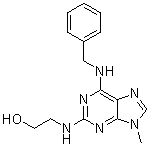
Olomoucine, a purine derivative, is a novel and potent CDK (cyclin-dependent kinases) inhibitor that competes for the ATP binding site of the kinase and induces G arrest.. Olomoucine has been demonstrated to reversibly stop cycling Arabidopsis cells in late G1 and G2, as well as differentiated Petunia cells that have been induced to divide at the G1 phase.
Physicochemical Properties
| Molecular Formula | C15H18N6O |
| Molecular Weight | 298.34302 |
| Exact Mass | 298.154 |
| Elemental Analysis | C, 60.39; H, 6.08; N, 28.17; O, 5.36 |
| CAS # | 101622-51-9 |
| Related CAS # | 101622-51-9 |
| PubChem CID | 4592 |
| Appearance | White to off-white solid powder |
| Density | 1.4±0.1 g/cm3 |
| Boiling Point | 579.6±60.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 120-130 °C |
| Flash Point | 304.3±32.9 °C |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±1.7 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.691 |
| LogP | -0.08 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 3 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 6 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 6 |
| Heavy Atom Count | 22 |
| Complexity | 338 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| SMILES | CN1C=NC2=C(NCC3=CC=CC=C3)NC(=NCCO)N=C21 |
| InChi Key | GTVPOLSIJWJJNY-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| InChi Code | InChI=1S/C15H18N6O/c1-21-10-18-12-13(17-9-11-5-3-2-4-6-11)19-15(16-7-8-22)20-14(12)21/h2-6,10,22H,7-9H2,1H3,(H2,16,17,19,20) |
| Chemical Name | 2-[[6-(benzylamino)-9-methylpurin-2-yl]amino]ethanol |
| Synonyms | Olomoucine |
| HS Tariff Code | 2934.99.9001 |
| Storage |
Powder-20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
| Shipping Condition | Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs) |
Biological Activity
| Targets | cdk2-cyclin A (IC50 = 7 μM); cdk2-cyclin E (IC50 = 7 μM); cdk5-p35 (IC50 = 25 μM) |
| ln Vitro |
Olomoucine suppresses the kinases CDK2 and CDC2, with IC50 values of 7 μM for CDC2/cyclin B, 7 μM for CDK2/cyclin A, 7 μM for CDK2/cyclin E, 3 μm for CDK5/p35, and 25 μM for ERK1/p44 MAPK, respectively[1]. Olomoucine is a non-competitive inhibitor of histone H and a competitive inhibitor of ATP at concentrations of 0, 5, 10, 15, and 25 μM[1]. Olomoucine (0-1000 μM) causes a Gl arrest akin to interleukin-2 deprivation and suppresses DNA synthesis in interleukin-2-stimulated T lymphocytes (CTLL-2 cells)[2]. Olomoucine (0-100 μM) inhibits the MB65 cell line's Gl/S transition in non-small cell lung cancer[2]. Olomoucine (0-150 μM) inhibits the Rdditapes oocytes' prophase/metaphase transition[2]. Olomoucine has been shown to inhibit the survival of tumor cells, with IC50s of 32.35 μM for dog melanoma, 42.15 μM for mouse B16 melanoma, and 82.30 μM for human melanoma, respectively[3]. |
| ln Vivo |
Olomoucine (8 mg/kg; i.v.; once daily; 7 d) causes tumor cells to undergo apoptosis without causing any side effects on the third day following treatment[3]. It has been discovered that, in comparison to single dosage administration, cassette dosing underestimates the Cmax and overestimates the AUC[4]. |
| Animal Protocol |
Dog with spontaneous melanoma (oral and maxillofacial tumors)[3] 8 mg/kg Intravenous injection; once daily; for 7 days |
| References |
[1]. Inhibition of cyclin-dependent kinases by purine analogues. European Journal of Biochemistry 224, 771-786 (1994). [2]. Cellular effects of olomoucine, an inhibitor of cyclin-dependent kinases. Biology of the Cell 83(2), 105-120 (1995). [3]. Induction of apoptosis and regression of spontaneous dog melanoma following in vivo application of synthetic cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor olomoucine. Anticancer Drugs. 1997 Nov. 8(10):1007-13. [4]. Cassette dosing pharmacokinetics of a library of 2,6,9-trisubstituted purine cyclin-dependent kinase 2 inhibitors prepared by parallel synthesis. Mol Cancer Ther. 2004 Mar. 3(3):353-62. |
| Additional Infomation | Olomoucine is a 9H-purine that is substituted by a (2-hydroxyethyl)nitrilo, benzylnitrilo and a methyl group at positions 2,6 and 9, respectively. It is a cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor. It has a role as an EC 2.7.11.22 (cyclin-dependent kinase) inhibitor. It is a member of 2,6-diaminopurines and a member of ethanolamines. |
Solubility Data
| Solubility (In Vitro) | DMSO: ~66.7 mg/mL (~223.5 mM) |
| Solubility (In Vivo) |
Solubility in Formulation 1: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (8.38 mM) (saturation unknown) in 10% DMSO + 40% PEG300 + 5% Tween80 + 45% Saline (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), clear solution. For example, if 1 mL of working solution is to be prepared, you can add 100 μL of 25.0 mg/mL clear DMSO stock solution to 400 μL PEG300 and mix evenly; then add 50 μL Tween-80 to the above solution and mix evenly; then add 450 μL normal saline to adjust the volume to 1 mL. Preparation of saline: Dissolve 0.9 g of sodium chloride in 100 mL ddH₂ O to obtain a clear solution. Solubility in Formulation 2: 2.5 mg/mL (8.38 mM) in 10% DMSO + 90% (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline) (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), suspension solution; with ultrasonication. For example, if 1 mL of working solution is to be prepared, you can add 100 μL of 25.0 mg/mL clear DMSO stock solution to 900 μL of 20% SBE-β-CD physiological saline solution and mix evenly. Preparation of 20% SBE-β-CD in Saline (4°C,1 week): Dissolve 2 g SBE-β-CD in 10 mL saline to obtain a clear solution. Solubility in Formulation 3: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (8.38 mM) (saturation unknown) in 10% DMSO + 90% Corn Oil (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), clear solution. For example, if 1 mL of working solution is to be prepared, you can add 100 μL of 25.0 mg/mL clear DMSO stock solution to 900 μL of corn oil and mix evenly. (Please use freshly prepared in vivo formulations for optimal results.) |
| Preparing Stock Solutions | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 3.3519 mL | 16.7594 mL | 33.5188 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.6704 mL | 3.3519 mL | 6.7038 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.3352 mL | 1.6759 mL | 3.3519 mL |