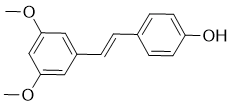
Pterostilbene is a naturally occuring stilbenoid isolated from blueberries and Pterocarpus marsupium with anti-oxidant, anti-inflammatory, anti-carcinogenic, anti-diabetic and anti-obesity activities. It primarily exists in blueberries, grapevines and heartwood of red sandalwood. Pterostilbene also has chemopreventive, antiinflammatory, antidiabetic, antidyslipidemic, antiatherosclerotic and neuroprotective effects. Pterostilbene blocks ROS production, also exhibits inhibitory activity against various free radicals such as DPPH, ABTS, hydroxyl, superoxide and hydrogen peroxide.
Physicochemical Properties
| Molecular Formula | C16H16O3 |
| Molecular Weight | 256.2964 |
| Exact Mass | 256.109 |
| CAS # | 537-42-8 |
| PubChem CID | 5281727 |
| Appearance | White to off-white solid powder |
| Density | 1.2±0.1 g/cm3 |
| Boiling Point | 420.5±35.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 89-92ºC |
| Flash Point | 208.1±25.9 °C |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±1.0 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.640 |
| LogP | 4.13 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 1 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 3 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 4 |
| Heavy Atom Count | 19 |
| Complexity | 270 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| SMILES | COC1=CC(=CC(=C1)/C=C/C2=CC=C(C=C2)O)OC |
| InChi Key | VLEUZFDZJKSGMX-ONEGZZNKSA-N |
| InChi Code | InChI=1S/C16H16O3/c1-18-15-9-13(10-16(11-15)19-2)4-3-12-5-7-14(17)8-6-12/h3-11,17H,1-2H3/b4-3+ |
| Chemical Name | 4-[(E)-2-(3,5-Dimethoxyphenyl)ethenyl]phenol |
| Synonyms | Pterostilbene PS |
| HS Tariff Code | 2934.99.9001 |
| Storage |
Powder-20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
| Shipping Condition | Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs) |
Biological Activity
| Targets | Natural stilbenoid; anti-oxidant, anti-inflammatory, anti-carcinogenic, anti-diabetic, anti-obesity |
| ln Vitro | Pterostilbene exhibits inhibitory action on HeLa cell growth at concentrations of 0, 5, 25, 50, 100, 200, and 400 μM. At 24 and 48 hours, the IC50 values are 101.2 μM and 65.9 μM, respectively. HeLa cells can undergo apoptosis when exposed to ipterostilbene at concentrations of 0, 25, 100, and 200 μM [2]. High antioxidant activity against DPPH, ABTS, hydroxyl, superoxide, and hydrogen peroxide is exhibited by pterostilbene (0.05, 0.1, 0.15, and 0.2 mM) in a dose-dependent manner. When proteins are damaged by TBHP and As-Fe2+, pterostilbene can mitigate the effects by reducing lipid peroxides and hydroperoxides, as well as restoring protein sulfhydryl groups. Additionally, in pBR322, pterostilbene prevents single-strand breaks [4]. |
| ln Vivo | In animal models of inflammation, pterostilbene (30 mg/kg per day, orally for 21 days) can inhibit the production of reactive oxygen species [3]. |
| ADME/Pharmacokinetics |
Metabolism / Metabolites Pterostilbene has known human metabolites that include (2S,3S,4S,5R)-6-[4-[(E)-2-(3,5-dimethoxyphenyl)ethenyl]phenoxy]-3,4,5-trihydroxyoxane-2-carboxylic acid. |
| References |
[1]. A review of pterostilbene antioxidant activity and disease modification. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2013;2013:575482. [2]. Pterostilbene (3',5'-dimethoxy-resveratrol) exerts potent antitumor effects in HeLa human cervical cancer cells via disruption of mitochondrial membrane potential, apoptosis induction and targeting m-TOR/PI3K/Akt signalling pathway. J BUON. 2018 Sep-Oct;23(5):1384-1389. [3]. The effects of pterostilbene on neutrophil activity in experimental model of arthritis. Biomed Res Int. 2013;2013:106041. [4]. Protective effect of Pterostilbene against free radical mediated oxidative damage. BMC Complement Altern Med. 2013 Sep 26;13:238. |
