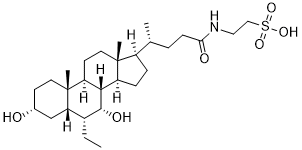
Tauro-Obeticholic acid is an active metabolite of Obeticholic acid (Ocaliva; 6-ECDCA; INT747; 6-Ethylchenodeoxycholic acid) formed by conjugating with taurine, or 2-aminoethanesulfonic acid. Obeticholic acid is a farnesoid X receptor (FXR) agonist and semisynthetic bile acid analog (derivative of chenodeoxycholic acid) approved by FDA in 2016 to treat primary biliary cholangitis. Tauro-obeticholic acid is produced in vivo from obeticholic acid by taurine conjugation in the liver but can be reconverted back to obeticholic acid by intestinal microflora.
Physicochemical Properties
| Molecular Formula | C28H49NO6S |
| Molecular Weight | 527.756767988205 |
| Exact Mass | 527.328 |
| Elemental Analysis | C, 63.72; H, 9.36; N, 2.65; O, 18.19; S, 6.07 |
| CAS # | 863239-61-6 |
| Related CAS # | Tauro-obeticholic acid-d5 sodium |
| PubChem CID | 122201312 |
| Appearance | White to yellow solid powder |
| LogP | 4.3 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 4 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 6 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 8 |
| Heavy Atom Count | 36 |
| Complexity | 904 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 11 |
| SMILES | C[C@]12CC[C@@H](O)C[C@H]1[C@@H](CC)[C@@H](O)[C@H]1[C@@H]3CC[C@H]([C@H](C)CCC(=O)NCCS(O)(=O)=O)[C@]3(CC[C@H]21)C |
| InChi Key | JEZXQTZLWHAKAC-NQGMLVFVSA-N |
| InChi Code | InChI=1S/C28H49NO6S/c1-5-19-23-16-18(30)10-12-28(23,4)22-11-13-27(3)20(7-8-21(27)25(22)26(19)32)17(2)6-9-24(31)29-14-15-36(33,34)35/h17-23,25-26,30,32H,5-16H2,1-4H3,(H,29,31)(H,33,34,35)/t17-,18-,19-,20-,21+,22+,23+,25+,26-,27-,28-/m1/s1 |
| Chemical Name | 2-[[(4R)-4-[(3R,5S,6R,7R,8S,9S,10S,13R,14S,17R)-6-ethyl-3,7-dihydroxy-10,13-dimethyl-2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,11,12,14,15,16,17-tetradecahydro-1H-cyclopenta[a]phenanthren-17-yl]pentanoyl]amino]ethanesulfonic acid |
| Synonyms | Tauro-Obeticholic acid; Tauro-Obeticholic acid; 863239-61-6; 6-Etcdca; Obeticholic acid metabolite UPF-1443; T5IG4XE90K; UNII-T5IG4XE90K; Ethanesulfonic acid,2-[[(3a,5b,6a,7a)-6-ethyl-3,7-dihydroxy-24-oxocholan-24-yl]amino]-; 2-[[(4R)-4-[(3R,5S,6R,7R,8S,9S,10S,13R,14S,17R)-6-ethyl-3,7-dihydroxy-10,13-dimethyl-2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,11,12,14,15,16,17-tetradecahydro-1H-cyclopenta[a]phenanthren-17-yl]pentanoyl]amino]ethanesulfonic acid; Tauro Obeticholic acid |
| HS Tariff Code | 2934.99.9001 |
| Storage |
Powder-20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month Note: (1). This product requires protection from light (avoid light exposure) during transportation and storage.(2). Please store this product in a sealed and protected environment (e.g. under nitrogen), avoid exposure to moisture. |
| Shipping Condition | Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs) |
Biological Activity
| Targets | Active metabolite of obeticholic acid; FXR |
| ln Vitro | Microorganisms in the ileum and colon can cleave taurobeticholic acid and transform it into the parent drug, which can subsequently be reabsorbed or expelled in the feces. Obeticholic acid interacts with taurine in the liver to create taurobeticholic acid, which is secreted into the bile [1]. |
| References |
[1]. Obeticholic Acid: First Global Approval. Drugs. 2016 Aug;76(12):1221-6. |
| Additional Infomation | Obeticholic acid (Ocaliva(TM)) is a farnesoid-X receptor (FXR) agonist that is being developed by Intercept Pharmaceuticals for the treatment of various liver diseases, and has recently been granted accelerated approval in the USA for the treatment of primary biliary cholangitis in combination with ursodeoxycholic acid in adults with an inadequate response to ursodeoxycholic acid, or as monotherapy in adults unable to tolerate ursodeoxycholic acid. The drug is in preregistration for this indication in the EU. This article summarizes the milestones in the development of obeticholic acid leading to this first approval for primary biliary cholangitis.[1] |
