Physicochemical Properties
| Molecular Formula | C19H26O4S |
| Molecular Weight | 350.47234 |
| Exact Mass | 350.155 |
| CAS # | 2312-35-8 |
| PubChem CID | 4936 |
| Appearance |
Brownish-yellow, oily viscous liquid (tech.) Light to dark brown viscous liquid |
| Density | 1.2±0.1 g/cm3 |
| Boiling Point | 450.7±45.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Flash Point | 226.4±28.7 °C |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±1.1 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.561 |
| LogP | 4.81 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 0 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 5 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 7 |
| Heavy Atom Count | 24 |
| Complexity | 454 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
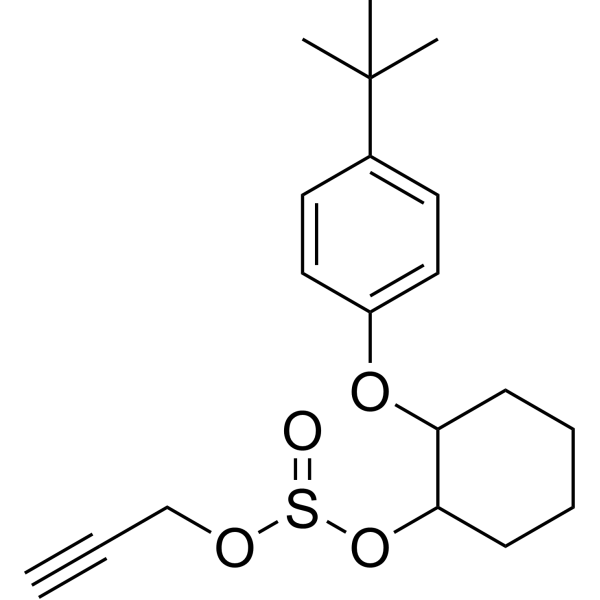
| SMILES | C#CCOS(=O)OC1CCCCC1OC2=CC=C(C=C2)C(C)(C)C |
| InChi Key | ZYHMJXZULPZUED-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| InChi Code | InChI=1S/C19H26O4S/c1-5-14-21-24(20)23-18-9-7-6-8-17(18)22-16-12-10-15(11-13-16)19(2,3)4/h1,10-13,17-18H,6-9,14H2,2-4H3 |
| Chemical Name | [2-(4-tert-butylphenoxy)cyclohexyl] prop-2-ynyl sulfite |
| HS Tariff Code | 2934.99.9001 |
| Storage |
Powder-20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
| Shipping Condition | Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs) |
Biological Activity
| Targets | Mite |
| ADME/Pharmacokinetics |
Metabolism / Metabolites When 50-mg samples of bulb mites, Rhizoglyphus echinopus (Fumouze and Robin), were placed for 1 hr in glass vials coated with 0.53 mug of radiocarbon-labeled propargite, about 12% (1.27 ug/g) of the acaricide was transferred to the mites. Mites treated with propargite were kept in holding vials and the extent of metabolism was evaluated after 6, 12, 24, and 48 hr. Internal levels of radiocarbon ranged from 14.8 to 17.4% of the dose and were divided about equally between the mite extrat and mite residue fractions. Levels of propargite in the internal extract decreased from 5.9 at 6 hr to 2.5 at 48 hr when expressed as percentage of total recovered radiocarbon and from 61.5 at 6 hr to 29.8 at 48 hr when expressed as relative percentage of radiocarbon in the internal extract. Thus, propargite was degraded slowly by the mites. The metabolites 4-tert-butylphenol and 2-(4-tert-butylphenoxy) cyclohexanol (glycol ether) were present at low levels (< 0.5%). Propargite was degraded in vitro by bulb mite homogenates with the 12,000 pernatant being about four times more active than the corresponding pellet. Exogenous NADPH and glutathione greatly enhanced propargite degradation by the supernatant fraction. However, not all of the degradation in the presence of glutathione was enzymatic; about 15% of the propargite was converted to 4-tert-butylphenol when the acaricide was incubated with cofactor in buffer in the absence of the mite supernatant. In vitro propargite degradation products consisted mainly of unindentified polar metabolites, but low levels of 4-tert-butylphenol and glyol ether also were present. |
| Toxicity/Toxicokinetics |
Toxicity Data LC50 (rat) = 890 mg/m3 Non-Human Toxicity Values LD50 Rabbit acute dermal >2000 mg/kg LD50 Rat (female) acute oral 2947 mg/kg LD50 Rat (male) acute oral 2639 mg/kg LD50 Rat (male and female) acute oral 2800 mg/kg For more Non-Human Toxicity Values (Complete) data for PROPARGITE (8 total), please visit the HSDB record page. |
| References | [1]. Ting Zhou, et al. A hPSC-based Platform to Discover Gene-Environment Interactions That Impact Human β-cell and Dopamine Neuron Survival. Nat Commun. 2018 Nov 16;9(1):4815. |
| Additional Infomation |
Propargite can cause cancer and developmental toxicity according to The Environmental Protection Agency (EPA). Propargite is a dark colored liquid. It is a wettable powder or water emulsifiable liquid. It can cause illness by inhalation, skin absorption and/or ingestion. The primary hazard is the threat to the environment. Immediate steps should be taken to limit its spread to the environment. Since it is a liquid it can easily penetrate the soil and contaminate groundwater and nearby streams. It is used as a pesticide. Practically insoluble in water (10.5 mg/L). Used as an acaricide. Propargite is a sulfite ester and a terminal acetylenic compound. It has a role as a sulfite ester acaricide. Propargite (IUPAC name 2-(4-tert-butylphenoxy)cyclohexyl prop-2-yne-1-sulfonate, trade names Omite and Comite) is a pesticide used to kill mites (an acaricide). Symptoms of exposure and poisoning to it are eye and skin irritation, as well as sensitization. It is highly toxic to amphibians, fish, and zooplankton, as well as having potential carcinogenity. |
