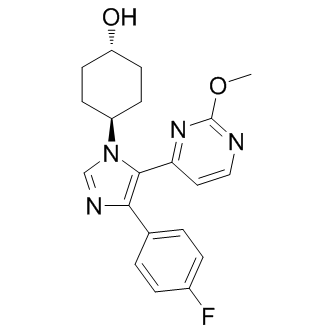
SB239063 (SB-239063) is a novel, highly potent, orally bioactive and selective p38 MAPKα/β inhibitor with potential anti-inflammatory activity. With an IC50 of 44 nM, it inhibits p38 MAPKα/β but exhibits little or no activity against the p38 MAPK γ- and δ-isoforms. SB 239063 is approximately three times more selective than SB 203580 and exhibits > 220 fold selectivity for p38 MAPK over ERK, JNK1, and other kinases. Interleukin-1 and tumor necrosis factor-alpha production in human peripheral blood monocytes stimulated with LPS was inhibited by SB 239063 (IC(50) values: 0.12 and 0.35 microM, respectively). SB 239063 might be helpful in the management of inflammatory conditions such as asthma.
Physicochemical Properties
| Molecular Formula | C20H21FN4O2 | |
| Molecular Weight | 368.4 | |
| Exact Mass | 368.165 | |
| Elemental Analysis | C, 65.20; H, 5.75; F, 5.16; N, 15.21; O, 8.69 | |
| CAS # | 193551-21-2 | |
| Related CAS # |
|
|
| PubChem CID | 5166 | |
| Appearance | White to yellow solid powder | |
| Density | 1.35g/cm3 | |
| Boiling Point | 594.8ºC at 760 mmHg | |
| Flash Point | 313.5ºC | |
| Vapour Pressure | 5.42E-15mmHg at 25°C | |
| Index of Refraction | 1.655 | |
| LogP | 3.63 | |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 1 | |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 6 | |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 4 | |
| Heavy Atom Count | 27 | |
| Complexity | 469 | |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 | |
| SMILES | FC1C([H])=C([H])C(=C([H])C=1[H])C1=C(C2C([H])=C([H])N=C(N=2)OC([H])([H])[H])N(C([H])=N1)C1([H])C([H])([H])C([H])([H])C([H])(C([H])([H])C1([H])[H])O[H] |
|
| InChi Key | ZQUSFAUAYSEREK-UHFFFAOYSA-N | |
| InChi Code | InChI=1S/C20H21FN4O2/c1-27-20-22-11-10-17(24-20)19-18(13-2-4-14(21)5-3-13)23-12-25(19)15-6-8-16(26)9-7-15/h2-5,10-12,15-16,26H,6-9H2,1H3 | |
| Chemical Name | 4-[4-(4-fluorophenyl)-5-(2-methoxypyrimidin-4-yl)imidazol-1-yl]cyclohexan-1-ol | |
| Synonyms |
|
|
| HS Tariff Code | 2934.99.9001 | |
| Storage |
Powder-20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
|
| Shipping Condition | Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs) |
Biological Activity
| Targets | p38α (IC50 = 44 nM); p38β (IC50 = 44 nM) |
| ln Vitro | SB 239063 potently inhibits IL-1 and TNF-α production in LPS-stimulated human peripheral blood monocytes with IC50 of 120 and 350 nM, respectively. [1] In oxygen-glucose deprived hippocampal slice cultures, SB239063 causes cell death after oxygen-glucose deprivation and significantly lowers microglia activation. It also dramatically lowers the levels of the pro-inflammatory cytokine IL-1beta. [2] SB 239063 prevents TGF-β(2) and FGF-2-induced cell migration in human corneal endothelial cells. [4] |
| ln Vivo | SB 239063 (10 mg/kg, p.o.) lessens antigen-induced eosinophilia in the airways of mice and guinea pigs. [1] SB239063 prevents bronchial contraction in C57/BL6 and MKP-1(-/-) mice that have been exposed to air and ozone. [3] |
| Enzyme Assay | SB 239063 is a potent and selective p38 MAPK inhibitor (IC50 = 44 nM for p38α). It displays > 220-fold selectivity over ERK, JNK1 and other kinases; and is ~ 3-fold more selective than SB 203580. |
| Cell Assay |
