Physicochemical Properties
| Molecular Formula | C17H17N3O2 |
| Molecular Weight | 295.3358 |
| Exact Mass | 295.132 |
| CAS # | 344458-19-1 |
| Related CAS # | PJ34 hydrochloride;344458-15-7 |
| PubChem CID | 4858 |
| Appearance | Light yellow to khaki solid powder |
| Density | 1.3±0.1 g/cm3 |
| Boiling Point | 453.3±38.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Flash Point | 227.9±26.8 °C |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±1.1 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.649 |
| LogP | 0.57 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 2 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 3 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 3 |
| Heavy Atom Count | 22 |
| Complexity | 438 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| InChi Key | UYJZZVDLGDDTCL-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| InChi Code | InChI=1S/C17H17N3O2/c1-20(2)10-16(21)18-11-7-8-15-14(9-11)12-5-3-4-6-13(12)17(22)19-15/h3-9H,10H2,1-2H3,(H,18,21)(H,19,22) |
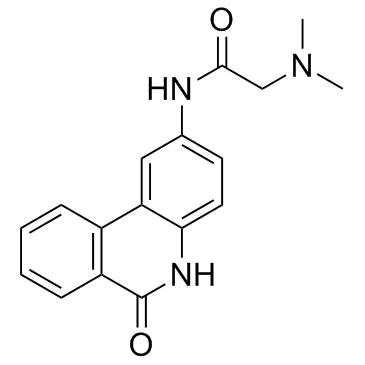
| Chemical Name | 2-(dimethylamino)-N-(6-oxo-5H-phenanthridin-2-yl)acetamide |
| Synonyms | PJ34 |
| HS Tariff Code | 2934.99.9001 |
| Storage |
Powder-20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
| Shipping Condition | Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs) |
Biological Activity
| Targets | PARP ( IC50 = 110 nM ); PARP-2 ( IC50 = 86 nM ); PARP-1 ( IC50 = 110 nM ) |
| ln Vitro | The PARP enzyme activity is inhibited by PJ34, with an IC50 of 110±1.9 nM. The LDH neuroassay was utilized to assess PJ34's protective capabilities in PC12 cells in comparison to those of other PARP enzymes. Cell death in the concentration range of 10-7 to 10-5 M is also significantly and centrally inhibited by PJ34 treatment [1]. |
| ln Vivo | At dosages of 3.2 and 10 mg/kg, respectively, PJ34 was assessed for efficacy and comparability with other PARPs. A 33% reduction in skin lesions was shown when PJ34 was administered at a dose of 3.2 mg/kg; however, a 17% reduction was observed when the dose of 10 mg/kg was administered [1]. TNF-α mRNA levels were considerably reduced by 70% in animals when treated with PJ34 (25 mg/kg), and treated mice did not differ in these values from sham or naive animals. Treatment with PJ34 decreased ICAM-1 mRNA levels by 54% and E-selectin mRNA levels by 81% as compared to vehicle-treated treatments [2]. |
| Enzyme Assay | Minor modifications are made to PARP activity in order to evaluate the inhibitory activity of PARP-1 or PARP-2 of FR247304, 3-AB, and PJ34. The PARP enzyme assay is performed in a final volume of 100 μL with the following contents: 50 mM Tris-HCl (pH 8.0), 25 mM MgCl2, 1 mM dithiothreitol, 10 μg activated salmon sperm DNA, 0.1 μCi of [adenylate-32P]NAD, 0.2 units of recombinant mouse PARP-2 for the PARP-2 assay, 0.1 units of recombinant human PARP for the PARP-1 assay, and different concentrations of FR261529 or 3-AB. After 15 minutes of room temperature (23°C) incubation, 200 μL of ice-cold 20% trichloroacetic acid (TCA) is added to the reaction mixture, and it is further incubated for 10 minutes at 4°C. The precipitate is moved to a GF/B filter, where it is cleaned three times using 70% ethanol and 10% TCA solution. Liquid scintillation counting is used to measure the radioactivity once the filter has dried. |
| Cell Assay | PC12 cell cultures are maintained in Dulbecco's modified Eagle's medium, which is supplemented with 1% (v/v) of penicillin-streptomycin antibiotic mixture, 5% (v/v) of horse serum, and 5% (v/v) of fetal calf serum. At 37°C, cells are grown in an environment consisting of 95% air and 5% CO2. In every experiment, 96-well culture plates are seeded with 4×104 cells/well and left overnight for the cells to attach. Hydrogen peroxide-induced cytotoxicity is measured using an LDH assay kit to measure LDH release as a standard method of assessing cell viability. In summary, 20 μL of the medium from each well is collected 6 hours after the hydrogen peroxide exposure, and the LDH assay kit solution is added. The reaction is halted by adding 1 N HCl after 30 minutes of room temperature incubation, and absorbance is measured at 450 nm using a microplate reader. |
