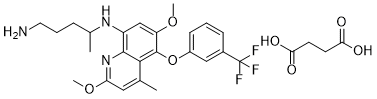
Tafenoquine succinate (formerly WR-238605; Krintafel), the succinate salt of tafenoquine, is an orally bioactive 8-aminoquinoline based anti-malarial drug approved for the treatment and prophylaxis of malaria.
Physicochemical Properties
| Molecular Formula | C28H34F3N3O7 | |
| Molecular Weight | 581.590 | |
| Exact Mass | 581.235 | |
| Elemental Analysis | C, 57.83; H, 5.89; F, 9.80; N, 7.23; O, 19.26 | |
| CAS # | 106635-81-8 | |
| Related CAS # | Tafenoquine;106635-80-7 | |
| PubChem CID | 163761 | |
| Appearance | Solid powder | |
| Density | 1.237g/cm3 | |
| Boiling Point | 565.6ºC at 760mmHg | |
| Flash Point | 295.9ºC | |
| LogP | 6.619 | |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 4 | |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 13 | |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 12 | |
| Heavy Atom Count | 41 | |
| Complexity | 690 | |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 | |
| SMILES | O=C(O)CCC(O)=O.CC(NC1=C2N=C(OC)C=C(C)C2=C(OC3=CC=CC(C(F)(F)F)=C3)C(OC)=C1)CCCN |
|
| InChi Key | CQBKFGJRAOXYIP-UHFFFAOYSA-N | |
| InChi Code | InChI=1S/C24H28F3N3O3.C4H6O4/c1-14-11-20(32-4)30-22-18(29-15(2)7-6-10-28)13-19(31-3)23(21(14)22)33-17-9-5-8-16(12-17)24(25,26)27;5-3(6)1-2-4(7)8/h5,8-9,11-13,15,29H,6-7,10,28H2,1-4H3;1-2H2,(H,5,6)(H,7,8) | |
| Chemical Name | N4-(2,6-dimethoxy-4-methyl-5-(3-(trifluoromethyl)phenoxy)quinolin-8-yl)pentane-1,4-diamine succinate | |
| Synonyms |
|
|
| HS Tariff Code | 2934.99.9001 | |
| Storage |
Powder-20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month Note: Please store this product in a sealed and protected environment, avoid exposure to moisture. |
|
| Shipping Condition | Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs) |
Biological Activity
| Targets | Anti-malarial |
| ln Vivo | When administered at the 3 mg/kg ED100 values established in WT mice, tafenoquine does not show any anti-malarial activity in CYP 2D knock-out mice. In humanized/CYP 2D6 knock-in mice, tafenoquine's anti-malarial activity is partially restored when tested at twice its ED100 (6 mg/kg)[1]. |
| Toxicity/Toxicokinetics |
Effects During Pregnancy and Lactation ◉ Summary of Use during Lactation No information is available on the use of tafenoquine during breastfeeding. Tafenoquine can cause hemolysis in patients with glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase (G6PD) deficiency. If tafenoquine is needed by the mother, testing the mother and infant for G6PD deficiency is required before the drug is given. Because the half-life of tafenoquine averages 15 days, the manufacturer recommends that breastfeeding should not breastfeed for 3 months after the dose if the infant is G6PD deficient. ◉ Effects in Breastfed Infants Relevant published information was not found as of the revision date. ◉ Effects on Lactation and Breastmilk Relevant published information was not found as of the revision date. |
| References |
[1]. Malar J. 2014 Jan 3;13:2. [2]. J Travel Med.2018 Jan 1;25(1). [3]. J Travel Med.2018 Dec 11. |
| Additional Infomation |
Tafenoquine Succinate is the succinate salt form of tafenoquine, an orally bioavailable 8-aminoquinoline derivative, with antimalarial activity. Although the mechanism is not completely understood, upon administration, tafenoquine inhibits the parasitic enzyme heme polymerase in the blood stages of the parasites. This inhibits the conversion of the toxic heme into non-toxic hemazoin, thereby resulting in the accumulation of toxic heme within the parasite. Tafenoquine is active against all the stages of Plasmodium species and is also active against the pre-erythrocytic liver stages of the parasites. This prevents the development of the erythrocytic forms of the parasite which are responsible for relapses in P. vivax malaria. See also: Tafenoquine (has active moiety). |
Solubility Data
| Solubility (In Vitro) | DMSO: ~125 mg/mL (~214.93 mM) |
| Solubility (In Vivo) |
Solubility in Formulation 1: ≥ 2.08 mg/mL (3.58 mM) (saturation unknown) in 10% DMSO + 40% PEG300 + 5% Tween80 + 45% Saline (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), clear solution. For example, if 1 mL of working solution is to be prepared, you can add 100 μL of 20.8 mg/mL clear DMSO stock solution to 400 μL PEG300 and mix evenly; then add 50 μL Tween-80 to the above solution and mix evenly; then add 450 μL normal saline to adjust the volume to 1 mL. Preparation of saline: Dissolve 0.9 g of sodium chloride in 100 mL ddH₂ O to obtain a clear solution. Solubility in Formulation 2: ≥ 2.08 mg/mL (3.58 mM) (saturation unknown) in 10% DMSO + 90% (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline) (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), clear solution. For example, if 1 mL of working solution is to be prepared, you can add 100 μL of 20.8 mg/mL clear DMSO stock solution to 900 μL of 20% SBE-β-CD physiological saline solution and mix evenly. Preparation of 20% SBE-β-CD in Saline (4°C,1 week): Dissolve 2 g SBE-β-CD in 10 mL saline to obtain a clear solution. Solubility in Formulation 3: ≥ 2.08 mg/mL (3.58 mM) (saturation unknown) in 10% DMSO + 90% Corn Oil (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), clear solution. For example, if 1 mL of working solution is to be prepared, you can add 100 μL of 20.8 mg/mL clear DMSO stock solution to 900 μL of corn oil and mix evenly. Solubility in Formulation 4: 10% DMSO+40% PEG300+5% Tween-80+45% Saline: ≥ 2.08 mg/mL (3.58 mM) (Please use freshly prepared in vivo formulations for optimal results.) |
| Preparing Stock Solutions | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 1.7194 mL | 8.5971 mL | 17.1942 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.3439 mL | 1.7194 mL | 3.4388 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.1719 mL | 0.8597 mL | 1.7194 mL |