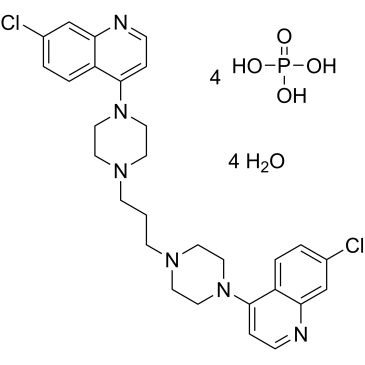
Piperaquine tetraphosphate tetrahydrate, a bisquinoline analog, is a potent antiparasitic agent that has been widely used in combination with other antimalarial agents such as dihydroartemisinin to treat malaria. Piperaquine was developed under the Chinese National Malaria Elimination Programme in the 1960s and was adopted throughout China as a replacement for the structurually similar antimalarial drug chloroquine. Due to widespread parasite resistance to piperaquine, the drug fell out of use as a monotherapy, and is instead used as a partner drug for artemisinin combination therapy. Piperaquine kills parasites by disrupting the detoxification of host heme.
Physicochemical Properties
| Molecular Formula | C29H52CL2N6O20P4 |
| Molecular Weight | 999.552430152893 |
| Exact Mass | 998.156 |
| CAS # | 915967-82-7 |
| Related CAS # | Piperaquine phosphate;85547-56-4;Piperaquine tetraphosphate;911061-10-4;Piperaquine;4085-31-8 |
| PubChem CID | 49849842 |
| Appearance | White to off-white solid powder |
| Melting Point | 252 °C(dec.) |
| LogP | 1.458 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 16 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 26 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 6 |
| Heavy Atom Count | 61 |
| Complexity | 704 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| SMILES | O=P(O)(O)O.ClC1C=C2N=CC=C(C2=CC=1)N1CCN(CCCN2CCN(C3C4C(=CC(=CC=4)Cl)N=CC=3)CC2)CC1.O |
| InChi Key | AMCQDGFOKTXHSY-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| InChi Code | InChI=1S/C29H32Cl2N6.4H3O4P.4H2O/c30-22-2-4-24-26(20-22)32-8-6-28(24)36-16-12-34(13-17-36)10-1-11-35-14-18-37(19-15-35)29-7-9-33-27-21-23(31)3-5-25(27)29;4*1-5(2,3)4;;;;/h2-9,20-21H,1,10-19H2;4*(H3,1,2,3,4);4*1H2 |
| Chemical Name | 7-chloro-4-[4-[3-[4-(7-chloroquinolin-4-yl)piperazin-1-yl]propyl]piperazin-1-yl]quinoline;phosphoric acid;tetrahydrate |
| Synonyms | Piperaquine phosphate hydrate; Piperaquine phosphate; Piperaquine tetraphosphate hydrate |
| HS Tariff Code | 2934.99.9001 |
| Storage |
Powder-20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month Note: Please store this product in a sealed and protected environment, avoid exposure to moisture. |
| Shipping Condition | Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs) |
Biological Activity
| ln Vivo | In mice, piperaquine (10-90 mg/kg; single intraperitoneal injection) decreases parasitemia at all tested doses [1]. The piperaquine (90 mg/kg; single intraperitoneal injection) had the following t1/2, apparent clearance, and apparent volume of distribution: 17.8 days, 33.5 mg·h/L, 1.55 L/h/kg, and 956 L/kg, respectively; 16.1 days for healthy mice and 16.1 days for mice with malaria, 27.3 mg·h/L, 1.9 L/h/kg, and 1,059 L/kg[1]. |
| Animal Protocol |
Animal/Disease Models: Male balb/c (Bagg ALBino) mouse (7 to 8 weeks) inoculated with Plasmodium berghei parasites [1] Doses: 0, 10, 30, 90 mg/kg Route of Administration: Single ip administration Experimental Results:Median Survival time is 10 days at a dose of 10 mg/kg. At the 30 mg/kg dose, the median survival time was 54 days. All mice were active, alert, and had stable weight throughout the study at 90 mg/kg. Animal/Disease Models: Male Swiss mice (6 weeks old) [1] Doses: 90 mg/kg (pharmacokinetic/PK/PK analysis) Route of Administration: Single intraperitonealadministration Experimental Results: t1/2=17.8 d; AUC=33.5 mg·h/L; apparent clearance rate=1.55L/h/kg; apparent volume of distribution=956L/kg. |
| References |
[1]. Moore BR, et, al. Pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of piperaquine in a murine malaria model. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 2008 Jan; 52(1): 306-11. [2]. Davis TME, et, al. Piperaquine: a resurgent antimalarial drug. Drugs. 2005; 65(1): 75-87. |
