SBI-0206965 is a cell permeable and selective autophagy kinase ULK1 inhibitor with IC50 of 108 nM, it is about 7-fold selectivity over ULK2. SBI-0206965 is a highly selective ULK1 kinase inhibitor in vitro and suppressed ULK1-mediated phosphorylation events in cells, regulating autophagy and cell survival. SBI-0206965 greatly synergized with mechanistic target of rapamycin (mTOR) inhibitors to kill tumor cells, providing a strong rationale for their combined use in the clinic.
Physicochemical Properties
| Molecular Formula | C21H21BRN4O5 | |
| Molecular Weight | 489.32 | |
| Exact Mass | 488.069 | |
| Elemental Analysis | C, 51.55; H, 4.33; Br, 16.33; N, 11.45; O, 16.35 | |
| CAS # | 1884220-36-3 | |
| Related CAS # |
|
|
| PubChem CID | 92044402 | |
| Appearance | White to off-white solid powder | |
| Density | 1.4±0.1 g/cm3 | |
| Index of Refraction | 1.619 | |
| LogP | 3.26 | |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 2 | |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 8 | |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 8 | |
| Heavy Atom Count | 31 | |
| Complexity | 560 | |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 | |
| InChi Key | NEXGBSJERNQRSV-UHFFFAOYSA-N | |
| InChi Code | InChI=1S/C21H21BrN4O5/c1-23-19(27)13-7-5-6-8-15(13)31-20-14(22)11-24-21(26-20)25-12-9-16(28-2)18(30-4)17(10-12)29-3/h5-11H,1-4H3,(H,23,27)(H,24,25,26) | |
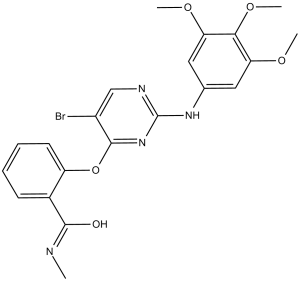
| Chemical Name | 2-((5-bromo-2-((3,4,5-trimethoxyphenyl)amino)pyrimidin-4-yl)oxy)-N-methylbenzamide | |
| Synonyms |
|
|
| HS Tariff Code | 2934.99.9001 | |
| Storage |
Powder-20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
|
| Shipping Condition | Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs) |
Biological Activity
| Targets | ULK1 (IC50 = 108 nM); ULK2 (IC50 = 711 nM) |
| ln Vitro |
SBI-0206965 (5–20 μM; 24 hours) causes A498 and ACHN cells to undergo apoptosis in response to hunger[1]. SBI-0206965 (5-20 μM; 24 hours) increases the levels of cleaved Caspase 8 and PARP, indicators of apoptosis, and attenuates the phosphorylation of Ser108 of the AMPK β1 subunit[1]. ULK1 mRNA expression was significantly upregulated in clear cell renal cell carcinoma (ccRCC) and overexpression of ULK1 correlated with poor outcomes. We found that ULK1 was highly expressed in 66.7% of ccRCC tumours (p < 0·05). Knockdown of ULK1 and selective inhibition of ULK1 by SBI-0206965 induced cell apoptosis in ccRCC cells. We demonstrated that SBI-0206965 triggered apoptosis by preventing autophagy and pentose phosphate pathway (PPP) flux. Interpretation: Taken together, our results suggested that ULK1 was upregulated in ccRCC tumours and may be a potential therapeutic target. Therefore, SBI-0206965 should be further considered as an anti-ccRCC agent. [1] The compound SBI-0206965 is a highly selective ULK1 kinase inhibitor in vitro and suppressed ULK1-mediated phosphorylation events in cells, regulating autophagy and cell survival. SBI-0206965 greatly synergized with mechanistic target of rapamycin (mTOR) inhibitors to kill tumor cells, providing a strong rationale for their combined use in the clinic.[2] |
| ln Vivo |
SBI-0206965 (50 mg/kg; ip; once every 3 days for 37 days) reduces tumor growth and causes apoptosis in A498 xenograft tumours[1]. To evaluate the anti-tumour efficacy in vivo, nude mice inoculated subcutaneously with A498 cells were intraperitoneally injected with either vehicle (DMSO) or SBI-0206965 (50 mg/kg) once every three days for 37 d starting 14 d after injection of the ccRCC cells. The A498 xenograft tumour growth rate was significantly suppressed by SBI-0206965 compared with that of the vehicle (Fig. 5a, b, and c). In contrast, no significant differences in weight of the mice were observed comparing the vehicle control and SBI-0206965 groups (Fig. 5e). Mice in the SBI-0206965 group did not display signs of toxicity such as agitation, indigestion, or diarrhoea, impaired movement or posture, or areas of redness or swelling. Moreover, treatment with SBI-0206965 did not affect the renal structure in mice (Fig. S2).[1] |
| Enzyme Assay |
