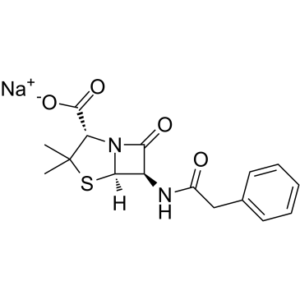
Penicillin G sodium, the sodium salt of penicillin G, is a typical penicillin derivative and β-lactam antibiotic commonly used in the form of its sodium or potassium salts in the treatment of a variety of infections. It is effective against most gram-positive bacteria and against gram-negative cocci. It has also been used as an experimental convulsant because of its actions on GAMMA-AMINOBUTYRIC ACID mediated synaptic transmission.
Physicochemical Properties
| Molecular Formula | C16H17N2NAO4S |
| Molecular Weight | 356.3720 |
| Exact Mass | 356.08 |
| Elemental Analysis | C, 53.93; H, 4.81; N, 7.86; Na, 6.45; O, 17.96; S, 9.00 |
| CAS # | 69-57-8 |
| Related CAS # | Penicillin G potassium;113-98-4;Penicillin G procaine hydrate;6130-64-9;Penicillin G benzathine;1538-09-6;Penicillin G benzathine tetrahydrate;41372-02-5;Penicillin G;61-33-6 |
| PubChem CID | 23668834 |
| Appearance | White to off-white solid powder |
| Density | 1.41 |
| Boiling Point | 663.3ºC at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 209-212°C |
| Index of Refraction | 300 ° (C=2, H2O) |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 1 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 5 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 4 |
| Heavy Atom Count | 24 |
| Complexity | 536 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 3 |
| SMILES | S1C(C([H])([H])[H])(C([H])([H])[H])[C@]([H])(C(=O)[O-])N2C([C@]([H])([C@@]12[H])N([H])C(C([H])([H])C1C([H])=C([H])C([H])=C([H])C=1[H])=O)=O.[Na+] |
| InChi Key | FCPVYOBCFFNJFS-LQDWTQKMSA-M |
| InChi Code | InChI=1S/C16H18N2O4S.Na/c1-16(2)12(15(21)22)18-13(20)11(14(18)23-16)17-10(19)8-9-6-4-3-5-7-9;/h3-7,11-12,14H,8H2,1-2H3,(H,17,19)(H,21,22);/q;+1/p-1/t11-,12+,14-;/m1./s1 |
| Chemical Name | 4-Thia-1-azabicyclo(3.2.0)heptane-2-carboxylic acid, 3,3-dimethyl-7-oxo-6-((2-phenylacetyl)amino)- (2S,5R,6R)-, sodium salt (1:1) |
| Synonyms | Benzylpenicillin sodium salt; Penicillin G sodium salt; Monosodium benzylpenicillin; Mycofarm; Novocillin; NSC 402815; OK 431; Pen-A-Brasive; |
| HS Tariff Code | 2934.99.9001 |
| Storage |
Powder-20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month Note: (1). This product is not stable in solution, please use freshly prepared working solution for optimal results.(2). Please store this product in a sealed and protected environment, avoid exposure to moisture. |
| Shipping Condition | Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs) |
Biological Activity
| Targets | β-lactam |
| ln Vitro | The Penicillin G sodium salt-TEM-1 system's ultraviolet-visible (UV-Vis) absorption spectrum differs significantly from that of Penicillin G sodium salt and TEM-1 β-lactamase, suggesting the formation of new complexes between the two enzymes. As the concentration of Penicillin G sodium salt increases, the UV-Vis absorption of TEM-1 β-lactamase increases and there is a slight red-shift, suggesting that the interaction between Penicillin G sodium salt and TEM-1 β-lactamase causes minor conformational changes in TEM-1 β-lactamase[1]. |
| ln Vivo | According to the logistic regression model, the pigs treated with Penicillin G sodium salt had a 1.6-fold lower probability of a positive swab than the control group (P<0.05). Compared to having zero colonies per plate, the control group's risk of a swab containing 10 to 99 colonies was 2.3 times higher than that of the pigs given Penicillin G sodium salt treatment (P=0.022)[2]. |
| Enzyme Assay | TEM-1β-lactamase solution (5×10-6 M) is mixed with solutions of cefalexin, cefoxitin, and Penicillin G sodium salt at different concentrations at 278 K. The three antibiotics are progressively added to a concentration of 0 to 25×10-6 M. Ultraviolet-visible (UV-Vis) absorption spectra are recorded on a spectrophotometer with a 2 nm slit and a 400 nm/min scanning speed after mixing and interacting for 2 minutes, with 0.02 M phosphate buffer (pH 7.0) serving as a reference[1]. |
| Animal Protocol | For this study, a randomized complete block design with two replicates is employed. With 16 pens and 28 pigs per pen, a replicate has 448 pigs total. Pigs are also sorted by weight, with animals grouped together in blocks according to visual observation of similar weight. Through the use of a formal randomization procedure, two treatments are assigned at random within each block of two adjacent pens. The two treatment groups are Treated (sodium salt of penicillin G) and Control (no treatment). Drinking water containing Penicillin G sodium salt is given for five days during two treatment sessions. Day 1 (the day the pigs are moved into the nursery barns) marks the start of the first treatment period, which ends on Day 5. Day 21 marks the start of the second treatment phase, which lasts until Day 25. There is no treatment given to the Control group[2]. |
