Physicochemical Properties
| Molecular Formula | C16H16CL2N4O2S |
| Molecular Weight | 399.29 |
| Exact Mass | 398.037 |
| CAS # | 1782109-09-4 |
| Related CAS # | RKI-1447;1342278-01-6 |
| PubChem CID | 90489001 |
| Appearance | Off-white to light yellow solid powder |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 5 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 5 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 4 |
| Heavy Atom Count | 25 |
| Complexity | 392 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| InChi Key | GBXLRAPHQIRDNS-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| InChi Code | InChI=1S/C16H14N4O2S.2ClH/c21-13-3-1-2-11(8-13)9-18-15(22)20-16-19-14(10-23-16)12-4-6-17-7-5-12;;/h1-8,10,21H,9H2,(H2,18,19,20,22);2*1H |
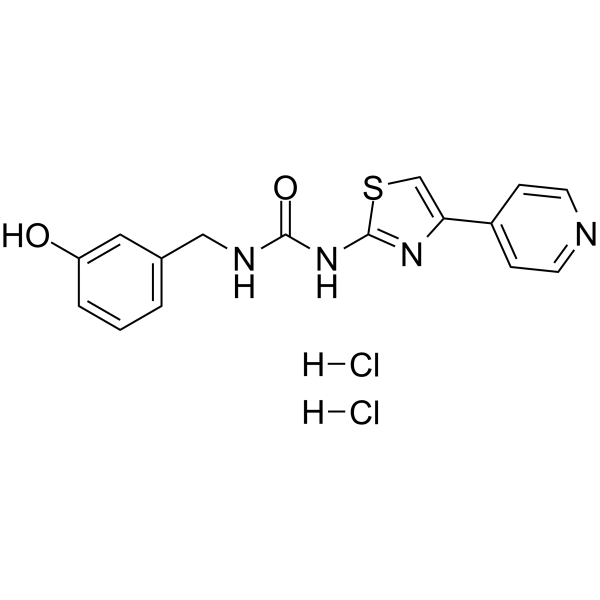
| Chemical Name | 1-[(3-hydroxyphenyl)methyl]-3-(4-pyridin-4-yl-1,3-thiazol-2-yl)urea;dihydrochloride |
| HS Tariff Code | 2934.99.9001 |
| Storage |
Powder-20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month Note: Please store this product in a sealed and protected environment (e.g. under nitrogen), avoid exposure to moisture and light. |
| Shipping Condition | Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs) |
Biological Activity
| Targets | ROCK1 14.5 nM (IC50) ROCK2 6.2 nM (IC50) Apoptosis |
| ln Vitro | In human cancer cells, RKI 1447 inhibits the phosphorylation of the ROCK substrates MLC-2 and MYPT-1, but at doses as high as 10 μM, it had no influence on the phosphorylation levels of AKT, MEK, and S6 kinase[1]. (0.003-10 μM) is effective in preventing human cancer cells' phosphorylation of the ROCK substrates MLC-2 and MYPT-1[1]. Effective anticancer efficacy against colorectal carcinoma (CRC) is demonstrated by RKI 1447. HCT-8 and HCT-116 cell growth is significantly suppressed by RKI 1447 (10-320 μM; 24 hours)[2]. A dose-dependent manner of inducing apoptosis is observed with RKI 1447 (20-80 μM; 24 hours)[2]. |
| ln Vivo | The growth of breast tumors is inhibited in vivo by RKI 1447 (200 mg/kg; intraperitoneal; daily for 14 days)[1]. On CRC in vivo, RKI 1447 (100 mg/kg; ip; once every 3 days; for 14 days) exhibits anticancer efficacy. The mice are not physiologically harmed by RKI 1447[2]. |
| Cell Assay |
Cell Viability Assay[2] Cell Types: CRC cell lines HCT-8 and HCT-116 cells Tested Concentrations: 0, 10, 20, 40, 80, 160, 320 μM Incubation Duration: 24 hrs (hours) Experimental Results: HCT-8 and HCT-116 viability was drastically diminished in a dose-dependent manner. Apoptosis Analysis[2] Cell Types: CRC cell lines HCT-8 and HCT-116 cells Tested Concentrations: 0, 20, 40, 80 μM Incubation Duration: 24 hrs (hours) Experimental Results: Treatment promoted apoptosis. Western Blot Analysis[1] Cell Types: MDA-MB-231 human breast cancer cells Tested Concentrations: 0.003, 0.01, 0.03, 0.1, 0.3, 1, 3,10 μM Incubation Duration: Experimental Results: diminished the levels of P-MLC-2, but not total MLC-2, in a concentration-dependent manner with significant effects starting at 100 nM. |
| Animal Protocol |
