Physicochemical Properties
| Molecular Formula | C29H33FN8O |
| Molecular Weight | 528.623728513718 |
| Exact Mass | 528.276 |
| CAS # | 1038620-68-6 |
| PubChem CID | 24762166 |
| Appearance | White to off-white solid powder |
| LogP | 4.7 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 3 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 8 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 6 |
| Heavy Atom Count | 39 |
| Complexity | 798 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| InChi Key | KRCOMOOXOZSNAJ-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| InChi Code | InChI=1S/C29H33FN8O/c30-20-5-4-6-24(17-20)38-18-32-25-26(35-29(36-27(25)38)34-23-13-9-21(31)10-14-23)33-22-11-7-19(8-12-22)28(39)37-15-2-1-3-16-37/h4-8,11-12,17-18,21,23H,1-3,9-10,13-16,31H2,(H2,33,34,35,36) |
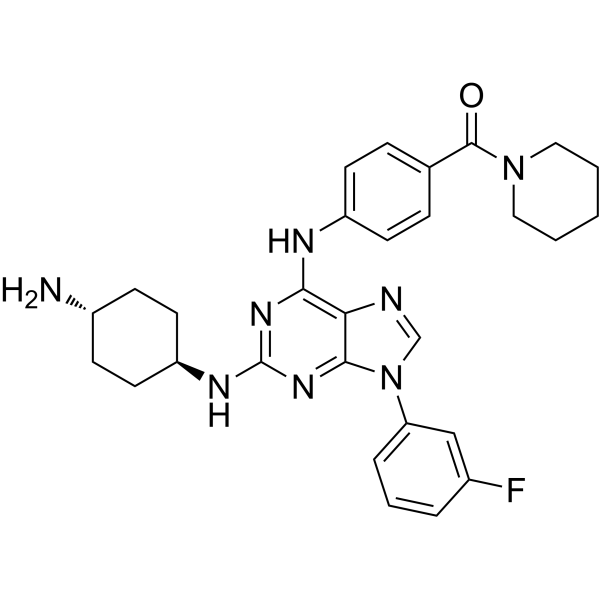
| Chemical Name | [4-[[2-[(4-aminocyclohexyl)amino]-9-(3-fluorophenyl)purin-6-yl]amino]phenyl]-piperidin-1-ylmethanone |
| HS Tariff Code | 2934.99.9001 |
| Storage |
Powder-20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
| Shipping Condition | Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs) |
Biological Activity
| Targets | Plasmodium Toxoplasma |
| ln Vitro | Purfalcamine exhibits minimal efficacy against the calcium-dependent protein kinase 3 (TgCDPK3) of Toxoplasma gondii [1]. For the first 32 hours, purfalcamine (225, 450 nM) has no effect on the parasitemia. The parasite level stays constant for almost 40 hours before starting to decline[1]. For P. falciparum strains (3D7, Dd2, FCB, HB3, and W2), purfalcamine inhibits proliferation with EC50s of 171-259 nM, indicating efficacy against drug-resistant parasites[1]. Purfalcamine exhibits a therapeutic window extending from 23-fold to 36-fold (EC50s for CHO=12.33 μM, HEp2=7.235 μM, HeLa=7.029 μM, and Huh7=5.476 μM), because the EC50 value for P. falciparum (3D7) is 230 nM[1]. |
| ln Vivo | In treated mice, purfalcamine (10 mg/kg; oral gavage; BID; for 6 days) shows a delay in the development of parasitemia[1]. The half-life of purfalcamine (20 mg/kg; oral gavage) is 3.1 hours, and its Cmax is 2.6 μM[1]. |
| Animal Protocol |
Animal/Disease Models: Male balb/c (Bagg ALBino) mouse:, 7 weeks of age with the malaria parasite[1] Doses: 10 mg /kg Route of Administration: po (oral gavage); BID; for 6 days Experimental Results: Demonstrated a delay in the onset of parasitemia in treated mice when compared with control mice. Animal/Disease Models: Five- to sixweeks old male balb/c (Bagg ALBino) mouse: (22- 25 g)[1] Doses: 20 mg/kg (pharmacokinetic/PK Analysis) Route of Administration: Orally gavage Experimental Results: demonstrated a maximum plasma exposure (Cmax) of 2.6 μM with a half-life of 3.1 hrs (hours). |
| References |
[1]. Nobutaka Kato, et al. Gene expression signatures and small-molecule compounds link a protein kinase to Plasmodium falciparum motility. Nat Chem Biol. 2008 Jun;4(6):347-56. [2]. Rajshekhar Y Gaji, et al. Expression of the essential Kinase PfCDPK1 from Plasmodium falciparum in Toxoplasma gondii facilitates the discovery of novel antimalarial drugs. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2014 May;58(5):2598-607. |
Solubility Data
| Solubility (In Vitro) | DMSO : 12.5 mg/mL (23.65 mM) |
| Solubility (In Vivo) |
Solubility in Formulation 1: ≥ 1.25 mg/mL (2.36 mM) (saturation unknown) in 10% DMSO + 40% PEG300 + 5% Tween80 + 45% Saline (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), clear solution. For example, if 1 mL of working solution is to be prepared, you can add 100 μL of 12.5 mg/mL clear DMSO stock solution to 400 μL PEG300 and mix evenly; then add 50 μL Tween-80 to the above solution and mix evenly; then add 450 μL normal saline to adjust the volume to 1 mL. Preparation of saline: Dissolve 0.9 g of sodium chloride in 100 mL ddH₂ O to obtain a clear solution. Solubility in Formulation 2: ≥ 1.25 mg/mL (2.36 mM) (saturation unknown) in 10% DMSO + 90% (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline) (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), clear solution. For example, if 1 mL of working solution is to be prepared, you can add 100 μL of 12.5 mg/mL clear DMSO stock solution to 900 μL of 20% SBE-β-CD physiological saline solution and mix evenly. Preparation of 20% SBE-β-CD in Saline (4°C,1 week): Dissolve 2 g SBE-β-CD in 10 mL saline to obtain a clear solution. Solubility in Formulation 3: ≥ 1.25 mg/mL (2.36 mM) (saturation unknown) in 10% DMSO + 90% Corn Oil (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), clear solution. For example, if 1 mL of working solution is to be prepared, you can add 100 μL of 12.5 mg/mL clear DMSO stock solution to 900 μL of corn oil and mix evenly. (Please use freshly prepared in vivo formulations for optimal results.) |
| Preparing Stock Solutions | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 1.8917 mL | 9.4586 mL | 18.9172 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.3783 mL | 1.8917 mL | 3.7834 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.1892 mL | 0.9459 mL | 1.8917 mL |