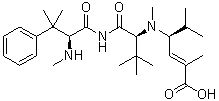
Taltobulin (HTI-286; SPA-110), an analog of the natural tripeptide hemiasterlin, is a tubulin inhibitor with anticancer activity. It inhibits the polymerization of microtubules.
Physicochemical Properties
| Molecular Formula | C27H43N3O4 |
| Molecular Weight | 473.65 |
| Exact Mass | 473.325 |
| Elemental Analysis | C, 68.47; H, 9.15; N, 8.87; O, 13.51 |
| CAS # | 228266-40-8 |
| Related CAS # | Taltobulin trifluoroacetate;228266-41-9;Taltobulin hydrochloride;(R)-Taltobulin;228266-44-2 |
| PubChem CID | 6918637 |
| Appearance | Light yellow to yellow solid powder |
| Density | 1.063g/cm3 |
| Boiling Point | 662.4ºC at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 135-137ºC |
| Flash Point | 354.4ºC |
| LogP | 4.378 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 3 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 5 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 11 |
| Heavy Atom Count | 34 |
| Complexity | 746 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 3 |
| SMILES | CC(C)(C)[C@H](NC([C@H](C(C)(C1=CC=CC=C1)C)NC)=O)C(N([C@@H](C(C)C)/C=C(C(O)=O)\C)C)=O |
| InChi Key | CNTMOLDWXSVYKD-PSRNMDMQSA-N |
| InChi Code | InChI=1S/C27H43N3O4/c1-17(2)20(16-18(3)25(33)34)30(10)24(32)22(26(4,5)6)29-23(31)21(28-9)27(7,8)19-14-12-11-13-15-19/h11-17,20-22,28H,1-10H3,(H,29,31)(H,33,34)/b18-16+/t20-,21-,22-/m1/s1 |
| Chemical Name | (E,4S)-4-[[(2S)-3,3-dimethyl-2-[[(2S)-3-methyl-2-(methylamino)-3-phenylbutanoyl]amino]butanoyl]-methylamino]-2,5-dimethylhex-2-enoic acid |
| Synonyms | SPA 110; SPA-110; HTI-286; SPA110; HTI 286; HTI286; Taltobulin |
| HS Tariff Code | 2934.99.9001 |
| Storage |
Powder-20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
| Shipping Condition | Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs) |
Biological Activity
| Targets | c-Kit (IC50 = 0.17 μM); PDGFRβ (IC50 = 0.20 μM); FLT3 (IC50 = 0.22 μM); CSF-1R (IC50 = 3.43 μM) |
| ln Vitro | Tandutinib has minimal action against MAPKs, PKC, PKA, FGFR, KDR, InsR, Src, and Abl. With an IC50 of 10-100 nM, tantutinib inhibits both FLT3-ITD autophosphorylation and IL-3-independent cell growth. Tandutinib also prevents the growth of FLT3-ITD-mutant human leukemia Ba/F3 cells, which have an IC50 of 10 nM, and FLT3-positive Molm-13 and Molm-14 cells, which have an IC50 of 30 nM. Tandutinib treatment causes a significant amount of apoptosis by 51% and 78% at 24 and 96 hours, respectively, in FLT3-ITD-positive Molm-14 cells, but not in FLT3-ITD-negative THP-1 cells. This is because of specific FLT3 inhibition.[1] Tandutinib does not alter the formation of colonies by normal human progenitor cells, but it preferentially inhibits the growth of blast colonies from FLT3 ITD-positive AML patients as opposed to ITD-negative patients.[2] |
| ln Vivo | Tandutinib, when administered orally at a dose of 60 mg/kg bid, has been shown to significantly reduce mortality in a mouse bone marrow transplantation model and to improve survival in mice harboring Ba/F3 cells expressing the W51 FLT3-ITD mutant.[1] Mice with FLT3 ITD-positive leukemia can be successfully treated with tantutinib at a dose of 180 mg/kg twice day, although this dosage has mild toxicity toward normal hematopoiesis.[2] |
| Enzyme Assay | Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays (ELISA) based on autophosphorylation of PDGFR family kinase assays are conducted on CHO cells expressing wild-type PDGFRβ, chimeric protein PDGFRβ/c-Kit, and PDGFRβ/Flt3, which contain the cytoplasmic domain of Flt-3 and c-Kit and the extracellular and transmembrane domains of PDGFRβ. Following standard tissue culture conditions, cells are grown to confluency in 96-well microtiter plates and then serum starved for 16 hours. In summary, 8 nM PDGF-BB is added to quiescent cells and incubated for 10 minutes at 37 °C after increasing the concentration of tantutinib for 30 minutes. Lysate is obtained by centrifuging the cell lysate at 15,000g for 5 minutes after it has been lysed in 100 mM Tris, pH 7.5, 750 mM NaCl, 0.5% Triton X-100, 10 mM sodium pyrophosphate, 50 mM NaF, 10 μg/mL aprotinin, 10 μg/mL leupeptin, 1 mM phenylmethylsulfonyl fluoride, and 1 mM sodium vanadate. The lysates that have been clarified are then moved into a second microtiter plate, where the wells have been coated with 500 ng/well of 1B5B11 anti-PDGFRβ mAb and allowed to sit at room temperature for two hours. Plates are incubated at 37 °C for 60 minutes after being washed three times with binding buffer (0.3% gelatin, 25 mM HEPES, pH 7.5, 100 mM NaCl, 0.01% Tween 20). Following this, 250 ng/mL of rabbit polyclonal anti-phosphotyrosine antibody is added. Then, each well is incubated with 1 μg/mL of horseradish peroxidase-conjugated anti-rabbit antibody for 60 minutes at 37 °C after being cleaned three times with binding buffer. Before adding 2,2'-azino-bis(3-ethylbenzthiazoline-6-sulfonic acid), the wells are cleaned, and the rate of substrate formation is kept track of at 650 nm. |
