combination with [heparin] - marketed as Defencath - received FDA approval under the Limited Population Pathway for Antibacterial and Antifungal Drugs (LPAD pathway) for the prevention of catheter-related bloodstream infections in a limited and specific patient population. Taurolidine is a synthetic broad-spectrum antimicrobial with antibacterial, antifungal, anticoagulant, and potential antiangiogenic activities. Taurolidine, derived from the amino acid taurine, binds to and neutralizes bacterial exotoxins and endotoxins, or lipopolysaccharides (LPS). Taurolidine binding to LPS prevents bacterial adherence to host epithelial cells, thereby prevents bacterial invasion of uninfected host cells. Although the mechanism underlying its antineoplastic activity has not been fully elucidated, it may be related to this agent's anti-adherence property. In addition, taurolidine also promotes apoptosis by inducing various apoptotic factors and suppresses the production of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF), a protein that plays an important role in angiogenesis. Drug Indication Taurolidine is indicated in combination with [heparin] to reduce the incidence of catheter-related bloodstream infections (CRBSI) in adult patients with kidney failure receiving chronic hemodialysis (HD) through a central venous catheter (CVC). Mechanism of Action Taurolidine is a broad-spectrum antimicrobial with activity against both Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria, in addition to mycobacteria and certain strains of fungi. The mechanism of action of taurolidine and its active metabolites is non-specific and involves the irreversible binding of its methylol groups to microbial cell walls, resulting in a subsequent loss of cell wall integrity and eventual cell death. In addition, it appears to reduce bacterial adhesion to mammalian cells and neutralize bacterial endo- and exotoxins. |
Solubility Data
| Solubility (In Vitro) | DMSO : ~62.5 mg/mL (~219.80 mM) |
| Solubility (In Vivo) |
Solubility in Formulation 1: ≥ 2.08 mg/mL (7.31 mM) (saturation unknown) in 10% DMSO + 40% PEG300 + 5% Tween80 + 45% Saline (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), clear solution. For example, if 1 mL of working solution is to be prepared, you can add 100 μL of 20.8 mg/mL clear DMSO stock solution to 400 μL PEG300 and mix evenly; then add 50 μL Tween-80 to the above solution and mix evenly; then add 450 μL normal saline to adjust the volume to 1 mL. Preparation of saline: Dissolve 0.9 g of sodium chloride in 100 mL ddH₂ O to obtain a clear solution. Solubility in Formulation 2: ≥ 2.08 mg/mL (7.31 mM) (saturation unknown) in 10% DMSO + 90% (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline) (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), clear solution. For example, if 1 mL of working solution is to be prepared, you can add 100 μL of 20.8 mg/mL clear DMSO stock solution to 900 μL of 20% SBE-β-CD physiological saline solution and mix evenly. Preparation of 20% SBE-β-CD in Saline (4°C,1 week): Dissolve 2 g SBE-β-CD in 10 mL saline to obtain a clear solution. Solubility in Formulation 3: ≥ 2.08 mg/mL (7.31 mM) (saturation unknown) in 10% DMSO + 90% Corn Oil (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), clear solution. For example, if 1 mL of working solution is to be prepared, you can add 100 μL of 20.8 mg/mL clear DMSO stock solution to 900 μL of corn oil and mix evenly. (Please use freshly prepared in vivo formulations for optimal results.) |
| Preparing Stock Solutions | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 3.5167 mL | 17.5833 mL | 35.1667 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.7033 mL | 3.5167 mL | 7.0333 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.3517 mL | 1.7583 mL | 3.5167 mL |