PF-04991532 is a novel, potent, hepatoselective glucokinase activator with EC50 of 80 and 100 nM in human and rat, respectively. It is able to ameliorate hyperglycemia without causing hepatic steatosis in diabetic rats. Hyperglycemia resulting from type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) is the main cause of diabetic complications such as retinopathy and neuropathy. A reduction in hyperglycemia has been shown to prevent these associated complications supporting the importance of glucose control. Glucokinase converts glucose to glucose-6-phosphate and determines glucose flux into the β-cells and hepatocytes. Since activation of glucokinase in β-cells is associated with increased risk of hypoglycemia, selectively activating hepatic glucokinase would reduce fasting and postprandial glucose with minimal risk of hypoglycemia. Previous studies have shown that hepatic glucokinase overexpression is able to restore glucose homeostasis in diabetic models; however, these overexpression experiments have also revealed that excessive increases in hepatic glucokinase activity may also cause hepatosteatosis. PF-04991532 reduced plasma glucose concentrations independent of changes in insulin concentrations in a dose-dependent manner both acutely and after 28 days of sub-chronic treatment. During a hyperglycemic clamp in Goto-Kakizaki rats, the glucose infusion rate was increased approximately 5-fold with PF-04991532. This increase in glucose infusion can be partially attributed to the 60% reduction in endogenous glucose production. While PF-04991532 induced dose-dependent increases in plasma triglyceride concentrations it had no effect on hepatic triglyceride concentrations in Goto-Kakizaki rats. Interestingly, PF-04991532 decreased intracellular AMP concentrations and increased hepatic futile cycling. These data suggest that hepatoselective glucokinase activation may offer glycemic control without inducing hepatic steatosis supporting the evaluation of tissue specific activators in clinical trials.
Physicochemical Properties
| Molecular Formula | C18H19F3N4O3 |
| Molecular Weight | 396.363674402237 |
| Exact Mass | 396.14 |
| CAS # | 1215197-37-7 |
| Related CAS # | (R)-PF-04991532 |
| PubChem CID | 46181428 |
| Appearance | White to off-white solid powder |
| Density | 1.5±0.1 g/cm3 |
| Boiling Point | 646.5±55.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Flash Point | 344.8±31.5 °C |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±2.0 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.618 |
| LogP | 3.09 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 2 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 8 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 6 |
| Heavy Atom Count | 28 |
| Complexity | 569 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 1 |
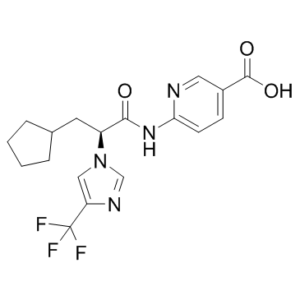
| SMILES | C1CCC(C1)C[C@@H](C(=O)NC2=NC=C(C=C2)C(=O)O)N3C=C(N=C3)C(F)(F)F |
| InChi Key | GKMLFBRLRVQVJO-ZDUSSCGKSA-N |
| InChi Code | InChI=1S/C18H19F3N4O3/c19-18(20,21)14-9-25(10-23-14)13(7-11-3-1-2-4-11)16(26)24-15-6-5-12(8-22-15)17(27)28/h5-6,8-11,13H,1-4,7H2,(H,27,28)(H,22,24,26)/t13-/m0/s1 |
| Chemical Name | (S)-6-(3-Cyclopentyl-2-(4-(trifluoromethyl)-1H-imidazol-1-yl)propanamido)nicotinic Acid |
| Synonyms | PF-04991532; PF 04991532; PF04991532; PF-4991532; PF4991532; PF 4991532. |
| HS Tariff Code | 2934.99.9001 |
| Storage |
Powder-20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
| Shipping Condition | Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs) |
Biological Activity
| ln Vitro | PF-04991532, a strong liver-selective glucokinase activator that is a Phase 2 clinical candidate, has an EC50 of 80 nM in humans and 100 nM in rats. Mechanistic studies conducted on recently obtained primary rat hepatocytes treated with PF-04991532 for 60 minutes revealed enhanced uptake of 2-[14C]-deoxyglucose (EC50 = 1.261 µM) and oxidation of glucose (EC50 = 5.769 µM). Additionally, PF-04991532 decreased the amount of glucose produced from 1-[14C]-lactate in a way that was dependent on dose (EC50 = 0.626 µM). PF-04991532 enhanced G6Pase expression in isolated rat hepatocytes as compared to cells treated with 100 nM glucagon alone. The combination of 25 mM glucose and 100 nM glucagon produced the greatest increase in G6Pase mRNA expression. Glucagon with PF-04991532 in this instance[1]. |