Peptide kinase assays [1] For peptide library screening, ULK1/FIP200/Atg13 complexes were used to phosphorylate peptide mixtures (50 mM) by incubation for 2 hours at 30ºC in 1536-well plates in 50 mM HEPES, pH 7.4, 15 mM MgCl2, 0.1 mM Na3VO4, 1 mM EGTA, 0.1% BSA, 0.1% Tween 20, and 50 mM γ33P-ATP (0.03 mCi/ml), essentially as previously described (Chen and Turk, 2010). Aliquots (200 nl) of each reaction were transferred to a streptavidin-coated membrane, which was processed as described previously (Hutti et al., 2004) and then exposed to a phosphor screen to quantify radiolabel incorporation. For ULKtide phosphorylation assays, the indicated peptide (15 mM) was incubated with ULK1/FIP200/Atg13 complexes in 20 mM HEPES, pH 7.4, 10 mM MgCl2, 1 mM DTT, 0.1% BSA for 15 minutes. At 5 minute intervals, an aliquot of the reaction was spotted onto P81 phosphocellulose filters, which were washed, dried, and subjected to scintillation counting. Assays were performed in duplicate and data show the average of three separate experiments. ULK1 kinase assays [1] γ32P-ATP assays to measure ULK1 kinase activity were performed as previously described (Jung et al., 2009). Briefly, Flag-ULK1 was transfected into HEK-293T cells and 20 hours later treated as indicated. The immmunoprecipitate was washed in IP buffer 3 times, and washed in kinase buffer (25 mM MOPS, pH 7.5, 1 mM EGTA, 0.1 mM Na3VO4, 15 mM MgCl2,). Hot and cold ATP were added at a 100 µM final concentration. As substrates, GST or the recombinant protein GST-Atg101 purified from E. coli were used at 1 µg for each reaction. Reactions were boiled and run out on SDS-PAGE gels. Gels were dried and imaged using PhosphoImager software. Kinase inhibitor selectivity profiling [1] Kinase inhibitor specificity profiling assays were first carried out using DiscoveRx KINOMEscan competition binding assay against a panel of 456 kinases (www.discoverx.com) using 1 mM SBI0206965. Kinases that potentially interacted with SBI-0206965 (inhibited to less than 10% DMSO control) were then tested in classic in vitro kinase assays (Reaction Biology; http://www.reactionbiology.com/) with a dose curve of SBI-0206965 to monitor enzymatic activity and determine IC50 curves. |
| Cell Assay |
Apoptosis Analysis[1] Cell Types: A498 and ACHN cells (starvation medium (EBSS) treatment) Tested Concentrations: 5, 10 ,20 μM Incubation Duration: 24 hrs (hours) Experimental Results: Induced significant levels of apoptosis. Western Blot Analysis[1] Cell Types: A498 and ACHN cells (EBSS treatment) Tested Concentrations: 5, 10, 20 μM Incubation Duration: 24 hrs (hours) Experimental Results: Attenuated the phosphorylation of Ser108 of the AMPK β1 subunit and increased the levels of cleaved Caspase 8 and PARP, markers of apoptosis. Autophagy was evaluated by analysis of LC3B and p62. |
| Animal Protocol |
Animal/Disease Models: Sixweeks old male BALB/c nude mice (A498 xenograft tumours)[1] Doses: 50 mg/kg Route of Administration: intraperitoneal (ip)injection; once every three days for 37 days Experimental Results: Dramatically suppressed tumour growth. Six-week-old male BALB/c nude mice were used. A498 cells (5 × 106) suspended in 100 μL PBS/Matrigel (1:1) were injected into the hind flank of the mice. The mice were randomly divided 14-d post implantation into two groups of six mice each. Mice were intraperitoneally injected with dimethyl sulfoxide (DMSO) used as the vehicle solution or SBI-0206965 in DMSO (50 mg/kg/d) every 3 d for a total of nine times over a 30-d period. Tumour growth was evaluated every 3 d. Tumour volume was calculated using the formula volume = 1/2 (length × width2). At the end of the experiment, the mice were sacrificed by cervical dislocation and tumours were harvested. The tumour specimens were fixed in 4% paraformaldehyde, paraffin embedded, and sectioned. The tissue sections were analysed by terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase dUTP nick end labelling (TUNEL) assays.[1] |
| References |
[1]. Overexpression of ULK1 Represents a Potential Diagnostic Marker for Clear Cell RenalCarcinoma and the Antitumor Effects of SBI-0206965. EBioMedicine. 2018 Aug;34:85-93. [2]. Small Molecule Inhibition of the Autophagy Kinase ULK1 and Identification of ULK1 Substrates. Mol Cell. 2015 Jul 16;59(2):285-97. |
