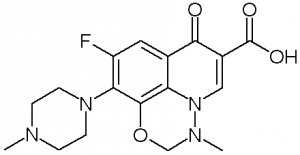
Marbofloxacin (Forcyl, Kelacyl, Zeniquin, Aristos, Boflox, Marbocyl, Aurizon), a carboxylic acid derivative, is a 3rd generation and broad spectrum antibiotic of the fluoroquinolone class used as a veterinary medication. Marbofloxacin showed notable antibacterial activity against both gram–and + bacteria.
Physicochemical Properties
| Molecular Formula | C17H19FN4O4 | |
| Molecular Weight | 362.36 | |
| Exact Mass | 362.139 | |
| Elemental Analysis | C, 56.35; H, 5.29; F, 5.24; N, 15.46; O, 17.66 | |
| CAS # | 115550-35-1 | |
| Related CAS # | 115551-26-3 | |
| PubChem CID | 60651 | |
| Appearance | Light yellow to yellow solid powder | |
| Density | 1.6±0.1 g/cm3 | |
| Boiling Point | 570.5±60.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Melting Point | 268-269ºC | |
| Flash Point | 298.8±32.9 °C | |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±1.7 mmHg at 25°C | |
| Index of Refraction | 1.701 | |
| LogP | -0.55 | |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 1 | |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 9 | |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 2 | |
| Heavy Atom Count | 26 | |
| Complexity | 636 | |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 0 | |
| SMILES | FC1C([H])=C2C(C(C(=O)O[H])=C([H])N3C2=C(C=1N1C([H])([H])C([H])([H])N(C([H])([H])[H])C([H])([H])C1([H])[H])OC([H])([H])N3C([H])([H])[H])=O |
|
| InChi Key | BPFYOAJNDMUVBL-UHFFFAOYSA-N | |
| InChi Code | InChI=1S/C17H19FN4O4/c1-19-3-5-21(6-4-19)14-12(18)7-10-13-16(14)26-9-20(2)22(13)8-11(15(10)23)17(24)25/h7-8H,3-6,9H2,1-2H3,(H,24,25) | |
| Chemical Name | 7-fluoro-2-methyl-6-(4-methylpiperazin-1-yl)-10-oxo-4-oxa-1,2-diazatricyclo[7.3.1.05,13]trideca-5(13),6,8,11-tetraene-11-carboxylic acid | |
| Synonyms |
|
|
| HS Tariff Code | 2934.99.9001 | |
| Storage |
Powder-20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
|
| Shipping Condition | Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs) |
Biological Activity
| Targets | Topoisomerase IV; Topoisomerase II | |
| ln Vitro |
|
|
| ln Vivo |
|
|
| Animal Protocol |
SPF piglets inoculated intratracheally with M. hyopneumoniae strain 116 ~2 mg/kg/day Intramuscular injection Tissue cages (TC), implanted subcutaneously in the neck in eight ponies, were inoculated with Staphylococcus aureus (S. aureus) to determine the clinical efficacy of marbofloxacin in the treatment of this infection. From 21 h after inoculation, marbofloxacin (6 mg/kg) was administered intravenously (i.v.) once daily for 7 days. Samples of the tissue cage fluid (TCF) were taken to determine marbofloxacin concentrations (days 1, 3 and 7), using high-pressure liquid chromatography, and numbers of viable bacteria [colony forming units (CFU)] (days 1, 3, 7, 14 and 21). Statistical analysis was used to compare CFU before and after treatment. Clinical signs and CFU were used to evaluate the efficacy of treatment. Although, there was a slight decrease in CFU in all TC initially, the infection was not eliminated by marbofloxacin treatment in any of the ponies and abscesses formed. As the MIC (0.25 microg/mL) did not change during treatment and the concentration of marbofloxacin during treatment (mean concentration in TCF was 0.89 microg/mL on day 1, 0.80 microg/mL on day 3 and 2.77 microg/mL on day 7) was above MIC, we consider that the treatment failure might be attributable to the formation of a biofilm by S. aureus. Based on the present results, i.v. administration of marbofloxacin alone is not suitable for the elimination of S. aureus infections from secluded sites.[2] |