Animal/Disease Models: MMTV/neu transgenic mice [FVB/N-Tg (MMTVneu) 202 Mul/J][1] Doses: 200 mg/kg Route of Administration: Treated ip daily for 14 days Experimental Results: Tumors from mice treated with vehicle increased in size with an average percent change in tumor volume of 68.3%. In contrast, tumors from mice treated with the RKI-1447 increased in size with an average percent change in tumor volume of only 8.8%. Thus, RKI-1447 inhibited mammary tumor growth by 87%. Animal/Disease Models: 5weeks old Male BALB/C nude mice[2] Doses: 100 mg/kg Route of Administration: intraperitoneally (ip) injected; once every 3 days; for 14 days Experimental Results: Efficiently blocked CRC tumor growth in vivo. |
| References |
[1]. RKI-1447 Is a Potent Inhibitor of the Rho-associated ROCK Kinases With Anti-Invasive and Antitumor Activities in Breast Cancer. Cancer Res. 2012 Oct 1;72(19):5025-34. [2]. RKI-1447 Suppresses Colorectal Carcinoma Cell Growth via Disrupting Cellular Bioenergetics and Mitochondrial Dynamics. J Cell Physiol. 2020 Jan;235(1):254-266. |
Solubility Data
| Solubility (In Vitro) |
DMSO : 50 mg/mL (125.22 mM) H2O : < 0.1 mg/mL |
| Solubility (In Vivo) |
Solubility in Formulation 1: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (6.26 mM) (saturation unknown) in 10% DMSO + 40% PEG300 + 5% Tween80 + 45% Saline (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), clear solution. For example, if 1 mL of working solution is to be prepared, you can add 100 μL of 25.0 mg/mL clear DMSO stock solution to 400 μL PEG300 and mix evenly; then add 50 μL Tween-80 to the above solution and mix evenly; then add 450 μL normal saline to adjust the volume to 1 mL. Preparation of saline: Dissolve 0.9 g of sodium chloride in 100 mL ddH₂ O to obtain a clear solution. Solubility in Formulation 2: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (6.26 mM) (saturation unknown) in 10% DMSO + 90% (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline) (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), clear solution. For example, if 1 mL of working solution is to be prepared, you can add 100 μL of 25.0 mg/mL clear DMSO stock solution to 900 μL of 20% SBE-β-CD physiological saline solution and mix evenly. Preparation of 20% SBE-β-CD in Saline (4°C,1 week): Dissolve 2 g SBE-β-CD in 10 mL saline to obtain a clear solution. Solubility in Formulation 3: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (6.26 mM) (saturation unknown) in 10% DMSO + 90% Corn Oil (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), clear solution. For example, if 1 mL of working solution is to be prepared, you can add 100 μL of 25.0 mg/mL clear DMSO stock solution to 900 μL of corn oil and mix evenly. (Please use freshly prepared in vivo formulations for optimal results.) |
| Preparing Stock Solutions | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.5044 mL | 12.5222 mL | 25.0445 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.5009 mL | 2.5044 mL | 5.0089 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.2504 mL | 1.2522 mL | 2.5044 mL |