| References |
[1]. Spectroscopic analysis and docking simulation on the recognition and binding of TEM-1 β-lactamase with β-lactam antibiotics. Exp Ther Med. 2017 Oct;14(4):3288-3298. [2]. Decreased mortality of weaned pigs with Streptococcus suis with the use of in-water potassium penicillin G. Can Vet J. 2011 Mar;52(3):272-6. |
| Additional Infomation |
Penicillin g, sodium salt is a white to slightly yellow crystalline powder with a faint odor. pH (10% solution) 5.5-7.5. (NTP, 1992) Benzylpenicillin sodium is an organic sodium salt. It contains a benzylpenicillin(1-). Penicillin G (potassium or sodium) is an antibacterial prescription medicine approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for the treatment of certain serious bacterial infections, such as pneumonia, meningitis, gonorrhea, syphilis, and others. Pneumonia and syphilis can be opportunistic infections (OI) of HIV. Penicillin G Sodium is the sodium salt form of benzylpenicillin, a semi-synthetic, broad-spectrum penicillin antibiotic with bactericidal activity. Benzylpenicillin sodium binds to and inactivates penicillin-binding proteins (PBP) located on the inner membrane of the bacterial cell wall. Inactivation of PBPs interferes with the cross-linkage of peptidoglycan chains necessary for bacterial cell wall strength and rigidity. This results in the weakening of the bacterial cell wall and causes cell lysis. A penicillin derivative commonly used in the form of its sodium or potassium salts in the treatment of a variety of infections. It is effective against most gram-positive bacteria and against gram-negative cocci. It has also been used as an experimental convulsant because of its actions on GAMMA-AMINOBUTYRIC ACID mediated synaptic transmission. See also: Penicillin G (has active moiety). |
Solubility Data
| Solubility (In Vitro) |
DMSO : 71~100 mg/mL ( 199.23~280.61 mM ) Water : 71~125 mg/mL(~350.76 mM) Ethanol : ~1 mg/mL |
| Solubility (In Vivo) |
Solubility in Formulation 1: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (7.02 mM) (saturation unknown) in 10% DMSO + 40% PEG300 + 5% Tween80 + 45% Saline (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), clear solution. For example, if 1 mL of working solution is to be prepared, you can add 100 μL of 25.0 mg/mL clear DMSO stock solution to 400 μL PEG300 and mix evenly; then add 50 μL Tween-80 to the above solution and mix evenly; then add 450 μL normal saline to adjust the volume to 1 mL. Preparation of saline: Dissolve 0.9 g of sodium chloride in 100 mL ddH₂ O to obtain a clear solution. Solubility in Formulation 2: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (7.02 mM) (saturation unknown) in 10% DMSO + 90% (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline) (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), clear solution. For example, if 1 mL of working solution is to be prepared, you can add 100 μL of 25.0 mg/mL clear DMSO stock solution to 900 μL of 20% SBE-β-CD physiological saline solution and mix evenly. Preparation of 20% SBE-β-CD in Saline (4°C,1 week): Dissolve 2 g SBE-β-CD in 10 mL saline to obtain a clear solution. Solubility in Formulation 3: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (7.02 mM) (saturation unknown) in 10% DMSO + 90% Corn Oil (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), clear solution. For example, if 1 mL of working solution is to be prepared, you can add 100 μL of 25.0 mg/mL clear DMSO stock solution to 900 μL of corn oil and mix evenly. Solubility in Formulation 4: 10% DMSO+40% PEG300+5% Tween-80+45% Saline: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (7.02 mM) Solubility in Formulation 5: 100 mg/mL (280.61 mM) in PBS (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), clear solution; with ultrasonication. (Please use freshly prepared in vivo formulations for optimal results.) |
| Preparing Stock Solutions | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.8061 mL | 14.0304 mL | 28.0607 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.5612 mL | 2.8061 mL | 5.6121 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.2806 mL | 1.4030 mL | 2.8061 mL |