| Cell Assay | Tandutinib is exposed to cells at escalating concentrations (0.004-30 μM). Viable cells are counted after 3–7 days of cell growth in tissue culture, as assessed by Trypan blue dye exclusion. Cells are taken out, cleaned, and resuspended in 100 uL of binding buffer that has 140 mM NaCl, 2.5 mM CaCl2, and 10 mM HEPES (pH 7.4) in it every day. The cell suspension is mixed with 100 ng of annexin V-FITC and 250 ng of propidium iodide, and then it is incubated for 15 minutes at room temperature. Using a FACSort flow cytometer with an excitation wavelength of 488 nm, flow cytometry is carried out right after staining. The fluorescence of DNA propidium iodide staining and annexin V-FITC staining is measured at 585 nm and 515 nm, respectively. |
| Animal Protocol |
Female athymic nude (nu/nu) mice injected with Ba/F3 cells expressing W51 FLT3-ITD mutant 40-120 mg/kg/day Orally by gavage |
| References |
[1]. Cancer Cell . 2002 Jun;1(5):421-32. [2]. Blood . 2004 Nov 1;104(9):2912-8. [3]. Cell Cycle . 2009 Aug 15;8(16):2621-30. |
| Additional Infomation | Taltobulin is an analogue of the naturally occurring tripeptide hemiasterlin, with potential antimitotic and antineoplastic activities. Taltobulin binds tubulin in a similar manner as colchicine and inhibits tubulin polymerization. This results in the disruption of the cytoskeleton, ultimately leading to cell cycle arrest in G2/M phase, blockage of cell division and apoptosis. |
Solubility Data
| Solubility (In Vitro) |
Ethanol: ~100 mg/mL (~177.7 mM) DMSO: ~35 mg/mL (~62.2 mM) |
| Solubility (In Vivo) |
Solubility in Formulation 1: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (5.28 mM) (saturation unknown) in 10% DMSO + 40% PEG300 + 5% Tween80 + 45% Saline (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), clear solution. For example, if 1 mL of working solution is to be prepared, you can add 100 μL of 25.0 mg/mL clear DMSO stock solution to 400 μL PEG300 and mix evenly; then add 50 μL Tween-80 to the above solution and mix evenly; then add 450 μL normal saline to adjust the volume to 1 mL. Preparation of saline: Dissolve 0.9 g of sodium chloride in 100 mL ddH₂ O to obtain a clear solution. Solubility in Formulation 2: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (5.28 mM) (saturation unknown) in 10% DMSO + 90% (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline) (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), clear solution. For example, if 1 mL of working solution is to be prepared, you can add 100 μL of 25.0 mg/mL clear DMSO stock solution to 900 μL of 20% SBE-β-CD physiological saline solution and mix evenly. Preparation of 20% SBE-β-CD in Saline (4°C,1 week): Dissolve 2 g SBE-β-CD in 10 mL saline to obtain a clear solution. Solubility in Formulation 3: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (5.28 mM) (saturation unknown) in 10% DMSO + 90% Corn Oil (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), clear solution. For example, if 1 mL of working solution is to be prepared, you can add 100 μL of 25.0 mg/mL clear DMSO stock solution to 900 μL of corn oil and mix evenly. Solubility in Formulation 4: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (5.28 mM) (saturation unknown) in 5% DMSO + 40% PEG300 + 5% Tween80 + 50% Saline (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), clear solution. Preparation of saline: Dissolve 0.9 g of sodium chloride in 100 mL ddH₂ O to obtain a clear solution. Solubility in Formulation 5: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (5.28 mM) (saturation unknown) in 5% DMSO + 95% (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline) (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), clear solution. Preparation of 20% SBE-β-CD in Saline (4°C,1 week): Dissolve 2 g SBE-β-CD in 10 mL saline to obtain a clear solution. Solubility in Formulation 6: ≥ 0.5 mg/mL (1.06 mM) (saturation unknown) in 1% DMSO 99% Saline (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), clear solution. Preparation of saline: Dissolve 0.9 g of sodium chloride in 100 mL ddH₂ O to obtain a clear solution. Solubility in Formulation 7: 0.5% methylcellulose: 30 mg/mL (Please use freshly prepared in vivo formulations for optimal results.) |
| Preparing Stock Solutions | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.1113 mL | 10.5563 mL | 21.1126 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.4223 mL | 2.1113 mL | 4.2225 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.2111 mL | 1.0556 mL | 2.1113 mL |