Physicochemical Properties
| Molecular Formula | C14H12O3 |
| Molecular Weight | 228.24 |
| Exact Mass | 228.079 |
| CAS # | 523-59-1 |
| PubChem CID | 68229 |
| Appearance | White to off-white solid powder |
| Density | 1.222g/cm3 |
| Boiling Point | 403ºC at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 119 - 120 °C |
| Flash Point | 170.5ºC |
| Index of Refraction | 1.583 |
| LogP | 2.977 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 0 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 3 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 0 |
| Heavy Atom Count | 17 |
| Complexity | 394 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| InChi Key | QUVCQYQEIOLHFZ-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| InChi Code | InChI=1S/C14H12O3/c1-14(2)8-7-10-11(17-14)5-3-9-4-6-12(15)16-13(9)10/h3-8H,1-2H3 |
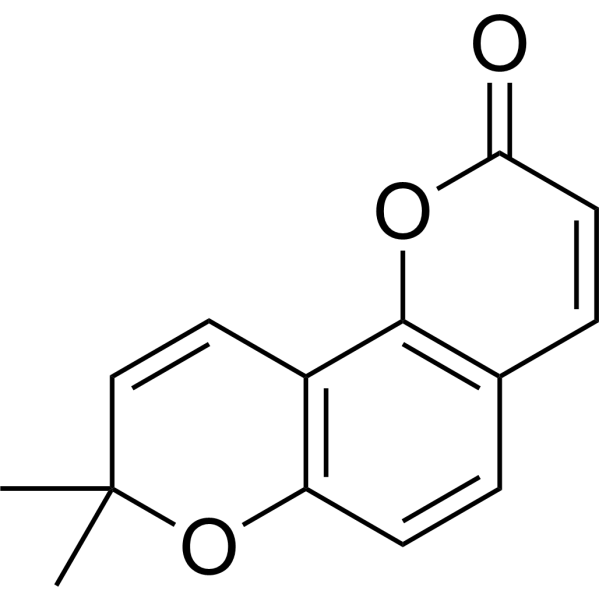
| Chemical Name | 8,8-dimethylpyrano[2,3-f]chromen-2-one |
| HS Tariff Code | 2934.99.9001 |
| Storage |
Powder-20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
| Shipping Condition | Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs) |
Biological Activity
| ln Vitro | P-388 and HT-29 cells are hazardous to selenium, with ED50 values of 8.66 and 9.94 μg/mL, respectively [1]. The cytokine output of LPS- and IFN-γ-stimulated macrophages is inhibited by selvin (5–20 μM; 0.5–24 h) [3]. The expression of pro-inflammatory macrophage markers (iNOS, phagocytosis, and CD11c) in BMDMs is inhibited by selvin (5–20 μM; 12 h) [3]. The STAT1 signaling pathway is blocked by selvin (5–20 μM; 0.5–6 h) [3]. |
| ln Vivo | In mice, selenium (0.5–40.5 mg/kg; sc; once) has antinociceptive and peripheral anti-inflammatory effects [2]. Mice with sepsis brought on by cecal ligation and puncture respond better to sevelin (3–30 mg/kg; ig; once) [3]. |
| Cell Assay |
RT-PCR[3] Cell Types: Bone marrow-derived macrophages (BMDMs) Tested Concentrations: 5, 10 and 20 μM Incubation Duration: 6 h Experimental Results: decreased the mRNA for cytokines (IL-1β, IL-6, Tnf-α and IL-23) and chemokines (Ccl3, Ccl7, Cxcl9 and Cxcl11) concentration-dependently in BMDMs. Western Blot Analysis[3] Cell Types: BMDMs Tested Concentrations: 5, 10 and 20 μM Incubation Duration: 0.5, 1.5, 3 and 6 h Experimental Results: Suppressed expression of p-STAT1 and p-p65 both concentration and time dependently. |
| Animal Protocol |
Animal/Disease Models: Male Swiss mice[2] Doses: 0.5, 4.5 or 40.5 mg/kg Route of Administration: subcutaneous (sc)injection; once Experimental Results: Inhibited the writhing response induced by acetic acid in a significant and dose-dependent manner, by 19.5%, 26.2% and 41.4% at dose of 0.5, 4.5 or 40.5 mg/kg, respectively. Elicited a significant inhibition of formalin response during the second phase (inflammatory), by 90.3%, 97.8% and 95.3%, respectively. Animal/Disease Models: C57BL/6 mice, caecal ligation and puncture (CLP) induced sepsis model[3] Doses: 3, 10 and 30 mg/kg Route of Administration: intragastric (po)administration, once Experimental Results: Ameliorated lung injury and diminished JAK2 phosphorylation level in lung tissue during sepsis. diminished the immune cell counts in BALF induced by CLP. |
| References |
[1]. Cytotoxic and anti-platelet aggregation constituents from the root wood of Melicope semecarpifolia. Planta Med. 2005 Nov;71(11):1078-81. [2]. Antinociceptive activity of the pyranocoumarin seselin in mice. Fitoterapia. 2006 Dec;77(7-8):574-8. [3]. Seselin ameliorates inflammation via targeting Jak2 to suppress the proinflammatory phenotype of macrophages. Br J Pharmacol. 2019 Jan;176(2):317-333. |
| Additional Infomation |
Seselin is a member of coumarins. It has a role as a metabolite. Seselin has been reported in Angelica gigas, Ficus erecta var. beecheyana, and other organisms with data available. |
