SB408124 (SB-408124; SB 408124) is a potent, novel, selective, non-peptide antagonist for OX1 receptor with Ki of 57 nM and 27 nM in both whole cell and membrane, respectively, it exhibits 50-fold selectivity over OX2 receptor. In primary astrocyte cultures from the rat cerebral cortex, pretreatment with SB408124 significantly reduced the orexin A a stimulating effect on basal-induced cAMP production and forskolin.
Physicochemical Properties
| Molecular Formula | C19H18F2N4O | |
| Molecular Weight | 356.37 | |
| Exact Mass | 356.144 | |
| Elemental Analysis | C, 64.04; H, 5.09; F, 10.66; N, 15.72; O, 4.49 | |
| CAS # | 288150-92-5 | |
| Related CAS # | SB-408124 Hydrochloride; 1431697-90-3 | |
| PubChem CID | 4331799 | |
| Appearance | White to off-white solid powder | |
| Density | 1.4±0.1 g/cm3 | |
| Boiling Point | 430.3±45.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Flash Point | 214.0±28.7 °C | |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±1.0 mmHg at 25°C | |
| Index of Refraction | 1.697 | |
| LogP | 4.53 | |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 2 | |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 5 | |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 3 | |
| Heavy Atom Count | 26 | |
| Complexity | 484 | |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 | |
| SMILES | FC1=C([H])C(=C([H])C2C1=NC(C([H])([H])[H])=C([H])C=2N([H])C(N([H])C1C([H])=C([H])C(=C([H])C=1[H])N(C([H])([H])[H])C([H])([H])[H])=O)F |
|
| InChi Key | JTARFZSNUAGHRB-UHFFFAOYSA-N | |
| InChi Code | InChI=1S/C19H18F2N4O/c1-11-8-17(15-9-12(20)10-16(21)18(15)22-11)24-19(26)23-13-4-6-14(7-5-13)25(2)3/h4-10H,1-3H3,(H2,22,23,24,26) | |
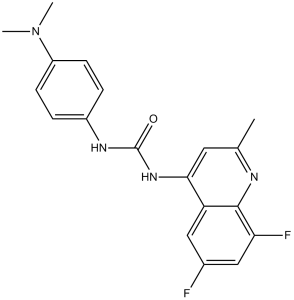
| Chemical Name | 1-(6,8-difluoro-2-methylquinolin-4-yl)-3-[4-(dimethylamino)phenyl]urea | |
| Synonyms |
|
|
| HS Tariff Code | 2934.99.9001 | |
| Storage |
Powder-20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
|
| Shipping Condition | Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs) |
Biological Activity
| Targets | OX1 Receptor ( Ki = 57 nM ); OX Receptor ( Ki = 27 nM ) | ||
| ln Vitro |
|
||
| ln Vivo |
|
||
| Enzyme Assay |
SB-408124 is a non-peptide antagonist that shows 50-fold selectivity over OX2 receptor and has a Ki of 57 nM and 27 nM in whole cell and membrane, respectively, for the OX1 receptor. [3H]SB-674042 whole cell binding assays[1] After overnight culture in 96-well Packard Cultur plates, the medium was discarded and cells were incubated in buffer containing 150 mM NaCl, 20 mM HEPES and 0.5% bovine serum albumin (pH 7.4) for 60 min at 25°C. Saturation studies were carried out by incubating cells with a range of concentrations of [3H]SB-674042 (0.2–24 nM); the total assay volume was 250 μl. Protein content was assayed by lysing cells with 0.1 M NaOH and using the Bradford method (Bradford, 1976) with bovine serum albumin (BSA) as a standard. Association kinetic studies were performed by measuring the specific binding of [3H]SB-674042 (3 nM) at 1–60 min after addition of [3H]SB-674042. For dissociation studies, cells were first incubated with [3H]SB-674042 (3 nM) for 60 min. Specific binding was then measured at 2–120 min after the addition of 3 μM SB-408124. Competition studies were performed by incubating cells with [3H]SB-674042 (3 nM) and a range of concentrations of the test compound. All assays were terminated by washing the cells three times with 250 μl ice-cold phosphate-buffered saline. A volume of 100 μl of Microscint 40 was added to each well and the plate was left at room temperature for 2 h. Cell-associated radioactivity was then measured using a Packard Topcount, with a count time of 2 min well−1. [3H]SB-674042 membrane-based SPA binding assays[1] CHO-K1_OX1 cell membranes (75 μg ml−1) were precoupled by shaking with wheatgerm-agglutinin polyvinyltoluene (WGA-PVT) scintillation proximity assay (SPA) beads (5 mg ml−1) in buffer containing 25 mM HEPES, 2.5 mM MgCl2, 0.5 mM EDTA and 0.025% bacitracin (pH 7.4) at 4°C for 1 h. The bead-membrane suspension was centrifuged at 300 × g and resuspended in the same volume of room temperature assay buffer. A volume of 100 μl of bead-membrane suspension was incubated with [3H]SB-674042 (5 nM) in a total assay volume of 200 μl in a 96-well Packard Optiplate to give a final protein concentration of 7.5 μg well−1. Nonspecific binding was measured as that remaining in the presence of 3 μM SB-408124. Assay plates were shaken for 10 min and then incubated at room temperature for 4 h before being counted on a Packard TopCount scintillation counter (count time 2 min well−1). Saturation studies were carried out by incubating bead-membranes (equivalent to 7.5 μg protein well−1 and 2.5 mg beads ml−1) with a range of concentrations of [3H]SB-674042 (0.1–20 nM). Protein content was assayed using the Bradford method (Bradford, 1976) using bovine serum albumin as a standard. Association kinetic studies were performed by measuring specific binding of [3H]SB-674042 (5 nM) at 1–30 min after addition of bead-membranes (equivalent to 7.5 μg protein well−1 and 2.5 mg beads ml−1). For dissociation studies, bead-membranes were first incubated with [3H]SB-674042 (5 nM) for 30 min. Specific binding was then measured at 2–120 min after the addition of 3 μM SB-408124. Competition studies were performed by incubating bead-membranes (equivalent to 7.5 μg protein well−1 and 2.5 mg beads ml−1) with [3H]SB-674042 (5 nM) and a range of concentrations of the test compound. |
