Physicochemical Properties
| Molecular Formula | C53H93N7O13 |
| Molecular Weight | 1036.34 |
| Exact Mass | 1035.68 |
| CAS # | 24730-31-2 |
| PubChem CID | 443592 |
| Appearance | White to off-white solid powder |
| Density | 1.037±0.06 g/cm3 |
| Boiling Point | 1268.3±65.0℃ |
| LogP | 7.343 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 9 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 13 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 24 |
| Heavy Atom Count | 73 |
| Complexity | 1800 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 8 |
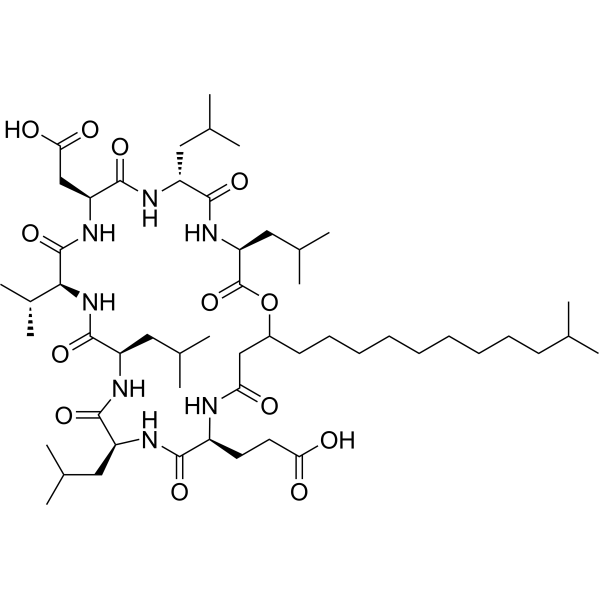
| SMILES | CC(C)CCCCCCCCC[C@@H]1CC(=O)N[C@H](C(=O)N[C@H](C(=O)N[C@@H](C(=O)N[C@H](C(=O)N[C@H](C(=O)N[C@@H](C(=O)N[C@H](C(=O)O1)CC(C)C)CC(C)C)CC(=O)O)C(C)C)CC(C)C)CC(C)C)CCC(=O)O |
| InChi Key | NJGWOFRZMQRKHT-WGVNQGGSSA-N |
| InChi Code | InChI=1S/C53H93N7O13/c1-30(2)20-18-16-14-13-15-17-19-21-36-28-43(61)54-37(22-23-44(62)63)47(66)55-38(24-31(3)4)48(67)57-40(26-33(7)8)51(70)60-46(35(11)12)52(71)58-41(29-45(64)65)50(69)56-39(25-32(5)6)49(68)59-42(27-34(9)10)53(72)73-36/h30-42,46H,13-29H2,1-12H3,(H,54,61)(H,55,66)(H,56,69)(H,57,67)(H,58,71)(H,59,68)(H,60,70)(H,62,63)(H,64,65)/t36-,37+,38+,39-,40-,41+,42+,46+/m1/s1 |
| Chemical Name | 3-[(3S,6R,9S,12S,15R,18S,21S,25R)-9-(carboxymethyl)-3,6,15,18-tetrakis(2-methylpropyl)-25-(10-methylundecyl)-2,5,8,11,14,17,20,23-octaoxo-12-propan-2-yl-1-oxa-4,7,10,13,16,19,22-heptazacyclopentacos-21-yl]propanoic acid |
| HS Tariff Code | 2934.99.9001 |
| Storage |
Powder-20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
| Shipping Condition | Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs) |
Biological Activity
| ln Vitro | Surfactin C1 (0.3–10 μg/mL; 24 h) prevents leukemia cells and monocytes from adhering to HUVEC and LPS[1]. Expression of adhesion molecules generated by LPS is inhibited by surfactin C1 (3 μg/mL; 1 h) [1]. The lipid A/LBP interaction is inhibited by surfactin C1 (3 μg/mL; 1 h) [1]. |
| Cell Assay |
Western Blot Analysis[1] Cell Types: HUVEC Tested Concentrations: 0.3 μg/mL, 1 μg/mL, 3 μg/mL, 10 μg/mL Incubation Duration: 2 hr and another 4 hr with 1 μg/mL LPS Experimental Results: diminished the protein level of ICAM-1 and VCAM-1. Completely inhibited the expression at 3μg/mL with no effect on E-selectin. Cell Viability Assay[1] Cell Types: HL-60, THP-1, Jurkat cells Tested Concentrations: 0.3 μg/mL, 1 μg/mL, 3 μg/mL, 10 μg/mL, and 100 μg/mL Incubation Duration: 24 hr accompanied with LPS for viability; 2 hr and another 4 hr with LPS for adhesion assay Experimental Results: Didn't inhibit cell viability. Inhibited cell adhesion to HUVEC with IC50s of 1.10 μg/mL, 1.45 μg/mL, and 1.43 μg/mL assay, respectively. |
| References |
