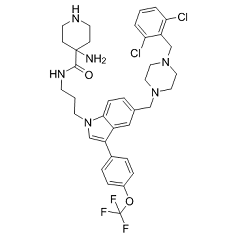
Ras-IN-3144 is a novel and potent pan-RAS inhibitor which disrupts the interaction of Ras proteins and their effectors, also inhibits RAS signaling pathways in cancer cells and prevents the growth of RAS mutant mouse cancer xenografts.
Physicochemical Properties
| Molecular Formula | C36H41CL2F3N6O2 |
| Molecular Weight | 717.650956869125 |
| Exact Mass | 716.262 |
| Elemental Analysis | C, 60.25; H, 5.76; Cl, 9.88; F, 7.94; N, 11.71; O, 4.46 |
| CAS # | 1835283-94-7 |
| Related CAS # | 1835283-94-7 |
| PubChem CID | 102004330 |
| Appearance | White to yellow solid powder |
| Density | 1.4±0.1 g/cm3 |
| Boiling Point | 809.7±65.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Flash Point | 443.5±34.3 °C |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±2.9 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.631 |
| LogP | 5.28 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 3 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 9 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 11 |
| Heavy Atom Count | 49 |
| Complexity | 1040 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| SMILES | O=C(C1(N)CCNCC1)NCCCN2C3=CC=C(CN4CCN(CC5=C(Cl)C=CC=C5Cl)CC4)C=C3C(C6=CC=C(OC(F)(F)F)C=C6)=C2 |
| InChi Key | GMDFJPPJWWJNKF-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| InChi Code | InChI=1S/C36H41Cl2F3N6O2/c37-31-3-1-4-32(38)30(31)23-46-19-17-45(18-20-46)22-25-5-10-33-28(21-25)29(26-6-8-27(9-7-26)49-36(39,40)41)24-47(33)16-2-13-44-34(48)35(42)11-14-43-15-12-35/h1,3-10,21,24,43H,2,11-20,22-23,42H2,(H,44,48) |
| Chemical Name | 4-amino-N-[3-[5-[[4-[(2,6-dichlorophenyl)methyl]piperazin-1-yl]methyl]-3-[4-(trifluoromethoxy)phenyl]indol-1-yl]propyl]piperidine-4-carboxamide |
| Synonyms | Ras IN-3144; Ras-IN-3144; Ras-IN 3144; RasIN3144; pan-RAS inhibitor-3144 |
| HS Tariff Code | 2934.99.9001 |
| Storage |
Powder-20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
| Shipping Condition | Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs) |
Biological Activity
| Targets | KRas G12D-GppNHp (Kd <20 μM) |
| ln Vitro | KRasG12D-GppNHp is bound by Pan-RAS-IN-1 with less than 20 μM of affinity. When Pan-RAS-IN-1 attaches to Ras protein, it becomes deadly to cells whose expression of Ras protein is partially reliant on them. Dependency on mutant isoforms throughout a concentration range of five times is correlated with the effectiveness of IN-1. Pan-RAS-IN-1 is cytostatic at certain concentrations, which may be related to pan-RAS inhibition. In primary T-cell acute leukemia (T-ALL) cells, RAS-IN-1 was assessed. After 5 μM treatment, it was found that mutant, selectively deadly NRAS cells only remained 20%–40% viable [1]. |
| ln Vivo | Tumor growth occurred after 15 days of pan-RAS-IN-1 therapy. Transcripts treated with pan-RAS-IN-1 showed lower tumor pERK levels than transcripts treated with vehicle. It was also possible to see increased antagonistic caspase-3 regulation, indicating that pan-RAS-IN-1 can activate caspase in this paradigm [1]. |
| Cell Assay | Trypsinized, counted, and 1,000 cells/well seeded into 384-well plates are the procedures used for 384-well cancer cell viability assays. After 16 hours, 384-well polypropylene plates with an 8- or 16-point dilution series are used to array pan-RAS-IN-1 (from 10 mM stocks in DMSO). The assay plates are filled with compound solutions at a 1:5 dilution. A 10% final concentration of Alamar blue is reached after 48 hours by adding a 50% solution. Fluorescence intensity at 535 and 590 nm is measured after 6 hours of incubation[1]. |
| Animal Protocol | Mice: Pan-RAS-IN-1 orally at 180 mg/kg (12 mg/mL, 10% DMSO, pH 4), orally administered vehicle, or administered in combination with intraperitoneal and intravenous injections at 30 mg/kg (4 mg/mL, 5% DMSO in HBSS at pH 4). Ten oral doses of pan-RAS-IN-1 or vehicle, or six intraperitoneal injections and four intravenous injections, are administered to the mice over a period of 14 days. Every two days, a tumor's size is computed using an electronic caliper[1]. |
| References |
[1]. Multivalent Small-Molecule Pan-RAS Inhibitors. Cell. 2017 Feb 23;168(5):878-889.e29. |
Solubility Data
| Solubility (In Vitro) |
DMSO: ~6 mg/mL (~8.4 mM) Ethanol: ~6 mg/mL (~8.4 mM) |
| Solubility (In Vivo) |
Solubility in Formulation 1: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (3.48 mM) (saturation unknown) in 10% DMSO + 40% PEG300 + 5% Tween80 + 45% Saline (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), clear solution. For example, if 1 mL of working solution is to be prepared, you can add 100 μL of 25.0 mg/mL clear DMSO stock solution to 400 μL PEG300 and mix evenly; then add 50 μL Tween-80 to the above solution and mix evenly; then add 450 μL normal saline to adjust the volume to 1 mL. Preparation of saline: Dissolve 0.9 g of sodium chloride in 100 mL ddH₂ O to obtain a clear solution. Solubility in Formulation 2: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (3.48 mM) (saturation unknown) in 10% DMSO + 90% (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline) (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), clear solution. For example, if 1 mL of working solution is to be prepared, you can add 100 μL of 25.0 mg/mL clear DMSO stock solution to 900 μL of 20% SBE-β-CD physiological saline solution and mix evenly. Preparation of 20% SBE-β-CD in Saline (4°C,1 week): Dissolve 2 g SBE-β-CD in 10 mL saline to obtain a clear solution. Solubility in Formulation 3: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (3.48 mM) (saturation unknown) in 10% DMSO + 90% Corn Oil (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), clear solution. For example, if 1 mL of working solution is to be prepared, you can add 100 μL of 25.0 mg/mL clear DMSO stock solution to 900 μL of corn oil and mix evenly. (Please use freshly prepared in vivo formulations for optimal results.) |
| Preparing Stock Solutions | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 1.3934 mL | 6.9672 mL | 13.9344 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.2787 mL | 1.3934 mL | 2.7869 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.1393 mL | 0.6967 mL | 1.3934 mL |