| Additional Infomation |
Pterostilbene is a stilbenol that consists of trans-stilbene bearing a hydroxy group at position 4 as well as two methoxy substituents at positions 3' and 5'. It has a role as an antioxidant, an antineoplastic agent, a neurotransmitter, a plant metabolite, an apoptosis inducer, a neuroprotective agent, an anti-inflammatory agent, a radical scavenger and a hypoglycemic agent. It is a stilbenol, a member of methoxybenzenes and a diether. It derives from a hydride of a trans-stilbene. Pterostilbene has been reported in Vitis riparia, Vitis vulpina, and other organisms with data available. Pterostilbene is a naturally-derived stilbenoid structurally related to resveratrol, with potential antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, pro-apoptotic, antineoplastic and cytoprotective activities. Upon administration, pterostilbene exerts its anti-oxidant activity by scavenging reactive oxygen species (ROS), thereby preventing oxidative stress and ROS-induced cell damage. It may also activate the nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 (Nrf2)-mediated pathway and increase the expression of various antioxidant enzymes, such as superoxide dismutase (SOD). In addition, pterostilbene is able to inhibit inflammation by reducing the expression of various inflammatory mediators, such as interleukin (IL) 1beta, tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-a), inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS), cyclooxygenases (COX), and nuclear factor kappa B (NF-kB). It also inhibits or prevents the activation of many signaling pathways involved in carcinogenesis, and increases expression of various tumor suppressor genes while decreasing expression of certain tumor promoting genes. It also directly induces apoptosis in tumor cells. See also: Pterocarpus marsupium wood (part of). |
Solubility Data
| Solubility (In Vitro) | DMSO : ~110 mg/mL (~429.18 mM) |
| Solubility (In Vivo) |
Solubility in Formulation 1: ≥ 3.93 mg/mL (15.33 mM) (saturation unknown) in 10% DMSO + 40% PEG300 + 5% Tween80 + 45% Saline (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), clear solution. For example, if 1 mL of working solution is to be prepared, you can add 100 μL of 39.3 mg/mL clear DMSO stock solution to 400 μL PEG300 and mix evenly; then add 50 μL Tween-80 to the above solution and mix evenly; then add 450 μL normal saline to adjust the volume to 1 mL. Preparation of saline: Dissolve 0.9 g of sodium chloride in 100 mL ddH₂ O to obtain a clear solution. Solubility in Formulation 2: ≥ 2.75 mg/mL (10.73 mM) (saturation unknown) in 10% DMSO + 90% (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline) (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), clear solution. For example, if 1 mL of working solution is to be prepared, you can add 100 μL of 27.5 mg/mL clear DMSO stock solution to 900 μL of 20% SBE-β-CD physiological saline solution and mix evenly. Preparation of 20% SBE-β-CD in Saline (4°C,1 week): Dissolve 2 g SBE-β-CD in 10 mL saline to obtain a clear solution. Solubility in Formulation 3: ≥ 2.75 mg/mL (10.73 mM) (saturation unknown) in 10% DMSO + 90% Corn Oil (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), clear solution. For example, if 1 mL of working solution is to be prepared, you can add 100 μL of 27.5 mg/mL clear DMSO stock solution to 900 μL of corn oil and mix evenly. (Please use freshly prepared in vivo formulations for optimal results.) |
| Preparing Stock Solutions | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 3.9017 mL | 19.5084 mL | 39.0168 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.7803 mL | 3.9017 mL | 7.8034 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.3902 mL | 1.9508 mL | 3.9017 mL |