Solubility Data
| Solubility (In Vitro) | May dissolve in DMSO (in most cases), if not, try other solvents such as H2O, Ethanol, or DMF with a minute amount of products to avoid loss of samples |
| Solubility (In Vivo) |
Note: Listed below are some common formulations that may be used to formulate products with low water solubility (e.g. < 1 mg/mL), you may test these formulations using a minute amount of products to avoid loss of samples. Injection Formulations (e.g. IP/IV/IM/SC) Injection Formulation 1: DMSO : Tween 80: Saline = 10 : 5 : 85 (i.e. 100 μL DMSO stock solution → 50 μL Tween 80 → 850 μL Saline) *Preparation of saline: Dissolve 0.9 g of sodium chloride in 100 mL ddH ₂ O to obtain a clear solution. Injection Formulation 2: DMSO : PEG300 :Tween 80 : Saline = 10 : 40 : 5 : 45 (i.e. 100 μL DMSO → 400 μLPEG300 → 50 μL Tween 80 → 450 μL Saline) Injection Formulation 3: DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90 (i.e. 100 μL DMSO → 900 μL Corn oil) Example: Take the Injection Formulation 3 (DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90) as an example, if 1 mL of 2.5 mg/mL working solution is to be prepared, you can take 100 μL 25 mg/mL DMSO stock solution and add to 900 μL corn oil, mix well to obtain a clear or suspension solution (2.5 mg/mL, ready for use in animals). Injection Formulation 4: DMSO : 20% SBE-β-CD in saline = 10 : 90 [i.e. 100 μL DMSO → 900 μL (20% SBE-β-CD in saline)] *Preparation of 20% SBE-β-CD in Saline (4°C,1 week): Dissolve 2 g SBE-β-CD in 10 mL saline to obtain a clear solution. Injection Formulation 5: 2-Hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin : Saline = 50 : 50 (i.e. 500 μL 2-Hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin → 500 μL Saline) Injection Formulation 6: DMSO : PEG300 : castor oil : Saline = 5 : 10 : 20 : 65 (i.e. 50 μL DMSO → 100 μLPEG300 → 200 μL castor oil → 650 μL Saline) Injection Formulation 7: Ethanol : Cremophor : Saline = 10: 10 : 80 (i.e. 100 μL Ethanol → 100 μL Cremophor → 800 μL Saline) Injection Formulation 8: Dissolve in Cremophor/Ethanol (50 : 50), then diluted by Saline Injection Formulation 9: EtOH : Corn oil = 10 : 90 (i.e. 100 μL EtOH → 900 μL Corn oil) Injection Formulation 10: EtOH : PEG300:Tween 80 : Saline = 10 : 40 : 5 : 45 (i.e. 100 μL EtOH → 400 μLPEG300 → 50 μL Tween 80 → 450 μL Saline) Oral Formulations Oral Formulation 1: Suspend in 0.5% CMC Na (carboxymethylcellulose sodium) Oral Formulation 2: Suspend in 0.5% Carboxymethyl cellulose Example: Take the Oral Formulation 1 (Suspend in 0.5% CMC Na) as an example, if 100 mL of 2.5 mg/mL working solution is to be prepared, you can first prepare 0.5% CMC Na solution by measuring 0.5 g CMC Na and dissolve it in 100 mL ddH2O to obtain a clear solution; then add 250 mg of the product to 100 mL 0.5% CMC Na solution, to make the suspension solution (2.5 mg/mL, ready for use in animals). Oral Formulation 3: Dissolved in PEG400 Oral Formulation 4: Suspend in 0.2% Carboxymethyl cellulose Oral Formulation 5: Dissolve in 0.25% Tween 80 and 0.5% Carboxymethyl cellulose Oral Formulation 6: Mixing with food powders Note: Please be aware that the above formulations are for reference only. InvivoChem strongly recommends customers to read literature methods/protocols carefully before determining which formulation you should use for in vivo studies, as different compounds have different solubility properties and have to be formulated differently. (Please use freshly prepared in vivo formulations for optimal results.) |
| Preparing Stock Solutions | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 1.8948 mL | 9.4740 mL | 18.9480 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.3790 mL | 1.8948 mL | 3.7896 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.1895 mL | 0.9474 mL | 1.8948 mL |