Solubility Data
| Solubility (In Vitro) |
H2O : ~6 mg/mL (~6.00 mM) DMSO : ~5 mg/mL (~5.00 mM) |
| Solubility (In Vivo) |
Note: Listed below are some common formulations that may be used to formulate products with low water solubility (e.g. < 1 mg/mL), you may test these formulations using a minute amount of products to avoid loss of samples. Injection Formulations (e.g. IP/IV/IM/SC) Injection Formulation 1: DMSO : Tween 80: Saline = 10 : 5 : 85 (i.e. 100 μL DMSO stock solution → 50 μL Tween 80 → 850 μL Saline) *Preparation of saline: Dissolve 0.9 g of sodium chloride in 100 mL ddH ₂ O to obtain a clear solution. Injection Formulation 2: DMSO : PEG300 :Tween 80 : Saline = 10 : 40 : 5 : 45 (i.e. 100 μL DMSO → 400 μLPEG300 → 50 μL Tween 80 → 450 μL Saline) Injection Formulation 3: DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90 (i.e. 100 μL DMSO → 900 μL Corn oil) Example: Take the Injection Formulation 3 (DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90) as an example, if 1 mL of 2.5 mg/mL working solution is to be prepared, you can take 100 μL 25 mg/mL DMSO stock solution and add to 900 μL corn oil, mix well to obtain a clear or suspension solution (2.5 mg/mL, ready for use in animals). Injection Formulation 4: DMSO : 20% SBE-β-CD in saline = 10 : 90 [i.e. 100 μL DMSO → 900 μL (20% SBE-β-CD in saline)] *Preparation of 20% SBE-β-CD in Saline (4°C,1 week): Dissolve 2 g SBE-β-CD in 10 mL saline to obtain a clear solution. Injection Formulation 5: 2-Hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin : Saline = 50 : 50 (i.e. 500 μL 2-Hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin → 500 μL Saline) Injection Formulation 6: DMSO : PEG300 : castor oil : Saline = 5 : 10 : 20 : 65 (i.e. 50 μL DMSO → 100 μLPEG300 → 200 μL castor oil → 650 μL Saline) Injection Formulation 7: Ethanol : Cremophor : Saline = 10: 10 : 80 (i.e. 100 μL Ethanol → 100 μL Cremophor → 800 μL Saline) Injection Formulation 8: Dissolve in Cremophor/Ethanol (50 : 50), then diluted by Saline Injection Formulation 9: EtOH : Corn oil = 10 : 90 (i.e. 100 μL EtOH → 900 μL Corn oil) Injection Formulation 10: EtOH : PEG300:Tween 80 : Saline = 10 : 40 : 5 : 45 (i.e. 100 μL EtOH → 400 μLPEG300 → 50 μL Tween 80 → 450 μL Saline) Oral Formulations Oral Formulation 1: Suspend in 0.5% CMC Na (carboxymethylcellulose sodium) Oral Formulation 2: Suspend in 0.5% Carboxymethyl cellulose Example: Take the Oral Formulation 1 (Suspend in 0.5% CMC Na) as an example, if 100 mL of 2.5 mg/mL working solution is to be prepared, you can first prepare 0.5% CMC Na solution by measuring 0.5 g CMC Na and dissolve it in 100 mL ddH2O to obtain a clear solution; then add 250 mg of the product to 100 mL 0.5% CMC Na solution, to make the suspension solution (2.5 mg/mL, ready for use in animals). Oral Formulation 3: Dissolved in PEG400 Oral Formulation 4: Suspend in 0.2% Carboxymethyl cellulose Oral Formulation 5: Dissolve in 0.25% Tween 80 and 0.5% Carboxymethyl cellulose Oral Formulation 6: Mixing with food powders Note: Please be aware that the above formulations are for reference only. InvivoChem strongly recommends customers to read literature methods/protocols carefully before determining which formulation you should use for in vivo studies, as different compounds have different solubility properties and have to be formulated differently. (Please use freshly prepared in vivo formulations for optimal results.) |
| Preparing Stock Solutions | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 1.0005 mL | 5.0023 mL | 10.0045 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.2001 mL | 1.0005 mL | 2.0009 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.1000 mL | 0.5002 mL | 1.0005 mL |