PT2399 is a novel, potent, and orally bioavailable small molecule inhibitor of HIF-2 which binds to HIF-2α PAS B domain with an IC50 of 6 nM, exhibiting potent antitumor activity in vivo.. It selectively disrupts the heterodimerization of HIF-2α with HIF-1β. Preclinical and clinical data indicate that PT2399 is effective in blocking cancer cell growth, proliferation, and tumor angiogenesis characteristic in ccRCC.
Physicochemical Properties
| Molecular Formula | C17H10F5NO4S |
| Molecular Weight | 419.322620868683 |
| Exact Mass | 419.03 |
| Elemental Analysis | C, 48.69; H, 2.40; F, 22.65; N, 3.34; O, 15.26; S, 7.65 |
| CAS # | 1672662-14-4 |
| Related CAS # | (Rac)-PT2399;1672662-07-5 |
| PubChem CID | 91663289 |
| Appearance | White to off-white solid powder |
| LogP | 3.3 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 1 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 10 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 4 |
| Heavy Atom Count | 28 |
| Complexity | 734 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 1 |
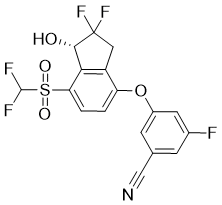
| SMILES | C1C2=C(C=CC(=C2[C@@H](C1(F)F)O)S(=O)(=O)C(F)F)OC3=CC(=CC(=C3)C#N)F |
| InChi Key | MXUSGDMIHGLCNC-HNNXBMFYSA-N |
| InChi Code | InChI=1S/C17H10F5NO4S/c18-9-3-8(7-23)4-10(5-9)27-12-1-2-13(28(25,26)16(19)20)14-11(12)6-17(21,22)15(14)24/h1-5,15-16,24H,6H2/t15-/m0/s1 |
| Chemical Name | 3-[(1S)-7-(Difluoromethylsulfonyl)-2,2-difluoro-1-hydroxy-indan-4-yl]oxy-5-fluoro-benzonitrile |
| Synonyms | PT2399 PT-2399 PT 2399 |
| HS Tariff Code | 2934.99.9001 |
| Storage |
Powder-20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month Note: Please store this product in a sealed and protected environment (e.g. under nitrogen), avoid exposure to moisture. |
| Shipping Condition | Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs) |
Biological Activity
| ln Vitro | PT2399 (compound 10f) has an IC50 of 6 nM for inhibiting HIF-2α [3]. Because it inhibits HIF translocation -2α-/- 786-O cells and other cell lines tested for HIF-2α, PT2399 (20 μM) can induce off-target damage. It directly binds to the HIF-2α PAS B domain and surpasses HIF-2α's ability to connect to aryl hydrocarbon receptor nuclear transporter (ARNT) [2]. In soft agar, PT2399 (0.2-2 μM) inhibits 786-O VHL/; 0-21 days) and prevents 786-O cell development [2]. In ccRCC cells, a number of HIF target genes, including BNIP3, do not suppress HIF-1α potential targets [2]. |
| ln Vivo | PT2399 reduces tumor cell density and increases fibrosis in RCC mice [1]. PT2399 (100 mg/kg; side wall gavage; every 12 hours) is more active than SU 11248 and inhibits several interactions in RCC tumor-bearing cells PT2399 directly inhibits HIF-2α in an inhibitory manner in primary and metastatic pVHL Defective ccRCC leads to tumor regression in preclinical models [2]. SU 11248 triggers tumor growth [1]. |
| Cell Assay |
Cell Viability Assay[1] Cell Types: 786-O cells Tested Concentrations: 0 μM, 0.2 μM, 2 μM Incubation Duration: 0-21 days Experimental Results: 0.2-2 μM concentration can inhibit the growth of 786-O cells in soft agar. |
| Animal Protocol |
Animal/Disease Models: Mouse RCC tumor graft [1] Doses: 100 mg/kg Route of Administration: po (oral gavage); every 12 hrs (hrs (hours)) Experimental Results: More active than SU 11248, and inhibits tumor growth of a variety of SU 11248-resistant tumors . |
| References |
[1]. Targeting renal cell carcinoma with a HIF-2 antagonist. Nature. 2016 Nov 3;539(7627):112-117. [2]. On-Target Efficacy of a HIF2α Antagonist in Preclinical Kidney Cancer Models. Nature. Nature. 2016 Nov 3;539(7627):107-111. [3]. Design and Activity of Specific Hypoxia-Inducible Factor-2α (HIF-2α) Inhibitors for the Treatment of Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma: Discovery of Clinical Candidate (S)-3-((2,2-Difluoro-1-hydroxy-7-(methylsulfonyl)-2,3-dihydro-1 H-inden-4-yl)oxy)-5-fluorobenzonitrile (PT2385). J Med Chem. 2018 Nov 8;61(21):9691-9721. |
Solubility Data
| Solubility (In Vitro) | DMSO : ≥ 200 mg/mL (~476.96 mM) |
| Solubility (In Vivo) |
Solubility in Formulation 1: ≥ 1.67 mg/mL (3.98 mM) (saturation unknown) in 10% DMSO + 40% PEG300 + 5% Tween80 + 45% Saline (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), clear solution. For example, if 1 mL of working solution is to be prepared, you can add 100 μL of 16.7 mg/mL clear DMSO stock solution to 400 μL PEG300 and mix evenly; then add 50 μL Tween-80 to the above solution and mix evenly; then add 450 μL normal saline to adjust the volume to 1 mL. Preparation of saline: Dissolve 0.9 g of sodium chloride in 100 mL ddH₂ O to obtain a clear solution. Solubility in Formulation 2: ≥ 1.67 mg/mL (3.98 mM) (saturation unknown) in 10% DMSO + 90% (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline) (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), clear solution. For example, if 1 mL of working solution is to be prepared, you can add 100 μL of 16.7 mg/mL clear DMSO stock solution to 900 μL of 20% SBE-β-CD physiological saline solution and mix evenly. Preparation of 20% SBE-β-CD in Saline (4°C,1 week): Dissolve 2 g SBE-β-CD in 10 mL saline to obtain a clear solution. Solubility in Formulation 3: ≥ 1.67 mg/mL (3.98 mM) (saturation unknown) in 10% DMSO + 90% Corn Oil (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), clear solution. For example, if 1 mL of working solution is to be prepared, you can add 100 μL of 16.7 mg/mL clear DMSO stock solution to 900 μL of corn oil and mix evenly. (Please use freshly prepared in vivo formulations for optimal results.) |
| Preparing Stock Solutions | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.3848 mL | 11.9241 mL | 23.8481 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.4770 mL | 2.3848 mL | 4.7696 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.2385 mL | 1.1924 mL | 2.3848 mL |