| Additional Infomation |
Many tumors become addicted to autophagy for survival, suggesting inhibition of autophagy as a potential broadly applicable cancer therapy. ULK1/Atg1 is the only serine/threonine kinase in the core autophagy pathway and thus represents an excellent drug target. Despite recent advances in the understanding of ULK1 activation by nutrient deprivation, how ULK1 promotes autophagy remains poorly understood. Here, we screened degenerate peptide libraries to deduce the optimal ULK1 substrate motif and discovered 15 phosphorylation sites in core autophagy proteins that were verified as in vivo ULK1 targets. We utilized these ULK1 substrates to perform a cell-based screen to identify and characterize a potent ULK1 small molecule inhibitor. The compound SBI-0206965 is a highly selective ULK1 kinase inhibitor in vitro and suppressed ULK1-mediated phosphorylation events in cells, regulating autophagy and cell survival. SBI-0206965 greatly synergized with mechanistic target of rapamycin (mTOR) inhibitors to kill tumor cells, providing a strong rationale for their combined use in the clinic.[2] Background: Uncoordinated 51-like kinase 1 (ULK1) plays a vital role in autophagy. ULK1 dysregulation has recently been found in several human cancers. Methods: mRNA expression levels of ULK1 and clinical information were analysed from The Cancer Genome Atlas data. ULK1 expression levels were verified in 36 paired fresh ccRCC tissue specimens by western blot analysis. Expression of ULK1 was knockdown by shRNA lentivirus. ULK1 activity was inhibited by SBI-0206965. The effect of inhibition of ULK1 was measured by detecting the apoptotic rate, autophagy, and the ratio of ROS and NADPH. The efficacy of SBI-0206965 in vivo was assessed by the murine xenograft model. Findings: ULK1 mRNA expression was significantly upregulated in clear cell renal cell carcinoma (ccRCC) and overexpression of ULK1 correlated with poor outcomes. We found that ULK1 was highly expressed in 66.7% of ccRCC tumours (p < 0·05). Knockdown of ULK1 and selective inhibition of ULK1 by SBI-0206965 induced cell apoptosis in ccRCC cells. We demonstrated that SBI-0206965 triggered apoptosis by preventing autophagy and pentose phosphate pathway (PPP) flux. Furthermore, blocking the kinase activity of ULK1 with SBI-0206965 resulted in a level of anticancer effect in vivo. Interpretation: Taken together, our results suggested that ULK1 was upregulated in ccRCC tumours and may be a potential therapeutic target. Therefore, SBI-0206965 should be further considered as an anti-ccRCC agent.[1] |
Solubility Data
| Solubility (In Vitro) |
|
|||
| Solubility (In Vivo) |
Solubility in Formulation 1: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (5.11 mM) (saturation unknown) in 10% DMSO + 40% PEG300 + 5% Tween80 + 45% Saline (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), clear solution. For example, if 1 mL of working solution is to be prepared, you can add 100 μL of 25.0 mg/mL clear DMSO stock solution to 400 μL PEG300 and mix evenly; then add 50 μL Tween-80 to the above solution and mix evenly; then add 450 μL normal saline to adjust the volume to 1 mL. Preparation of saline: Dissolve 0.9 g of sodium chloride in 100 mL ddH₂ O to obtain a clear solution. Solubility in Formulation 2: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (5.11 mM) (saturation unknown) in 10% DMSO + 90% Corn Oil (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), clear solution. For example, if 1 mL of working solution is to be prepared, you can add 100 μL of 25.0 mg/mL clear DMSO stock solution to 900 μL of corn oil and mix evenly. (Please use freshly prepared in vivo formulations for optimal results.) |
| Preparing Stock Solutions | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.0437 mL | 10.2183 mL | 20.4365 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.4087 mL | 2.0437 mL | 4.0873 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.2044 mL | 1.0218 mL | 2.0437 mL |