|
| ADME/Pharmacokinetics | Marbofloxacin is a fluoroquinolone antibiotic expected to be effective in the treatment of infections involving gram-negative and some gram-positive bacteria in horses. In order to design a rational dosage regimen for the substance in horses, the pharmacokinetic properties of marbofloxacin were investigated in 6 horses after i.v., subcutaneous and oral administration of a single dose of 2 mg/kg bwt and the minimal inhibitory concentrations (MIC) assessed for bacteria isolated from equine infectious pathologies. The clearance of marbofloxacin was mean +/- s.d. 0.25 +/- 0.05 l/kg/h and the terminal half-life 756 +/- 1.99 h. The marbofloxacin absolute bioavailabilities after subcutaneous and oral administration were 98 +/- 11% and 62 +/- 8%, respectively. The MIC required to inhibit 90% of isolates (MIC90) was 0.027 microg/ml for enterobacteriaceae and 0.21 microg/ml for Staphylococcus aureus. The values of surrogate markers of antimicrobial efficacy (AUIC, Cmax/MIC ratio, time above MIC90) were calculated and the marbofloxacin concentration profiles simulated for repeated administrations. These data were used to determine rational dosage regimens for target bacteria. Considering the breakpoint values of efficacy indices for fluoroquinolones, a marbofloxacin dosage regimen of 2 mg/kg bwt/24 h by i.v., subcutaneous or oral routes was more appropriate for enterobacteriaceae than for S. aureus. [3] | |
| Toxicity/Toxicokinetics | mouse LD50 oral >2 gm/kg United States Patent Document., #4801584 | |
| References |
[1]. Marbofloxacin. Acta Crystallogr Sect E Struct Rep Online. 2012 Apr 1;68(Pt 4):o998-9. [2]. Clinical efficacy of intravenous administration of marbofloxacin in a Staphylococcus aureus infection in tissue cages in ponies. J Vet Pharmacol Ther. 2006 Dec;29(6):555-60. [3]. Pharmacokinetics of marbofloxacin in horses. Equine Vet J. 2002 Jul;34(4):366-72. |
|
| Additional Infomation |
LSM-5799 is a member of quinolines. Marbofloxacin is a carboxylic acid, part of the third generation of antibiotic fluoroquinolones. It is used in veterinary medicine. A formulation of marbofloxacin combined with clotrimazole and dexamethasone is available under the name Aurizon. IN THE TITLE COMPOUND, [SYSTEMATIC NAME: 9-fluoro-2,3-dihydro-3-methyl-10-(4-methyl-piperazin-1-yl)-7-oxo-7H-pyrido[1,2,3-ij][1,2,4]benzoxadiazine-6-carb-oxy-lic acid], C(17)H(19)FN(4)O(4), the carbonyl and carboxyl groups are coplanar with the quinoline ring, making a dihedral angle of 2.39 (2)°. The piperazine ring adopts a chair conformation and the oxadiazinane ring displays an envelope conformation with the CH(2) group at the flap displaced by 0.650 (2) Å from the plane through the other five atoms. The mol-ecular structure exhibits an S(6) ring motif, owing to an intra-molecular O-H⋯O hydrogen bond. In the crystal, weak C-H⋯F hydrogen bonds link mol-ecules into layers parallel to the ab plane.[1] |
Solubility Data
| Solubility (In Vitro) |
|
|||
| Solubility (In Vivo) |
|
| Preparing Stock Solutions | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 2.7597 mL | 13.7984 mL | 27.5969 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.5519 mL | 2.7597 mL | 5.5194 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.2760 mL | 1.3798 mL | 2.7597 mL |