Apoptosis assay[1] Cell Types: Eosinophils (guinea pig BALs) Tested Concentrations: 0.1, 1, 10 μM Incubation Duration: 29, 47 hrs (hours) Experimental Results: Increased apoptosis of eosinophils in a dose-dependent manner in the presence of 10 pM IL-5 at every time point from 21 hours onwards. Treatment with 20 μM and 100 μM SB239063 significantly decreased the levels of the pro-inflammatory cytokine IL-1β, decreased cell death following oxygen-glucose deprivation, and dramatically decreased microglia activation in hippocampal slice cultures. |
| Animal Protocol |
Animal/Disease Models: Male BALB/c mice (18–20 g) [1] Doses: 12 mg/kg Route of Administration: Oral gavage; 1 h before and 4 h after OA challenge; bis in die for 3 days Experimental Results: dramatically inhibited the resultant antigen-induced airway eosinophilia. Guinea pigs [5] ~30 mg/kg p.o. In guinea pig cultured alveolar macrophages, SB 239063 inhibited LPS-induced IL-6 production (IC(50) of 362 nM). In a bleomycin-induced pulmonary fibrosis model in rats, treatment with SB 239063 (2.4 or 4.8 mg/day via osmotic pump) significantly inhibited bleomycin-induced right ventricular hypertrophy (indicative of secondary pulmonary hypertension) and increases in lung hydroxyproline synthesis (indicative of collagen synthesis and fibrosis). Therefore, SB 239063 demonstrates activity against a range of sequelae commonly associated with COPD and fibrosis, supporting the therapeutic potential of p38 MAPK inhibitors such as SB 239063 in chronic airway disease [5]. |
| References |
[1]. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2000 Apr;293(1):281-8. [2]. Eur J Pharmacol. 2008 Sep 11;592(1-3):55-61. [3]. Eur Respir J. 2011 Apr;37(4):933-42. [4]. Exp Eye Res. 2013 Mar:108:23-32. [5]. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 2000 Nov;279(5):L895-902. |
| Additional Infomation | SB-239063 is a member of the class of imidazoles carrying 4-hydroxycyclohexyl, 4-fluorophenyl and 2-methoxypyrimidin-4-yl substituents at positions 1, 4 and 5 respectively. It has a role as an EC 2.7.11.24 (mitogen-activated protein kinase) inhibitor. It is a member of cyclohexanols, a member of imidazoles, a member of pyrimidines, an aromatic ether, a member of monofluorobenzenes and a secondary alcohol. |
Solubility Data
| Solubility (In Vitro) |
|
|||
| Solubility (In Vivo) |
Solubility in Formulation 1: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (6.79 mM) (saturation unknown) in 10% DMSO + 40% PEG300 + 5% Tween80 + 45% Saline (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), clear solution. For example, if 1 mL of working solution is to be prepared, you can add 100 μL of 25.0 mg/mL clear DMSO stock solution to 400 μL PEG300 and mix evenly; then add 50 μL Tween-80 to the above solution and mix evenly; then add 450 μL normal saline to adjust the volume to 1 mL. Preparation of saline: Dissolve 0.9 g of sodium chloride in 100 mL ddH₂ O to obtain a clear solution. Solubility in Formulation 2: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (6.79 mM) (saturation unknown) in 10% DMSO + 90% Corn Oil (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), clear solution. For example, if 1 mL of working solution is to be prepared, you can add 100 μL of 25.0 mg/mL clear DMSO stock solution to 900 μL of corn oil and mix evenly. Solubility in Formulation 3: 5% DMSO+30% PEG 300+ddH2O: 4mg/mL (Please use freshly prepared in vivo formulations for optimal results.) |
| Preparing Stock Solutions | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.7144 mL | 13.5722 mL | 27.1444 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.5429 mL | 2.7144 mL | 5.4289 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.2714 mL | 1.3572 mL | 2.7144 mL |