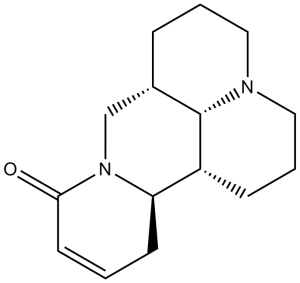
Sophocarpine monohydrate, a major and naturally occuring ingredient found in Sophora alopecuroides, has a wide range of pharmacological effects. Sophocarpine exerts anti-cachectic effects by inhibiting TNF-α and IL-6 production in both RAW264.7 cells and murine primary macrophages. Sophocarpine also shows antivirus activity by inhibiting HHV-6 replication in Molt-3 cells. In addition, Sophocarpine is a potent blocker of HERG K+ channels with an IC50 of about 200 mM.
Physicochemical Properties
| Molecular Formula | C15H22N2O | |
| Molecular Weight | 246.35 | |
| Exact Mass | 246.173 | |
| Elemental Analysis | C, 67.63; H, 9.84; N, 10.52; O, 12.01 | |
| CAS # | 145572-44-7 | |
| Related CAS # | Sophocarpine;6483-15-4 | |
| PubChem CID | 115269 | |
| Appearance | Light yellow to yellow solid powder | |
| Density | 1.2±0.1 g/cm3 | |
| Boiling Point | 425.4±45.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Flash Point | 194.0±21.1 °C | |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±1.0 mmHg at 25°C | |
| Index of Refraction | 1.603 | |
| LogP | 1.37 | |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 0 | |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 2 | |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 0 | |
| Heavy Atom Count | 18 | |
| Complexity | 392 | |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 4 | |
| SMILES | C1C[C@H]2CN3[C@H](CC=CC3=O)[C@@H]4[C@H]2N(C1)CCC4 |
|
| InChi Key | AAGFPTSOPGCENQ-JLNYLFASSA-N | |
| InChi Code | InChI=1S/C15H22N2O/c18-14-7-1-6-13-12-5-3-9-16-8-2-4-11(15(12)16)10-17(13)14/h1,7,11-13,15H,2-6,8-10H2/t11-,12+,13+,15-/m0/s1 | |
| Chemical Name | 1H,5H,10H-Dipyrido(2,1-f:3,2,1-ij)(1,6)naphthyridin-10-one, 2,3,6,7,7a,8,13,13a,13b,13c-decahydro-, (7aS,13aR,13bR,13cS)- | |
| Synonyms |
|
|
| HS Tariff Code | 2934.99.9001 | |
| Storage |
Powder-20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
|
| Shipping Condition | Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs) |
Biological Activity
| Targets | Biochemical reagent; natural alkaloid | |
| ln Vitro |
|
|
| ln Vivo |
|
|
| Enzyme Assay |
The virostatic activity of sophocarpines and gancyclovir (GCV) was tested using HHV-6 Z29 strain and Molt-3 cells. The cytotoxic (IC(50)) and the antiviral (ED(50)) values were first experimentally determined and selective indices (SI) were then calculated. The SI values for sophocarpines 1 and 2 and GCV were in the order 184, 183, and 23, respectively. Though preliminary, these findings indicate that sophocarpines have the potential to inhibit HHV-6 replication[3]. Human ether-à-go-go-related gene (HERG) encodes the rapid component of the cardiac delayed rectifier K+ current, which has an important role in the repolarization of the cardiac action potential. QT interval prolongation through HERG channel inhibition is associated with a risk of torsade de pointes arrhythmias and is a major challenge for drug development. The effects of the novel antiviral drug sophocarpine (SC) were examined on stably expressed HERG channels in human embryonic kidney (HEK293) cells using a whole-cell patch clamp technique, Western blot analysis and immunofluorescence experiments. SC inhibited HERG channels in a concentration-dependent manner, with an IC50 of 100-300 microM. SC significantly accelerated channel inactivation, recovery from inactivation and onset of inactivation. In addition, it had no effect on channel activation and deactivation. Based on Western blot and immunofluorescence results, SC had no significant effect on the expression of HERG protein. In summary, SC is a potent blocker of HERG K+ channels that functions by changing the channel inactivation kinetics. In addition, SC has no effect on the generation and trafficking of HERG protein[4]. |
|
| Cell Assay |
Cell viability assay [1] Cell Types: Normal cells: IOSE144, HL-7702 and LO2, BEAS-2B, GES-1, HEK 293 T, HPDE, FHC, human cancer cells: PANC-1, Mapaca-1, hepG2, SGC-7901, CBC-SD, SGC-996, PC-3, MKN-45, MGC-803, Hela and HCT116 cell Tested Concentrations: 0, 3.9, 7.8, 15.5, 31, 62.5, 125, 250, 500 μM Incubation Duration: 48 hrs (hours) Experimental Results: demonstrated the most effective cytotoxicity against cancer cells. Cell cycle analysis [1] Cell Types: PANC-1 cells; Miapca-2 cells Tested Concentrations: 20 μM Incubation Duration: 48 hrs (hours) Experimental Results: Resulting in S phase population accumulation. Western Blot Analysis [1] Cell Types: PANC-1 cells; Miapca-2 cells Tested Concentrations: 20 μM Incubation Duration: 48 hrs (hours) Experimental Results: Induction of activation of intrinsic apoptotic pathway. |
|
