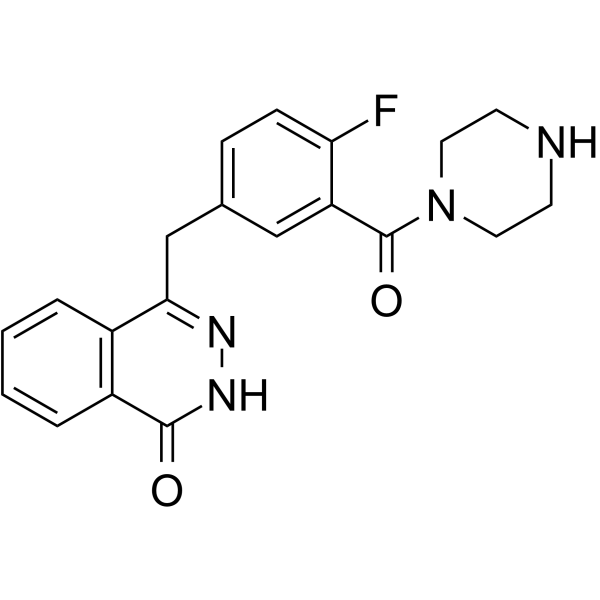
Physicochemical Properties
| Molecular Formula | C20H19FN4O2 |
| Molecular Weight | 366.389 |
| Exact Mass | 366.149 |
| CAS # | 763111-47-3 |
| PubChem CID | 11726399 |
| Appearance | White to off-white solid powder |
| LogP | 2.377 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 2 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 5 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 3 |
| Heavy Atom Count | 27 |
| Complexity | 605 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 |
| SMILES | C1CN(CCN1)C(=O)C2=C(C=CC(=C2)CC3=NNC(=O)C4=CC=CC=C43)F |
| InChi Key | MFFUYEOGICAKCK-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| InChi Code | InChI=1S/C20H19FN4O2/c21-17-6-5-13(11-16(17)20(27)25-9-7-22-8-10-25)12-18-14-3-1-2-4-15(14)19(26)24-23-18/h1-6,11,22H,7-10,12H2,(H,24,26) |
| Chemical Name | 4-[[4-fluoro-3-(piperazine-1-carbonyl)phenyl]methyl]-2H-phthalazin-1-one |
| Synonyms | N-Descyclopropanecarbaldehyde Olaparib; 763111-47-3; 4-(4-fluoro-3-(piperazine-1-carbonyl)benzyl)phthalazin-1(2H)-one; 4-[[4-fluoro-3-(piperazine-1-carbonyl)phenyl]methyl]-2H-phthalazin-1-one; N-Descyclopropanecarbaldehyde Olaparib; MFCD18251631; 1-[5-[(3,4-Dihydro-4-oxo-1-phthalazinyl)methyl]-2-fluorobenzoyl]piperazine; 4-[[4-Fluoro-3-(1-piperazinylcarbonyl)phenyl]methyl]-1(2H)-phthalazinone; 4-{[4-fluoro-3-(piperazine-1-carbonyl)phenyl]methyl}-1,2-dihydrophthalazin-1-one; |
| HS Tariff Code | 2934.99.9001 |
| Storage |
Powder-20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
| Shipping Condition | Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs) |
Biological Activity
| Targets | Cereblon |
| ln Vivo | Poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase (PARP) has emerged as an important molecular target for the treatment of several oncological diseases. A couple of molecular probes based on Olaparib scaffold have been developed by incorporation of F-18 or fluorophore for positron emission tomography (PET) or optical imaging in several types of tumor. PARP has been reported overexpressed in mesothelioma. We hereby synthesized an analogue of Olaparib containing DOTA moiety and radiolabeled it with Cu-64 to evaluate its utility of PET tracer for mesothelioma. The Cu-64 labeling was conveniently achieved at 90% yield with final compound at >99% radiochemistry purity. The biodistribution and PET imaging were performed at 0.5, 1, 2 and 18h to confirm the in vivo tumor targeting. The tumor uptake in study group was significant higher than that in control group (3.45±0.47% ID/g vs 2.26±0.30% ID/g) and tumor were clearly detected by PET imaging. These results suggest the feasibility to develop an Olaparib-based theranostic agent for mesothelioma [1]. |
| References |
[1]. Initial evaluation of Cu-64 labeled PARPi-DOTA PET imaging in mice with mesothelioma. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2017 Aug 1;27(15):3472-3476. [2]. Rational Design and Synthesis of Novel Dual PROTACs for Simultaneous Degradation of EGFR and PARP. J Med Chem. 2021 May 26. |
| Additional Infomation | Inspired by the success of dual-targeting drugs, especially bispecific antibodies, we propose to combine the concept of proteolysis targeting chimera (PROTAC) and dual targeting to design and synthesize dual PROTAC molecules with the function of degrading two completely different types of targets simultaneously. A library of novel dual-targeting PROTAC molecules has been rationally designed and prepared. A convergent synthetic strategy has been utilized to achieve high synthetic efficiency. These dual PROTAC structures are characterized using trifunctional natural amino acids as star-type core linkers to connect two independent inhibitors and E3 ligands together. In this study, gefitinib, olaparib, and CRBN or VHL E3 ligands were used as substrates to synthesize novel dual PROTACs. They successfully degraded both the epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) and poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase (PARP) simultaneously in cancer cells. Being the first successful example of dual PROTACs, this technique will greatly widen the range of application of the PROTAC method and open up a new field for drug discovery. [2] |
Solubility Data
| Solubility (In Vitro) |
DMSO : ≥ 100 mg/mL (~272.9 mM) H2O : < 0.1 mg/mL |
| Solubility (In Vivo) |
Solubility in Formulation 1: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (6.82 mM) (saturation unknown) in 10% DMSO + 40% PEG300 + 5% Tween80 + 45% Saline (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), clear solution. For example, if 1 mL of working solution is to be prepared, you can add 100 μL of 25.0 mg/mL clear DMSO stock solution to 400 μL PEG300 and mix evenly; then add 50 μL Tween-80 to the above solution and mix evenly; then add 450 μL normal saline to adjust the volume to 1 mL. Preparation of saline: Dissolve 0.9 g of sodium chloride in 100 mL ddH₂ O to obtain a clear solution. Solubility in Formulation 2: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (6.82 mM) (saturation unknown) in 10% DMSO + 90% (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline) (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), clear solution. For example, if 1 mL of working solution is to be prepared, you can add 100 μL of 25.0 mg/mL clear DMSO stock solution to 900 μL of 20% SBE-β-CD physiological saline solution and mix evenly. Preparation of 20% SBE-β-CD in Saline (4°C,1 week): Dissolve 2 g SBE-β-CD in 10 mL saline to obtain a clear solution. Solubility in Formulation 3: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (6.82 mM) (saturation unknown) in 10% DMSO + 90% Corn Oil (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), clear solution. For example, if 1 mL of working solution is to be prepared, you can add 100 μL of 25.0 mg/mL clear DMSO stock solution to 900 μL of corn oil and mix evenly. (Please use freshly prepared in vivo formulations for optimal results.) |
| Preparing Stock Solutions | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.7293 mL | 13.6467 mL | 27.2933 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.5459 mL | 2.7293 mL | 5.4587 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.2729 mL | 1.3647 mL | 2.7293 mL |