Solubility Data
| Solubility (In Vitro) | May dissolve in DMSO (in most cases), if not, try other solvents such as H2O, Ethanol, or DMF with a minute amount of products to avoid loss of samples |
| Solubility (In Vivo) |
Note: Listed below are some common formulations that may be used to formulate products with low water solubility (e.g. < 1 mg/mL), you may test these formulations using a minute amount of products to avoid loss of samples. Injection Formulations (e.g. IP/IV/IM/SC) Injection Formulation 1: DMSO : Tween 80: Saline = 10 : 5 : 85 (i.e. 100 μL DMSO stock solution → 50 μL Tween 80 → 850 μL Saline) *Preparation of saline: Dissolve 0.9 g of sodium chloride in 100 mL ddH ₂ O to obtain a clear solution. Injection Formulation 2: DMSO : PEG300 :Tween 80 : Saline = 10 : 40 : 5 : 45 (i.e. 100 μL DMSO → 400 μLPEG300 → 50 μL Tween 80 → 450 μL Saline) Injection Formulation 3: DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90 (i.e. 100 μL DMSO → 900 μL Corn oil) Example: Take the Injection Formulation 3 (DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90) as an example, if 1 mL of 2.5 mg/mL working solution is to be prepared, you can take 100 μL 25 mg/mL DMSO stock solution and add to 900 μL corn oil, mix well to obtain a clear or suspension solution (2.5 mg/mL, ready for use in animals). Injection Formulation 4: DMSO : 20% SBE-β-CD in saline = 10 : 90 [i.e. 100 μL DMSO → 900 μL (20% SBE-β-CD in saline)] *Preparation of 20% SBE-β-CD in Saline (4°C,1 week): Dissolve 2 g SBE-β-CD in 10 mL saline to obtain a clear solution. Injection Formulation 5: 2-Hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin : Saline = 50 : 50 (i.e. 500 μL 2-Hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin → 500 μL Saline) Injection Formulation 6: DMSO : PEG300 : castor oil : Saline = 5 : 10 : 20 : 65 (i.e. 50 μL DMSO → 100 μLPEG300 → 200 μL castor oil → 650 μL Saline) Injection Formulation 7: Ethanol : Cremophor : Saline = 10: 10 : 80 (i.e. 100 μL Ethanol → 100 μL Cremophor → 800 μL Saline) Injection Formulation 8: Dissolve in Cremophor/Ethanol (50 : 50), then diluted by Saline Injection Formulation 9: EtOH : Corn oil = 10 : 90 (i.e. 100 μL EtOH → 900 μL Corn oil) Injection Formulation 10: EtOH : PEG300:Tween 80 : Saline = 10 : 40 : 5 : 45 (i.e. 100 μL EtOH → 400 μLPEG300 → 50 μL Tween 80 → 450 μL Saline) Oral Formulations Oral Formulation 1: Suspend in 0.5% CMC Na (carboxymethylcellulose sodium) Oral Formulation 2: Suspend in 0.5% Carboxymethyl cellulose Example: Take the Oral Formulation 1 (Suspend in 0.5% CMC Na) as an example, if 100 mL of 2.5 mg/mL working solution is to be prepared, you can first prepare 0.5% CMC Na solution by measuring 0.5 g CMC Na and dissolve it in 100 mL ddH2O to obtain a clear solution; then add 250 mg of the product to 100 mL 0.5% CMC Na solution, to make the suspension solution (2.5 mg/mL, ready for use in animals). Oral Formulation 3: Dissolved in PEG400 Oral Formulation 4: Suspend in 0.2% Carboxymethyl cellulose Oral Formulation 5: Dissolve in 0.25% Tween 80 and 0.5% Carboxymethyl cellulose Oral Formulation 6: Mixing with food powders Note: Please be aware that the above formulations are for reference only. InvivoChem strongly recommends customers to read literature methods/protocols carefully before determining which formulation you should use for in vivo studies, as different compounds have different solubility properties and have to be formulated differently. (Please use freshly prepared in vivo formulations for optimal results.) |
| Preparing Stock Solutions | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 4.3814 mL | 21.9068 mL | 43.8135 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.8763 mL | 4.3814 mL | 8.7627 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.4381 mL | 2.1907 mL | 4.3814 mL |