Solubility Data
| Solubility (In Vitro) | May dissolve in DMSO (in most cases), if not, try other solvents such as H2O, Ethanol, or DMF with a minute amount of products to avoid loss of samples |
| Solubility (In Vivo) |
Note: Listed below are some common formulations that may be used to formulate products with low water solubility (e.g. < 1 mg/mL), you may test these formulations using a minute amount of products to avoid loss of samples. Injection Formulations (e.g. IP/IV/IM/SC) Injection Formulation 1: DMSO : Tween 80: Saline = 10 : 5 : 85 (i.e. 100 μL DMSO stock solution → 50 μL Tween 80 → 850 μL Saline) *Preparation of saline: Dissolve 0.9 g of sodium chloride in 100 mL ddH ₂ O to obtain a clear solution. Injection Formulation 2: DMSO : PEG300 :Tween 80 : Saline = 10 : 40 : 5 : 45 (i.e. 100 μL DMSO → 400 μLPEG300 → 50 μL Tween 80 → 450 μL Saline) Injection Formulation 3: DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90 (i.e. 100 μL DMSO → 900 μL Corn oil) Example: Take the Injection Formulation 3 (DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90) as an example, if 1 mL of 2.5 mg/mL working solution is to be prepared, you can take 100 μL 25 mg/mL DMSO stock solution and add to 900 μL corn oil, mix well to obtain a clear or suspension solution (2.5 mg/mL, ready for use in animals). Injection Formulation 4: DMSO : 20% SBE-β-CD in saline = 10 : 90 [i.e. 100 μL DMSO → 900 μL (20% SBE-β-CD in saline)] *Preparation of 20% SBE-β-CD in Saline (4°C,1 week): Dissolve 2 g SBE-β-CD in 10 mL saline to obtain a clear solution. Injection Formulation 5: 2-Hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin : Saline = 50 : 50 (i.e. 500 μL 2-Hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin → 500 μL Saline) Injection Formulation 6: DMSO : PEG300 : castor oil : Saline = 5 : 10 : 20 : 65 (i.e. 50 μL DMSO → 100 μLPEG300 → 200 μL castor oil → 650 μL Saline) Injection Formulation 7: Ethanol : Cremophor : Saline = 10: 10 : 80 (i.e. 100 μL Ethanol → 100 μL Cremophor → 800 μL Saline) Injection Formulation 8: Dissolve in Cremophor/Ethanol (50 : 50), then diluted by Saline Injection Formulation 9: EtOH : Corn oil = 10 : 90 (i.e. 100 μL EtOH → 900 μL Corn oil) Injection Formulation 10: EtOH : PEG300:Tween 80 : Saline = 10 : 40 : 5 : 45 (i.e. 100 μL EtOH → 400 μLPEG300 → 50 μL Tween 80 → 450 μL Saline) Oral Formulations Oral Formulation 1: Suspend in 0.5% CMC Na (carboxymethylcellulose sodium) Oral Formulation 2: Suspend in 0.5% Carboxymethyl cellulose Example: Take the Oral Formulation 1 (Suspend in 0.5% CMC Na) as an example, if 100 mL of 2.5 mg/mL working solution is to be prepared, you can first prepare 0.5% CMC Na solution by measuring 0.5 g CMC Na and dissolve it in 100 mL ddH2O to obtain a clear solution; then add 250 mg of the product to 100 mL 0.5% CMC Na solution, to make the suspension solution (2.5 mg/mL, ready for use in animals). Oral Formulation 3: Dissolved in PEG400 Oral Formulation 4: Suspend in 0.2% Carboxymethyl cellulose Oral Formulation 5: Dissolve in 0.25% Tween 80 and 0.5% Carboxymethyl cellulose Oral Formulation 6: Mixing with food powders Note: Please be aware that the above formulations are for reference only. InvivoChem strongly recommends customers to read literature methods/protocols carefully before determining which formulation you should use for in vivo studies, as different compounds have different solubility properties and have to be formulated differently. (Please use freshly prepared in vivo formulations for optimal results.) |
| Preparing Stock Solutions | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.8533 mL | 14.2666 mL | 28.5331 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.5707 mL | 2.8533 mL | 5.7066 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.2853 mL | 1.4267 mL | 2.8533 mL |