| ln Vivo | To sustain hyperglycemia, PF-04991532 is administered once, increasing the rate of glucose infusion. Remarkably, rats given PF-04991532 for 19 days had hepatic triglycerides that were the same as those of GK rats given a vehicle, while having higher plasma triglycerides. The liver lipid contents in rats given PF-04991532 and the vehicle were found to be the same in another group that received treatment for 28 days (vehicle: 9.89±0.31; PF-04991532 100 mg/kg: 9.91±0.31). Lipogenic genes, including acetyl-CoA carboxylase (ACC), ATP citrate lyase (ACLY), and fatty acid synthase (FAS), were expressed more often in rats given PF-04991532 treatment [1]. |
| References |
[1]. The hepatoselective glucokinase activator PF-04991532 ameliorates hyperglycemia without causing hepatic steatosis in diabetic rats. PLoS One. 2014 May 23;9(5):e97139. |
| Additional Infomation | PF-04991532 has been used in trials studying the basic science of Diabetes Mellitus, Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus, Diabetes Mellitus, Type 2, and Glucose Metabolism Disorders. |
Solubility Data
| Solubility (In Vitro) | DMSO : ~125 mg/mL (~315.37 mM) |
| Solubility (In Vivo) |
Note: Listed below are some common formulations that may be used to formulate products with low water solubility (e.g. < 1 mg/mL), you may test these formulations using a minute amount of products to avoid loss of samples. Injection Formulations (e.g. IP/IV/IM/SC) Injection Formulation 1: DMSO : Tween 80: Saline = 10 : 5 : 85 (i.e. 100 μL DMSO stock solution → 50 μL Tween 80 → 850 μL Saline) *Preparation of saline: Dissolve 0.9 g of sodium chloride in 100 mL ddH ₂ O to obtain a clear solution. Injection Formulation 2: DMSO : PEG300 :Tween 80 : Saline = 10 : 40 : 5 : 45 (i.e. 100 μL DMSO → 400 μLPEG300 → 50 μL Tween 80 → 450 μL Saline) Injection Formulation 3: DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90 (i.e. 100 μL DMSO → 900 μL Corn oil) Example: Take the Injection Formulation 3 (DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90) as an example, if 1 mL of 2.5 mg/mL working solution is to be prepared, you can take 100 μL 25 mg/mL DMSO stock solution and add to 900 μL corn oil, mix well to obtain a clear or suspension solution (2.5 mg/mL, ready for use in animals). Injection Formulation 4: DMSO : 20% SBE-β-CD in saline = 10 : 90 [i.e. 100 μL DMSO → 900 μL (20% SBE-β-CD in saline)] *Preparation of 20% SBE-β-CD in Saline (4°C,1 week): Dissolve 2 g SBE-β-CD in 10 mL saline to obtain a clear solution. Injection Formulation 5: 2-Hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin : Saline = 50 : 50 (i.e. 500 μL 2-Hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin → 500 μL Saline) Injection Formulation 6: DMSO : PEG300 : castor oil : Saline = 5 : 10 : 20 : 65 (i.e. 50 μL DMSO → 100 μLPEG300 → 200 μL castor oil → 650 μL Saline) Injection Formulation 7: Ethanol : Cremophor : Saline = 10: 10 : 80 (i.e. 100 μL Ethanol → 100 μL Cremophor → 800 μL Saline) Injection Formulation 8: Dissolve in Cremophor/Ethanol (50 : 50), then diluted by Saline Injection Formulation 9: EtOH : Corn oil = 10 : 90 (i.e. 100 μL EtOH → 900 μL Corn oil) Injection Formulation 10: EtOH : PEG300:Tween 80 : Saline = 10 : 40 : 5 : 45 (i.e. 100 μL EtOH → 400 μLPEG300 → 50 μL Tween 80 → 450 μL Saline) Oral Formulations Oral Formulation 1: Suspend in 0.5% CMC Na (carboxymethylcellulose sodium) Oral Formulation 2: Suspend in 0.5% Carboxymethyl cellulose Example: Take the Oral Formulation 1 (Suspend in 0.5% CMC Na) as an example, if 100 mL of 2.5 mg/mL working solution is to be prepared, you can first prepare 0.5% CMC Na solution by measuring 0.5 g CMC Na and dissolve it in 100 mL ddH2O to obtain a clear solution; then add 250 mg of the product to 100 mL 0.5% CMC Na solution, to make the suspension solution (2.5 mg/mL, ready for use in animals). Oral Formulation 3: Dissolved in PEG400 Oral Formulation 4: Suspend in 0.2% Carboxymethyl cellulose Oral Formulation 5: Dissolve in 0.25% Tween 80 and 0.5% Carboxymethyl cellulose Oral Formulation 6: Mixing with food powders Note: Please be aware that the above formulations are for reference only. InvivoChem strongly recommends customers to read literature methods/protocols carefully before determining which formulation you should use for in vivo studies, as different compounds have different solubility properties and have to be formulated differently. (Please use freshly prepared in vivo formulations for optimal results.) |
| Preparing Stock Solutions | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.5230 mL | 12.6148 mL | 25.2296 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.5046 mL | 2.5230 mL | 5.0459 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.2523 mL | 1.2615 mL | 2.5230 mL |