Physicochemical Properties
| Molecular Formula | C45H38O18 |
| Molecular Weight | 866.7724 |
| Exact Mass | 866.206 |
| CAS # | 37064-30-5 |
| Related CAS # | Cyanidin Chloride;528-58-5;Procyanidin B1;20315-25-7;Procyanidin B2;29106-49-8;Procyanidin A2;41743-41-3;Procyanidin A1;103883-03-0;Procyanidin B3;23567-23-9 |
| PubChem CID | 169853 |
| Appearance | Light yellow to yellow solid |
| Density | 1.747g/cm3 |
| Melting Point | 140.0 - 142.0 °C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.826 |
| LogP | 4.443 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 15 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 18 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 5 |
| Heavy Atom Count | 63 |
| Complexity | 1550 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 8 |
| SMILES | O1C2=C(C(=C([H])C(=C2[C@]([H])(C2=C(C([H])=C(C3C([H])([H])[C@]([H])([C@@]([H])(C4C([H])=C([H])C(=C(C=4[H])O[H])O[H])OC2=3)O[H])O[H])O[H])[C@]([H])([C@@]1([H])C1C([H])=C([H])C(=C(C=1[H])O[H])O[H])O[H])O[H])O[H])[C@@]1([H])C2=C(C([H])=C(C([H])=C2O[C@]([H])(C2C([H])=C([H])C(=C(C=2[H])O[H])O[H])[C@]1([H])O[H])O[H])O[H] |
| InChi Key | MOJZMWJRUKIQGL-XILRTYJMSA-N |
| InChi Code | InChI=1S/C45H38O18/c46-18-10-27(54)33-32(11-18)61-42(16-2-5-21(48)25(52)8-16)39(59)37(33)35-29(56)14-30(57)36-38(40(60)43(63-45(35)36)17-3-6-22(49)26(53)9-17)34-28(55)13-23(50)19-12-31(58)41(62-44(19)34)15-1-4-20(47)24(51)7-15/h1-11,13-14,31,37-43,46-60H,12H2/t31-,37-,38+,39-,40-,41-,42-,43-/m1/s1 |
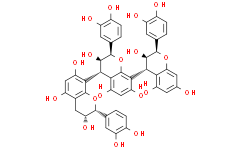
| Chemical Name | (2R,3R,4S)-2-(3,4-dihydroxyphenyl)-4-[(2R,3R)-2-(3,4-dihydroxyphenyl)-3,5,7-trihydroxy-3,4-dihydro-2H-chromen-8-yl]-8-[(2R,3R,4R)-2-(3,4-dihydroxyphenyl)-3,5,7-trihydroxy-3,4-dihydro-2H-chromen-4-yl]-3,4-dihydro-2H-chromene-3,5,7-triol |
| Synonyms | PCC1; Procyanidin C1 |
| HS Tariff Code | 2934.99.9001 |
| Storage |
Powder-20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month Note: This product requires protection from light (avoid light exposure) during transportation and storage. |
| Shipping Condition | Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs) |
Biological Activity
| Targets | MCF-7 (IC50 = 31.5 μg/mL); MDA-MB-231 (IC50 = 36.6 μg/mL) |
| ln Vitro | Procyanidin C1 induces DNA damage, cell cycle arrest, and increased checkpoint kinase expression. Procyanidin C1 increases the expression of BAX, caspase 3 and 9, while decreasing Bcl-2 levels in cancer cells. [1] |
| ln Vivo | Procyanidin C1 depletes senescent cells in a tumor microenvironment that has been harmed by treatment in rodent models, and when combined with chemotherapy, it improves therapeutic efficacy. Procyanidin C1 is a dietary supplement that can be administered intermittently to mice that have been exposed to radiation, implanted with senescent cells, or have simply aged.[2] |
| Cell Assay | Procyanidin C1 is applied to overnight-grown cells (5×103 cells/well) in a final volume of 150 ml for 48 hours at concentrations ranging from 6.25 to 100 mg/ml. Cells that weren't treated served as the standard. Cells are used for MTT assay and cell cycle phase distribution analysis after treatment. An ELISA technique is used to analyze Bcl-2 or BAX levels. |
| Animal Protocol |
C57BL/6J mice (males, 8–12 weeks) 20 mg/kg i.p. |
| References |
[1]. A comparative anticancer study on procyanidin C1 against receptor positive and receptor negative breast cancer. Nat Prod Res. 2019 Jan 8:1-8. [2]. The flavonoid procyanidin C1 has senotherapeutic activity and increases lifespan in mice. Nat Metab. 2021 Dec;3(12):1706-1726. |
| Additional Infomation |
Procyanidin C1 is a proanthocyanidin consisting of three (-)-epicatechin units joined by two successive (4beta->8)-linkages. It has a role as a metabolite, an anti-inflammatory agent, an antioxidant, a lipoxygenase inhibitor, an EC 1.17.3.2 (xanthine oxidase) inhibitor and an EC 3.2.1.20 (alpha-glucosidase) inhibitor. It is a hydroxyflavan, a proanthocyanidin and a polyphenol. It is functionally related to a (-)-epicatechin. Procyanidin C1 has been reported in Camellia sinensis, Camellia reticulata, and other organisms with data available. See also: Maritime Pine (part of). |
Solubility Data
| Solubility (In Vitro) | DMSO: ~100 mg/mL (~115.4 mM) |
| Solubility (In Vivo) |
Solubility in Formulation 1: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (2.88 mM) (saturation unknown) in 10% DMSO + 40% PEG300 + 5% Tween80 + 45% Saline (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), clear solution. For example, if 1 mL of working solution is to be prepared, you can add 100 μL of 25.0 mg/mL clear DMSO stock solution to 400 μL PEG300 and mix evenly; then add 50 μL Tween-80 to the above solution and mix evenly; then add 450 μL normal saline to adjust the volume to 1 mL. Preparation of saline: Dissolve 0.9 g of sodium chloride in 100 mL ddH₂ O to obtain a clear solution. Solubility in Formulation 2: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (2.88 mM) (saturation unknown) in 10% DMSO + 90% (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline) (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), clear solution. For example, if 1 mL of working solution is to be prepared, you can add 100 μL of 25.0 mg/mL clear DMSO stock solution to 900 μL of 20% SBE-β-CD physiological saline solution and mix evenly. Preparation of 20% SBE-β-CD in Saline (4°C,1 week): Dissolve 2 g SBE-β-CD in 10 mL saline to obtain a clear solution. Solubility in Formulation 3: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (2.88 mM) (saturation unknown) in 10% DMSO + 90% Corn Oil (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), clear solution. For example, if 1 mL of working solution is to be prepared, you can add 100 μL of 25.0 mg/mL clear DMSO stock solution to 900 μL of corn oil and mix evenly. Solubility in Formulation 4: 6.25 mg/mL (7.21 mM) in PBS (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), clear solution; with ultrasonication (<60°C). (Please use freshly prepared in vivo formulations for optimal results.) |
| Preparing Stock Solutions | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 1.1537 mL | 5.7685 mL | 11.5371 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.2307 mL | 1.1537 mL | 2.3074 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.1154 mL | 0.5769 mL | 1.1537 mL |