||
| Cell Assay | SB-408124 has a pKi of 7.57 when it comes to binding the hypocretin type 1 receptor (HcrtR1). According to studies on calcium mobilization, SB-408124 functions as a functional antagonist of the OX1 receptor and has an affinity that is roughly 50 times more selective than the OX2 receptor. According to a recent study, the stimulatory action of Orexin A on basal and forskolin-acivated cAMP production was significantly reduced when primary cultures of rat astrocytes were pretreated with SB-401824 prior to Orexin A administration. | ||
| Animal Protocol |
|
||
| References |
[1]. Br J Pharmacol . 2004 Jan;141(2):340-6. [2]. Pharmacol Rep . 2011;63(3):717-23. [3]. Pflugers Arch . 2012 Apr;463(4):531-6. [4]. Diabetes . 2009 Sep;58(9):1998-2005. |
||
| Additional Infomation |
1-(6,8-difluoro-2-methyl-4-quinolinyl)-3-[4-(dimethylamino)phenyl]urea is a member of quinolines and an organohalogen compound. 1. This study characterises the binding of a novel nonpeptide antagonist radioligand, [(3)H]SB-674042 (1-(5-(2-fluoro-phenyl)-2-methyl-thiazol-4-yl)-1-((S)-2-(5-phenyl-(1,3,4)oxadiazol-2-ylmethyl)-pyrrolidin-1-yl)-methanone), to the human orexin-1 (OX(1)) receptor stably expressed in Chinese hamster ovary (CHO) cells in both a whole cell assay and in a cell membrane-based scintillation proximity assay (SPA) format. 2. Specific binding of [(3)H]SB-674042 was saturable in both whole cell and membrane formats. Analyses suggested a single high-affinity site, with K(d) values of 3.76+/-0.45 and 5.03+/-0.31 nm, and corresponding B(max) values of 30.8+/-1.8 and 34.4+/-2.0 pmol mg protein(-1), in whole cell and membrane formats, respectively. Kinetic studies yielded similar K(d) values. 3. Competition studies in whole cells revealed that the native orexin peptides display a low affinity for the OX(1) receptor, with orexin-A displaying a approximately five-fold higher affinity than orexin-B (K(i) values of 318+/-158 and 1516+/-597 nm, respectively). 4. SB-334867, SB-408124 (1-(6,8-difluoro-2-methyl-quinolin-4-yl)-3-(4-dimethylamino-phenyl)-urea) and SB-410220 (1-(5,8-difluoro-quinolin-4-yl)-3-(4-dimethylamino-phenyl)-urea) all displayed high affinity for the OX(1) receptor in both whole cell (K(i) values 99+/-18, 57+/-8.3 and 19+/-4.5 nm, respectively) and membrane (K(i) values 38+/-3.6, 27+/-4.1 and 4.5+/-0.2 nm, respectively) formats. 5. Calcium mobilisation studies showed that SB-334867, SB-408124 and SB-410220 are all functional antagonists of the OX(1) receptor, with potencies in line with their affinities, as measured in the radioligand binding assays, and with approximately 50-fold selectivity over the orexin-2 receptor. 6. These studies indicate that [(3)H]SB-674042 is a specific, high-affinity radioligand for the OX(1) receptor. The availability of this radioligand will be a valuable tool with which to investigate the physiological functions of OX(1) receptors.[1] The effects of orexins, which are also named hypocretins, on cAMP formation were examined in primary cultures of rat astrocytes. Orexin A, an agonist of OX₁ and OX₂ receptors, stimulated cAMP production with an EC₅₀ value of 0.68 μM and potentiated the forskolin-induced increase in the nucleotide synthesis. [Ala¹¹-D-Leu¹⁵]orexin B, an agonist of OX₂ receptors, was inactive. The effects of orexin A were antagonized by SB 408124, a selective blocker of OX₁ receptors, but were not affected by TCS OX2 29, a selective antagonist of OX₃ receptors. We hypothesized that the activation of OX₁ receptors stimulated cAMP synthesis in primary rat astrocyte cultures.[2] |
Solubility Data
| Solubility (In Vitro) |
|
|||
| Solubility (In Vivo) |
Solubility in Formulation 1: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (7.02 mM) (saturation unknown) in 10% DMSO + 90% Corn Oil (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), clear solution. For example, if 1 mL of working solution is to be prepared, you can add 100 μL of 25.0 mg/mL clear DMSO stock solution to 900 μL of corn oil and mix evenly. Solubility in Formulation 2: 30% propylene glycol, 5% Tween 80, 65% D5W: 30mg/mL (Please use freshly prepared in vivo formulations for optimal results.) |
| Preparing Stock Solutions | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.8061 mL | 14.0304 mL | 28.0607 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.5612 mL | 2.8061 mL | 5.6121 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.2806 mL | 1.4030 mL | 2.8061 mL |