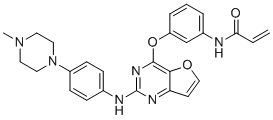
Poseltinib (HM71224; LY3337641; HM-71224; LY-3337641) is a covalent/irreversible BTK (Bruton's tyrosine kinase) tyrosine kinase inhibitor with the potential for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. Poseltinib acts by irreversibly binding to the cysteine 481 residue in the active site of BTK and thus inhibiting Btk with an IC50 of 1.95 nM.
Physicochemical Properties
| Molecular Formula | C26H26N6O3 |
| Molecular Weight | 470.5230 |
| Exact Mass | 470.206 |
| CAS # | 1353552-97-2 |
| PubChem CID | 56644522 |
| Appearance | Light yellow to yellow solid powder |
| LogP | 4.1 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 2 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 8 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 7 |
| Heavy Atom Count | 35 |
| Complexity | 709 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| SMILES | O1C([H])=C([H])C2=C1C(=NC(=N2)N([H])C1C([H])=C([H])C(=C([H])C=1[H])N1C([H])([H])C([H])([H])N(C([H])([H])[H])C([H])([H])C1([H])[H])OC1=C([H])C([H])=C([H])C(=C1[H])N([H])C(C([H])=C([H])[H])=O |
| InChi Key | LZMJNVRJMFMYQS-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| InChi Code | InChI=1S/C26H26N6O3/c1-3-23(33)27-19-5-4-6-21(17-19)35-25-24-22(11-16-34-24)29-26(30-25)28-18-7-9-20(10-8-18)32-14-12-31(2)13-15-32/h3-11,16-17H,1,12-15H2,2H3,(H,27,33)(H,28,29,30) |
| Chemical Name | N-[3-[2-[4-(4-methylpiperazin-1-yl)anilino]furo[3,2-d]pyrimidin-4-yl]oxyphenyl]prop-2-enamide |
| Synonyms | HM-71224 LY3337641HM 71224 LY 3337641PoseltinibHM71224 LY-3337641 |
| HS Tariff Code | 2934.99.9001 |
| Storage |
Powder-20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
| Shipping Condition | Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs) |
Biological Activity
| ln Vitro | In B cells, poseltinib (0.1–100 nM, 30 min) suppresses FcR and BCR signaling [1]. At dosages activated in activated Ramos B cells, poseltinib (1-1000 nM, 1 h) suppresses human monocyte production of interleukin (IL)-6, tumor factor (TNF)-alpha, and primary human B cells. The inhibition of human monocytogenes by IL-1β results in the inhibition of Btk's phosphorylation and that of its downstream components, including PLCγ2. In PBMCs, poseltinib (30 μM, 15 min) suppresses the phosphorylation of BTK, AKT, and PLCγ2 [3]. |
| ln Vivo | Poseltinib (3–30 mg/kg, lateral, once daily, from 18–40 weeks) inhibits BTK, which lowers B cell hyperactivity and attenuates lupus erythematosus (SLE) and lupus nephritis (LN) in mice. Poseltinib (1–30 mg/kg, lateral, once daily during the day) was created to alleviate experimental arthritis in mice [2]. |
| Cell Assay |
Western Blot Analysis[1] Cell Types: B Cell Tested Concentrations: Nucleated cells form osteoclasts[2]. 0.1-100 nM Incubation Duration: 30 minutes Experimental Results: Blocks the autophosphorylation of BTK and the phosphorylation of PLCγ2, with an IC50 value less than 10 nM. Reduces TNF-α and IL-6 production in a dose-dependent manner. |
| Animal Protocol |
Animal/Disease Models: MRL/lpr mouse and NZB/W F1 mouse model [1]. ] Doses: 3-30 mg/kg Route of Administration: Oral Experimental Results: Reduce spleen weight and prevent progression of skin lesions. Improves kidney damage and inflammation and improves survival. |
| References |
[1]. HM71224, a selective Bruton's tyrosine kinase inhibitor, attenuates the development of murine lupus. Arthritis Res Ther. 2017 Sep 26;19(1):211. [2]. HM71224, a novel Bruton's tyrosine kinase inhibitor, suppresses B cell and monocyte activation and ameliorates arthritis in a mouse model: a potential drug for rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Res Ther. 2016 Apr 18;18:91. [3]. Target modulation and pharmacokinetics/pharmacodynamics translation of the BTK inhibitor poseltinib for model-informed phase II dose selection. Sci Rep. 2021 Sep 21;11(1):18671. |
| Additional Infomation |
Poseltinib is under investigation in clinical trial NCT02628028 (A Study of LY3337641 in Rheumatoid Arthritis). Poseltinib is an inhibitor of Bruton's tyrosine kinase (BTK) with potential anti-inflammatory activity. Upon administration, poseltinib inhibits the activity of BTK and prevents the activation of the B-cell antigen receptor (BCR) signaling pathway. This prevents the activation of BTK-mediated inflammatory pathways. |
Solubility Data
| Solubility (In Vitro) | DMSO : ~100 mg/mL (~212.53 mM) |
| Solubility (In Vivo) |
Solubility in Formulation 1: ≥ 7.5 mg/mL (15.94 mM) (saturation unknown) in 10% DMSO + 90% (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline) (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), clear solution. For example, if 1 mL of working solution is to be prepared, you can add 100 μL of 75.0 mg/mL clear DMSO stock solution to 900 μL of 20% SBE-β-CD physiological saline solution and mix evenly. Preparation of 20% SBE-β-CD in Saline (4°C,1 week): Dissolve 2 g SBE-β-CD in 10 mL saline to obtain a clear solution. Solubility in Formulation 2: ≥ 7.5 mg/mL (15.94 mM) (saturation unknown) in 10% DMSO + 90% Corn Oil (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), clear solution. For example, if 1 mL of working solution is to be prepared, you can add 100 μL of 75.0 mg/mL clear DMSO stock solution to 900 μL of corn oil and mix evenly. (Please use freshly prepared in vivo formulations for optimal results.) |
| Preparing Stock Solutions | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.1253 mL | 10.6265 mL | 21.2531 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.4251 mL | 2.1253 mL | 4.2506 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.2125 mL | 1.0627 mL | 2.1253 mL |