Physicochemical Properties
| Molecular Formula | C54H86CLN15O14 |
| Molecular Weight | 1204.8057513237 |
| Exact Mass | 1203.616 |
| CAS # | 2408422-41-1 |
| Related CAS # | Upleganan;2407717-17-1 |
| PubChem CID | 165412291 |
| Appearance | Typically exists as solid at room temperature |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 18 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 19 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 22 |
| Heavy Atom Count | 84 |
| Complexity | 2090 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 12 |
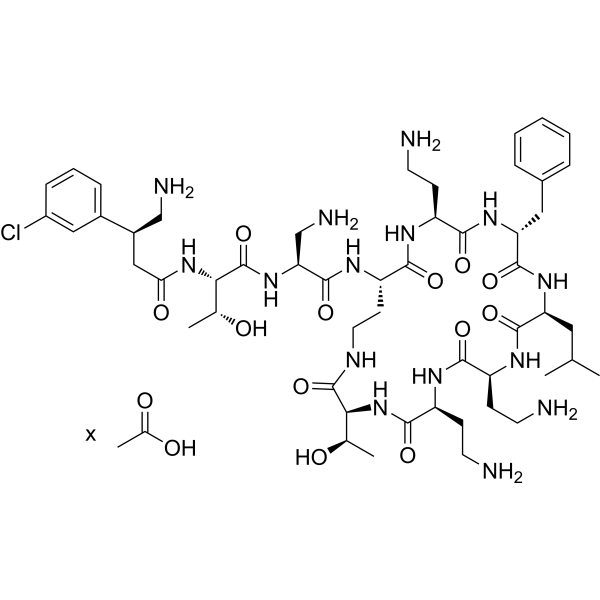
| SMILES | C[C@H]([C@H]1C(=O)NCC[C@@H](C(=O)N[C@H](C(=O)N[C@@H](C(=O)N[C@H](C(=O)N[C@H](C(=O)N[C@H](C(=O)N1)CCN)CCN)CC(C)C)CC2=CC=CC=C2)CCN)NC(=O)[C@H](CN)NC(=O)[C@H]([C@@H](C)O)NC(=O)C[C@H](CN)C3=CC(=CC=C3)Cl)O.CC(=O)O |
| InChi Key | YADKGXKKBAFXFJ-CYMYEOQJSA-N |
| InChi Code | InChI=1S/C52H82ClN15O12.C2H4O2/c1-27(2)21-38-48(76)62-34(13-17-54)44(72)61-36(15-19-56)47(75)68-42(28(3)69)51(79)59-20-16-37(46(74)60-35(14-18-55)45(73)65-39(49(77)64-38)22-30-9-6-5-7-10-30)63-50(78)40(26-58)66-52(80)43(29(4)70)67-41(71)24-32(25-57)31-11-8-12-33(53)23-31;1-2(3)4/h5-12,23,27-29,32,34-40,42-43,69-70H,13-22,24-26,54-58H2,1-4H3,(H,59,79)(H,60,74)(H,61,72)(H,62,76)(H,63,78)(H,64,77)(H,65,73)(H,66,80)(H,67,71)(H,68,75);1H3,(H,3,4)/t28-,29-,32-,34+,35+,36+,37+,38+,39-,40+,42+,43+;/m1./s1 |
| Chemical Name | acetic acid;(2S,3R)-2-[[(3S)-4-amino-3-(3-chlorophenyl)butanoyl]amino]-N-[(2S)-3-amino-1-oxo-1-[[(3S,6S,9S,12S,15R,18S,21S)-6,9,18-tris(2-aminoethyl)-15-benzyl-3-[(1R)-1-hydroxyethyl]-12-(2-methylpropyl)-2,5,8,11,14,17,20-heptaoxo-1,4,7,10,13,16,19-heptazacyclotricos-21-yl]amino]propan-2-yl]-3-hydroxybutanamide |
| HS Tariff Code | 2934.99.9001 |
| Storage |
Powder-20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month Note: Please store this product in a sealed and protected environment, avoid exposure to moisture. |
| Shipping Condition | Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs) |
Biological Activity
| Targets | MIC: 0.125 mg/L (Pseudomonas aeruginosa Pa14) and 0.125 mg/L (Acinetobacter baumannii NCTC13301)[1][2] |
| ln Vitro | SPR206 demonstrates significant antimicrobial activity against bacteria that are Gram-negative. SPR206 has decreased cytotoxicity with MIC values of 8 mg/L, 0.125 mg/L, 0.125 mg/L, 0.25 mg/L, 0.06 mg/L, and 0.125 mg/L against E. coli IHMA558090, E. coli ATCC 25922, K. pneumonia ATCC 13882, P. aeruginosa ATCC 27853, and A. baumannii ATCC 19003 [1]. |
| ln Vivo | In lung tissue and in the thigh model, SPR206 (0.125-30 mg/kg; intravenous injection or subcutaneous injection; every 8 hours or every 4 hours; for 16 hours or 24 hours; neutropenic mice) therapy decreases the burden of Pa14 and NCTC13301[2]. |
| Animal Protocol |