[1]. Inhibition of lipopolysaccharide activity by a bacterial cyclic lipopeptide surfactin. J Antibiot (Tokyo). 2006 Jan;59(1):35-43. |
| Additional Infomation |
Surfactin C is a cyclodepsipeptide that is N-[(3R)-3-hydroxy-13-methyltetradecanoyl]-L-alpha-glutamyl-L-leucyl-D-leucyl-L-valyl-L-alpha-aspartyl-D-leucyl-L-leucine in which the C-terminal carboxy group has been lactonised by condensation with the alcoholic hydroxy group. It has a role as an antibacterial agent, an antifungal agent, an antiviral agent, a surfactant, a metabolite, an antineoplastic agent and a platelet aggregation inhibitor. It is a cyclodepsipeptide, a lipopeptide antibiotic and a macrocyclic lactone. Surfactin has been reported in Bacillus subtilis, Bacillus mojavensis, and Bacillus thuringiensis with data available. See also: Surfactin peptide (annotation moved to). |
Solubility Data
| Solubility (In Vitro) | DMSO : 100 mg/mL (96.49 mM) |
| Solubility (In Vivo) |
Solubility in Formulation 1: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (2.41 mM) (saturation unknown) in 10% DMSO + 40% PEG300 + 5% Tween80 + 45% Saline (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), clear solution. For example, if 1 mL of working solution is to be prepared, you can add 100 μL of 25.0 mg/mL clear DMSO stock solution to 400 μL PEG300 and mix evenly; then add 50 μL Tween-80 to the above solution and mix evenly; then add 450 μL normal saline to adjust the volume to 1 mL. Preparation of saline: Dissolve 0.9 g of sodium chloride in 100 mL ddH₂ O to obtain a clear solution. Solubility in Formulation 2: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (2.41 mM) (saturation unknown) in 10% DMSO + 90% (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline) (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), clear solution. For example, if 1 mL of working solution is to be prepared, you can add 100 μL of 25.0 mg/mL clear DMSO stock solution to 900 μL of 20% SBE-β-CD physiological saline solution and mix evenly. Preparation of 20% SBE-β-CD in Saline (4°C,1 week): Dissolve 2 g SBE-β-CD in 10 mL saline to obtain a clear solution. Solubility in Formulation 3: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (2.41 mM) (saturation unknown) in 10% DMSO + 90% Corn Oil (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), clear solution. For example, if 1 mL of working solution is to be prepared, you can add 100 μL of 25.0 mg/mL clear DMSO stock solution to 900 μL of corn oil and mix evenly. (Please use freshly prepared in vivo formulations for optimal results.) |
| Preparing Stock Solutions | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 0.9649 mL | 4.8247 mL | 9.6493 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.1930 mL | 0.9649 mL | 1.9299 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.0965 mL | 0.4825 mL | 0.9649 mL |