| Animal Protocol |
50 mg/kg; Mice Animal/Disease Models: BALB/c homozygous (nu/nu) nude mice [1] Doses: 20 or 40 mg/kg Route of Administration: intraperitoneal (ip) injection; 20 or 40 mg/kg; 21-day Experimental Results: Xenograft pancreatic tumor mass reduction. |
|
| Toxicity/Toxicokinetics |
mouse LD50 oral 243 mg/kg Zhongguo Yaoxue Zazhi. Chinese Pharmacuetical Journal., 27(201), 1992 mouse LD50 intravenous 46800 ug/kg Yaowu Fenxi Zazhi. Journal of Pharmaceutical Analysis., 6(96), 1986 mouse LD50 intraperitoneal 64300 ug/kg Zhongguo Yaoli Xuebao. Acta Pharmacologica Sinica. Chinese Journal of Pharmacology., 8(153), 1987 [PMID:2959003] |
|
| References |
[1]. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2017 Sep 11;36(1):124. [2]. Int Immunopharmacol.2008 Dec 20;8(13-14):1767-72.[2]. Phytother Res.2002 Mar;16(2):154-6. [4]. Biol Pharm Bull.2008 Apr;31(4):627-32. |
|
| Additional Infomation |
Sophocarpine is an alkaloid. Sophocarpine has been reported in Daphniphyllum oldhamii, Daphniphyllum pentandrum, and other organisms with data available. Sophoridine has been reported in Euchresta japonica, Leontice leontopetalum, and other organisms with data available. Tetracyclic bis-quinolizidine alkaloids found in the family LEGUMINOSAE, mainly in the genus SOPHORA. Background: Pancreatic cancer is generally acknowledged as the most common primary malignant tumor, and it is known to be resistant to conventional chemotherapy. Novel, selective antitumor agents are pressingly needed. Methods: CCK-8 and colony formation assay were used to investigate the cell growth. Flow cytometry analysis was used to evaluate the cell cycle and cell apoptosis. The peroxide-sensitive fluorescent probe DCFH-DA was used to measure the intracellular ROS levels. Western blot assay was used to detect the levels of cell cycle and apoptosis related proteins. Xenografts in nude mice were used to evaluate the effect of Sophoridine on pancreatic cancer cell in vivo. Results: Sophoridine killed cancer cells but had low cytotoxicity to normal cells. Pancreatic cancer cells were particularly sensitive. Sophoridine inhibited the proliferation of pancreatic cancer cells and induced cell cycle arrest at S phase and mitochondrial-related apoptosis. Moreover, Sophoridine induced a sustained activation of the phosphorylation of ERK and JNK. In addition, Sophoridine provoked the generation of reactive oxygen species (ROS) in pancreatic cancer cells. Finally, in vivo, Sophoridine suppressed tumor growth in mouse xenograft models. Conclusion: These findings suggest Sophoridine is promising to be a novel, potent and selective antitumor drug candidate for pancreatic cancer.[1] |
Solubility Data
| Solubility (In Vitro) |
|
|||
| Solubility (In Vivo) |
Solubility in Formulation 1: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (9.46 mM) (saturation unknown) in 10% DMSO + 40% PEG300 + 5% Tween80 + 45% Saline (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), clear solution. For example, if 1 mL of working solution is to be prepared, you can add 100 μL of 25.0 mg/mL clear DMSO stock solution to 400 μL PEG300 and mix evenly; then add 50 μL Tween-80 to the above solution and mix evenly; then add 450 μL normal saline to adjust the volume to 1 mL. Preparation of saline: Dissolve 0.9 g of sodium chloride in 100 mL ddH₂ O to obtain a clear solution. Solubility in Formulation 2: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (9.46 mM) (saturation unknown) in 10% DMSO + 90% (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline) (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), clear solution. For example, if 1 mL of working solution is to be prepared, you can add 100 μL of 25.0 mg/mL clear DMSO stock solution to 900 μL of 20% SBE-β-CD physiological saline solution and mix evenly. Preparation of 20% SBE-β-CD in Saline (4°C,1 week): Dissolve 2 g SBE-β-CD in 10 mL saline to obtain a clear solution. Solubility in Formulation 3: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (9.46 mM) (saturation unknown) in 10% DMSO + 90% Corn Oil (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), clear solution. For example, if 1 mL of working solution is to be prepared, you can add 100 μL of 25.0 mg/mL clear DMSO stock solution to 900 μL of corn oil and mix evenly. (Please use freshly prepared in vivo formulations for optimal results.) |
| Preparing Stock Solutions | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 4.0593 mL | 20.2963 mL | 40.5927 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.8119 mL | 4.0593 mL | 8.1185 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.4059 mL | 2.0296 mL | 4.0593 mL |