Animal/Disease Models: Neutropenic mice infected Pa14 or NCTC13301[2] Doses: 3 mg/kg, 10 mg/kg, 20 mg/kg, 30 mg/kg (intravenous (iv)injection); 0.125 mg/kg, 0.5 mg/kg, 1 mg/kg, 4 mg/kg (subcutaneous (sc)injection) Route of Administration: intravenous (iv)injection or subcutaneous (sc)injection; every 8 hrs (hours) or every 4 hrs (hours); for 16 hrs (hours) or 24 hrs (hours) Experimental Results: In lung tissue, diminished the burden of Pa14 and NCTC13301 by 1.5 and 3.6 log10 CFU/mL. In the thigh model, diminished the burden of Ab13301 by 3.4 and 4.3 log10 CFU/g. |
| References |
[1]. Brown P, et al. Design of Next Generation Polymyxins with Lower Toxicity: The Discovery of SPR206. ACS Infect Dis. 2019 Oct 11;5(10):1645-1656. [2]. L. Grosser, et al. In Vivo Efficacy of SPR206 in Murine Lung and Thigh Infection Models Caused by Multidrug Resistant Pathogens Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Acinetobacter baumanii. Poster-139 ASM ESCMID 2018 Lisbon, Portugal. [3]. Noushin Akhoundsadegh, et al. Outer Membrane Interaction Kinetics of New Polymyxin B Analogs in Gram-Negative Bacilli. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2019 Sep 23;63(10):e00935-19. |
Solubility Data
| Solubility (In Vitro) | DMSO : ≥ 100 mg/mL |
| Solubility (In Vivo) |
Solubility in Formulation 1: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (Infinity mM) (saturation unknown) in 10% DMSO + 40% PEG300 + 5% Tween80 + 45% Saline (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), clear solution. For example, if 1 mL of working solution is to be prepared, you can add 100 μL of 25.0 mg/mL clear DMSO stock solution to 400 μL PEG300 and mix evenly; then add 50 μL Tween-80 to the above solution and mix evenly; then add 450 μL normal saline to adjust the volume to 1 mL. Preparation of saline: Dissolve 0.9 g of sodium chloride in 100 mL ddH₂ O to obtain a clear solution. Solubility in Formulation 2: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (Infinity mM) (saturation unknown) in 10% DMSO + 90% (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline) (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), clear solution. For example, if 1 mL of working solution is to be prepared, you can add 100 μL of 25.0 mg/mL clear DMSO stock solution to 900 μL of 20% SBE-β-CD physiological saline solution and mix evenly. Preparation of 20% SBE-β-CD in Saline (4°C,1 week): Dissolve 2 g SBE-β-CD in 10 mL saline to obtain a clear solution. Solubility in Formulation 3: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (Infinity mM) (saturation unknown) in 10% DMSO + 90% Corn Oil (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), clear solution. For example, if 1 mL of working solution is to be prepared, you can add 100 μL of 25.0 mg/mL clear DMSO stock solution to 900 μL of corn oil and mix evenly. (Please use freshly prepared in vivo formulations for optimal results.) |
| Preparing Stock Solutions | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 0.8300 mL | 4.1500 mL | 8.3001 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.1660 mL | 0.8300 mL | 1.6600 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.0830 mL | 0.4150 mL | 0.8300 mL |