Physicochemical Properties
| Molecular Formula | C27H32O14 |
| Molecular Weight | 580.539 |
| Exact Mass | 580.179 |
| Elemental Analysis | C, 55.86; H, 5.56; O, 38.58 |
| CAS # | 14259-46-2 |
| Related CAS # | Isonaringin;108815-81-2 |
| PubChem CID | 442431 |
| Appearance | Solid powder |
| Density | 1.7±0.1 g/cm3 |
| Boiling Point | 924.3±65.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 152-190ºC |
| Flash Point | 307.3±27.8 °C |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±0.3 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.708 |
| LogP | 2.07 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 8 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 14 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 6 |
| Heavy Atom Count | 41 |
| Complexity | 884 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 11 |
| SMILES | O1[C@]([H])([C@@]([H])([C@]([H])([C@@]([H])([C@@]1([H])C([H])([H])O[C@@]1([H])[C@@]([H])([C@@]([H])([C@]([H])([C@]([H])(C([H])([H])[H])O1)O[H])O[H])O[H])O[H])O[H])O[H])OC1=C([H])C(=C2C(C([H])([H])[C@@]([H])(C3C([H])=C([H])C(=C([H])C=3[H])O[H])OC2=C1[H])=O)O[H] |
| InChi Key | HXTFHSYLYXVTHC-AJHDJQPGSA-N |
| InChi Code | InChI=1S/C27H32O14/c1-10-20(31)22(33)24(35)26(38-10)37-9-18-21(32)23(34)25(36)27(41-18)39-13-6-14(29)19-15(30)8-16(40-17(19)7-13)11-2-4-12(28)5-3-11/h2-7,10,16,18,20-29,31-36H,8-9H2,1H3/t10-,16-,18+,20-,21+,22+,23-,24+,25+,26+,27+/m0/s1 |
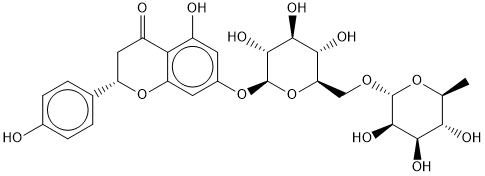
| Chemical Name | (S)-5-hydroxy-2-(4-hydroxyphenyl)-7-(((2S,3R,4S,5S,6R)-3,4,5-trihydroxy-6-((((2R,3R,4R,5R,6S)-3,4,5-trihydroxy-6-methyltetrahydro-2H-pyran-2-yl)oxy)methyl)tetrahydro-2H-pyran-2-yl)oxy)chroman-4-one |
| Synonyms | Naringenin 7-beta-rutinoside, Naringenin 7-O-rutinoside, (2S)-Narirutin;Isonaringenin, Isonaringin |
| HS Tariff Code | 2934.99.03.00 |
| Storage |
Powder-20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month Note: Please store this product in a sealed and protected environment (e.g. under nitrogen), avoid exposure to moisture and light. |
| Shipping Condition | Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs) |
Biological Activity
| ln Vitro | RBL-2H3 cells remain viable in the presence of narirutin (200 μM, 20 h). In RBL-2H3 cells, narirutin (25 μM, 2.5 h) inhibits the release of β-hex, histamine, IL-4, and TNF-a, with levels below 40%. [3]. |
| ln Vivo | Mice challenged with OVA have lower peripheral blood eosinophil counts when given nerirutin (10 mg/kg, p.o.) The OVA-induced increase in IL-4 is blocked by narirutin (10 mg/kg, p.o. ), but the increase in IL-5 is unaffected [2]. |
| Animal Protocol |
Animal Model: Allergic asthma female NC/Nga mice model[2] Dosage: 0.1, 1 or 10 mg/kg Administration: Orally, 7d Result: Reduced eosinophil counts in peripheral blood. Blocked the OVA-induced increase in IL-4. |
| References |
[1]. Structure-based Discovery of Narirutin as a Shikimate Kinase Inhibitor with Anti-tubercular Potency.Curr Comput Aided Drug Des. 2019 Oct 25. [2]. Narirutin inhibits airway inflammation in an allergic mouse model.Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 2007 Aug;34(8):766-70. [3]. Inhibitory activity of narirutin on RBL-2H3 cells degranulation. Immunopharmacol Immunotoxicol. 2021, 43, 1. |
| Additional Infomation |
Narirutin is a disaccharide derivative that is (S)-naringenin substituted by a 6-O-(6-deoxy-alpha-L-mannopyranosyl)-beta-D-glucopyranosyl moiety at position 7 via a glycosidic linkage. It has a role as an anti-inflammatory agent, an antioxidant and a metabolite. It is a disaccharide derivative, a dihydroxyflavanone, a member of 4'-hydroxyflavanones, a (2S)-flavan-4-one and a rutinoside. It is functionally related to a (S)-naringenin. Narirutin has been reported in Citrus sulcata, Citrus reticulata, and other organisms with data available. See also: Tangerine peel (part of). |
Solubility Data
| Solubility (In Vitro) | DMSO : 100~125 mg/mL ( 172.25~215.32 mM) |
| Solubility (In Vivo) |
Solubility in Formulation 1: 2.08 mg/mL (3.58 mM) in 10% DMSO + 40% PEG300 + 5% Tween80 + 45% Saline (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), clear solution; with sonication. For example, if 1 mL of working solution is to be prepared, you can add 100 μL of 20.8 mg/mL clear DMSO stock solution to 400 μL PEG300 and mix evenly; then add 50 μL Tween-80 to the above solution and mix evenly; then add 450 μL normal saline to adjust the volume to 1 mL. Preparation of saline: Dissolve 0.9 g of sodium chloride in 100 mL ddH₂ O to obtain a clear solution. Solubility in Formulation 2: ≥ 2.08 mg/mL (3.58 mM) (saturation unknown) in 10% DMSO + 90% (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline) (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), clear solution. For example, if 1 mL of working solution is to be prepared, you can add 100 μL of 20.8 mg/mL clear DMSO stock solution to 900 μL of 20% SBE-β-CD physiological saline solution and mix evenly. Preparation of 20% SBE-β-CD in Saline (4°C,1 week): Dissolve 2 g SBE-β-CD in 10 mL saline to obtain a clear solution. Solubility in Formulation 3: ≥ 2.08 mg/mL (3.58 mM) (saturation unknown) in 10% DMSO + 90% Corn Oil (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), clear solution. For example, if 1 mL of working solution is to be prepared, you can add 100 μL of 20.8 mg/mL clear DMSO stock solution to 900 μL of corn oil and mix evenly. Solubility in Formulation 4: 10% DMSO+40% PEG300+5% Tween-80+45% Saline: 2.08 mg/mL (3.58 mM) Solubility in Formulation 5: 10 mg/mL (17.23 mM) in 50% PEG300 50% Saline (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), clear solution; with ultrasonication. Preparation of saline: Dissolve 0.9 g of sodium chloride in 100 mL ddH₂ O to obtain a clear solution. (Please use freshly prepared in vivo formulations for optimal results.) |
| Preparing Stock Solutions | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 1.7225 mL | 8.6127 mL | 17.2253 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.3445 mL | 1.7225 mL | 3.4451 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.1723 mL | 0.8613 mL | 1.7225 mL |