SSE15206 is a mitotic inhibitor, specifically, a microtubule depolymerizing agent that can overcome multidrug resistance. In cancer cell lines of various origins, it possesses strong antiproliferative properties and overcomes resistance to agents that target microtubules. When cells are treated with SSE15206, they experience aberrant mitosis that leads to G2/M arrest because of insufficient spindle formation. This is a phenotype that is frequently connected to medications that disrupt microtubule dynamics. According to docking and competition studies, SSE15206 binds to the tubulin colchicine site to inhibit microtubule polymerization in biochemical and cellular assays. The compound causes apoptotic cell death in cells that are treated for an extended period of time. This is indicated by increased p53 induction and Poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase cleavage as well as Annexin V/PI staining. What's more, we show that SSE15206 can overcome chemotherapeutic drug resistance in a variety of cancer cell lines, including the multidrug-resistant KB-V1 and A2780-Pac-Res cell lines that overexpress MDR-1. This indicates that SSE15206 is a promising hit for lead optimization studies that target multidrug resistance.
Physicochemical Properties
| Molecular Formula | C19H21N3O3S | |
| Molecular Weight | 371.453343153 | |
| Exact Mass | 371.13 | |
| Elemental Analysis | C, 61.44; H, 5.70; N, 11.31; O, 12.92; S, 8.63 | |
| CAS # | 1370046-40-4 | |
| Related CAS # |
|
|
| PubChem CID | 56944939 | |
| Appearance | Light yellow to yellow solid powder | |
| LogP | 2.6 | |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 1 | |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 5 | |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 5 | |
| Heavy Atom Count | 26 | |
| Complexity | 510 | |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 | |
| InChi Key | GONIBFCARADPAC-UHFFFAOYSA-N | |
| InChi Code | InChI=1S/C19H21N3O3S/c1-23-16-9-13(10-17(24-2)18(16)25-3)15-11-14(21-22(15)19(20)26)12-7-5-4-6-8-12/h4-10,15H,11H2,1-3H3,(H2,20,26) | |
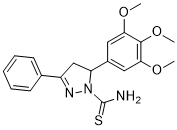
| Chemical Name | 5-phenyl-3-(3,4,5-trimethoxyphenyl)-3,4-dihydropyrazole-2-carbothioamide | |
| Synonyms |
|
|
| HS Tariff Code | 2934.99.9001 | |
| Storage |
Powder-20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
|
| Shipping Condition | Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs) |
Biological Activity
| Targets | microtubule (GI50 = 197 nM) | ||
| ln Vitro | SSE15206, at concentrations of 5 × and 10 × GI50 values, induces apoptosis in cells regardless of MDR-1 overexpression cell lines (KB-V1, A2780-Pac-Res), highly resistant to paclitaxel cells (HCT116-Pac-Res), and parental cells. In conclusion, SSE15206 can overcome chemotherapeutic drug resistance in various cancer cell lines, including paclitaxel resistance[1]. | ||
| ln Vivo |
|
||
| Enzyme Assay | SE15206 inhibits the polymerization of microtubules in biochemical and cellular assays by binding to the tubulin colchicine site, as demonstrated by studies on docking and competition. | ||
| Cell Assay | Treatment with SSE15206 results in aberrant mitosis, which leads to incomplete spindle formation and G2/M arrest. This is a phenotype that is frequently linked to medications that disrupt microtubule dynamics. Extended exposure to the substance causes p53 induction and apoptotic cell death, as evidenced by increased Poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase cleavage and Annexin V/PI staining. Of greater significance, we show that SSE15206 can overcome resistance to chemotherapeutic drugs in a variety of cancer cell lines, such as the multidrug-resistant KB-V1 and A2780-Pac-Res cell lines that overexpress MDR-1. This suggests that SSE15206 is a viable candidate for lead optimization studies that target multidrug resistance. | ||
| Animal Protocol |
|
||
| References |
[1]. Identification and characterization of SSE15206, a microtubule depolymerizing agent that overcomes multidrug resistance. Sci Rep. 2018 Feb 19;8(1):3305. |
Solubility Data
| Solubility (In Vitro) |
|
|||
| Solubility (In Vivo) |
Solubility in Formulation 1: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (6.73 mM) (saturation unknown) in 10% DMSO + 40% PEG300 + 5% Tween80 + 45% Saline (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), clear solution. For example, if 1 mL of working solution is to be prepared, you can add 100 μL of 25.0 mg/mL clear DMSO stock solution to 400 μL PEG300 and mix evenly; then add 50 μL Tween-80 to the above solution and mix evenly; then add 450 μL normal saline to adjust the volume to 1 mL. Preparation of saline: Dissolve 0.9 g of sodium chloride in 100 mL ddH₂ O to obtain a clear solution. Solubility in Formulation 2: 2.5 mg/mL (6.73 mM) in 10% DMSO + 90% (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline) (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), suspension solution; with ultrasonication. For example, if 1 mL of working solution is to be prepared, you can add 100 μL of 25.0 mg/mL clear DMSO stock solution to 900 μL of 20% SBE-β-CD physiological saline solution and mix evenly. Preparation of 20% SBE-β-CD in Saline (4°C,1 week): Dissolve 2 g SBE-β-CD in 10 mL saline to obtain a clear solution. Solubility in Formulation 3: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (6.73 mM) (saturation unknown) in 10% DMSO + 90% Corn Oil (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), clear solution. For example, if 1 mL of working solution is to be prepared, you can add 100 μL of 25.0 mg/mL clear DMSO stock solution to 900 μL of corn oil and mix evenly. (Please use freshly prepared in vivo formulations for optimal results.) |
| Preparing Stock Solutions | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.6922 mL | 13.4608 mL | 26.9215 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.5384 mL | 2.6922 mL | 5.3843 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.2692 mL | 1.3461 mL | 2.6922 mL |