| Animal Protocol | Rats: Male Wistar rats, aged 9 to 10 weeks, weighing 274-380 g, are used for transient focal ischemia. The suspension of FR247304, PJ34, or 3-AB, which is suspended in 0.5% methylcellulose, is given intraperitoneally twice at 10 min before MCA occlusion and 10 min before recirculation. The doses for FR247304 are 10 and 32 mg/kg, 3.2 and 10 mg/kg, and 32 and 100 mg/kg, respectively. A correction of 2 mL/kg is made to the administration volume. Mice: The mice used are male Swiss albino mice weighing 27–32 g. One hour prior to ischemia and again four hours after it starts, PJ34 (1.25, 12.5, or 25 mg/kg)—a PARP inhibitor—is dissolved in isotonic saline (NaCl, 0.9%) and injected intraperitoneally at a volume of 10 mL/kg. The vehicle (saline) is administered to sham animals and control ischemic mice. The studies also include naive animals. |
| References |
[1]. A novel and potent poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase-1 inhibitor, FR247304 (5-chloro-2-[3-(4-phenyl-3,6-dihydro-1(2H)-pyridinyl)propyl]-4(3H)-quinazolinone), attenuates neuronal damage in in vitro and in vivo models of cerebral ischemia. J Ph. [2]. Anti-inflammatory effects of PJ34, a poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase inhibitor, in transient focal cerebral ischemia in mice. Br J Pharmacol. 2006 Sep;149(1):23-30. |
| Additional Infomation | PJ34 is a member of the class of phenanthridines that is 5,6-dihydrophenanthridine substituted at positions 2 and 6 by (N,N-dimethylglycyl)amino and oxo groups, respectively. It is a potent inhibitor of poly(ADP-ribose) polymerases PARP1 and PARP2 (IC50 of 110 nM and 86 nM, respectively) and exhibits anti-cancer, cardioprotective and neuroprotective properties. It has a role as an EC 2.4.2.30 (NAD(+) ADP-ribosyltransferase) inhibitor, an antineoplastic agent, an apoptosis inducer, an angiogenesis inhibitor, an antiatherosclerotic agent, a cardioprotective agent, an anti-inflammatory agent and a neuroprotective agent. It is a member of phenanthridines, a secondary carboxamide and a tertiary amino compound. It is a conjugate base of a PJ34(1+). |
Solubility Data
| Solubility (In Vitro) | DMSO: ~25 mg/mL (~84.7) |
| Solubility (In Vivo) |
Solubility in Formulation 1: ≥ 2.08 mg/mL (7.04 mM) (saturation unknown) in 10% DMSO + 40% PEG300 + 5% Tween80 + 45% Saline (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), clear solution. For example, if 1 mL of working solution is to be prepared, you can add 100 μL of 20.8 mg/mL clear DMSO stock solution to 400 μL PEG300 and mix evenly; then add 50 μL Tween-80 to the above solution and mix evenly; then add 450 μL normal saline to adjust the volume to 1 mL. Preparation of saline: Dissolve 0.9 g of sodium chloride in 100 mL ddH₂ O to obtain a clear solution. Solubility in Formulation 2: ≥ 2.08 mg/mL (7.04 mM) (saturation unknown) in 10% DMSO + 90% (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline) (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), clear solution. For example, if 1 mL of working solution is to be prepared, you can add 100 μL of 20.8 mg/mL clear DMSO stock solution to 900 μL of 20% SBE-β-CD physiological saline solution and mix evenly. Preparation of 20% SBE-β-CD in Saline (4°C,1 week): Dissolve 2 g SBE-β-CD in 10 mL saline to obtain a clear solution. Solubility in Formulation 3: ≥ 2.08 mg/mL (7.04 mM) (saturation unknown) in 10% DMSO + 90% Corn Oil (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), clear solution. For example, if 1 mL of working solution is to be prepared, you can add 100 μL of 20.8 mg/mL clear DMSO stock solution to 900 μL of corn oil and mix evenly. (Please use freshly prepared in vivo formulations for optimal results.) |
| Preparing Stock Solutions | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 3.3859 mL | 16.9296 mL | 33.8593 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.6772 mL | 3.3859 mL | 6.7719 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.3386 mL | 1.6930 mL | 3.3859 mL |