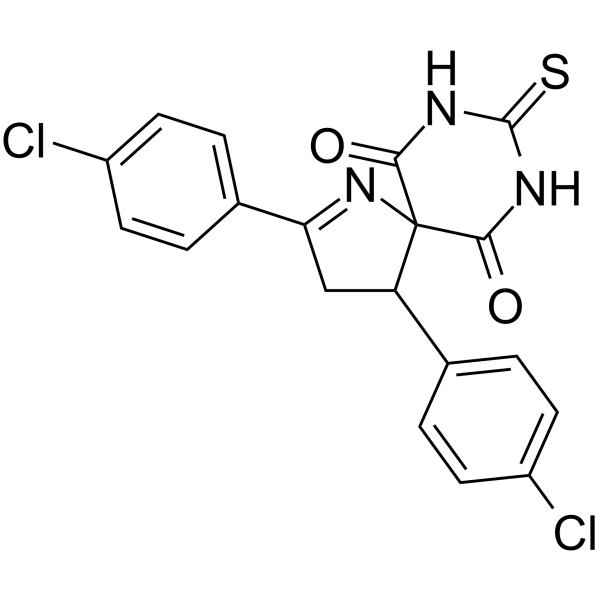
Physicochemical Properties
| Molecular Formula | C19H13CL2N3O2S |
| Molecular Weight | 418.296420812607 |
| Exact Mass | 417.01 |
| CAS # | 2377858-38-1 |
| PubChem CID | 146165950 |
| Appearance | Light yellow to brown solid powder |
| LogP | 3.6 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 2 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 4 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 2 |
| Heavy Atom Count | 27 |
| Complexity | 662 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| SMILES | ClC1C=CC(=CC=1)C1CC(C2C=CC(=CC=2)Cl)=NC21C(NC(NC2=O)=S)=O |
| InChi Key | QEMQLCCYJLGAKB-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| InChi Code | InChI=1S/C19H13Cl2N3O2S/c20-12-5-1-10(2-6-12)14-9-15(11-3-7-13(21)8-4-11)24-19(14)16(25)22-18(27)23-17(19)26/h1-8,14H,9H2,(H2,22,23,25,26,27) |
| Chemical Name | 2,4-bis(4-chlorophenyl)-8-sulfanylidene-1,7,9-triazaspiro[4.5]dec-1-ene-6,10-dione |
| HS Tariff Code | 2934.99.9001 |
| Storage |
Powder-20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
| Shipping Condition | Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs) |
Biological Activity
| ln Vitro | SCR130 (7-21 μM; 48 hours) increases in both early and late apoptotic cell counts. Through both internal and external routes, SCR130 causes apoptosis. p-p53, BCL2, and MCL1 expression are all upregulated by SCR130, along with CYTOCHROME C, BAX, and BAK. Increased expression of the FAS and SMAC-DIABLO proteins, as well as caspase 8 activation, have been reported[1]. The IC50 values of SCR130 (48 hours) in Reh, HeLa, CEM, Nalm6, and N114 cells are 14.1 μM, 5.9 μM, 6.5 μM, 2.2 μM, and 11 μM, respectively. These results indicate that SCR130 is cytotoxic]. By causing increased cell death when co-administered in Reh and Nalm6 cell lines, SCR130 can magnify the effects of radiation (0.5 and 1 Gy)[1]. Unrepaired DNA breaks accumulate when SCR130 inhibits the endogenous NHEJ. DNA double-strand breaks (DSBs) accumulate as a result of treatment with SCR130, which inhibits endogenous NHEJ and triggers apoptotic pathways, ultimately leading to cell death[1]. |
| Cell Assay |
Apoptosis Analysis[1] Cell Types: Reh cells Tested Concentrations: 7 μM, 14 μM, and 21 μM Incubation Duration: 48 hrs (hours) Experimental Results: demonstrated a concentration-dependent increase in the number of late and early apoptotic cells. Western Blot Analysis[1] Cell Types: Reh cells Tested Concentrations: 7 μM, 14 μM, and 21 μM Incubation Duration: 48 hrs (hours) Experimental Results: Revealed a concentration-dependent increase in levels of pATM and activation of p53 through phosphorylation. |
| References |
[1]. Identification and characterization of novel SCR7-based small-molecule inhibitor of DNA end-joining, SCR130 and its relevance in cancer therapeutics. Mol Carcinog. 2020 Jun;59(6):618-628. |
Solubility Data
| Solubility (In Vitro) | DMSO : 100 mg/mL (239.06 mM ) |
| Solubility (In Vivo) |
Solubility in Formulation 1: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (5.98 mM) (saturation unknown) in 10% DMSO + 90% Corn Oil (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), clear solution. For example, if 1 mL of working solution is to be prepared, you can add 100 μL of 25.0 mg/mL clear DMSO stock solution to 900 μL of corn oil and mix evenly. (Please use freshly prepared in vivo formulations for optimal results.) |
| Preparing Stock Solutions | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.3906 mL | 11.9531 mL | 23.9063 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.4781 mL | 2.3906 mL | 4.7813 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.2391 mL | 1.1953 mL | 2.3906 mL |