Physicochemical Properties
| Molecular Formula | C16H17NO4 |
| Molecular Weight | 287.3105 |
| Exact Mass | 287.115 |
| CAS # | 476-28-8 |
| Related CAS # | Lycorine hydrochloride monohydrate;6150-58-9;Lycorine hydrochloride;2188-68-3 |
| PubChem CID | 72378 |
| Appearance | White to off-white solid powder |
| Density | 1.5±0.1 g/cm3 |
| Boiling Point | 477.4±45.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 253-255ºC (dec.) |
| Flash Point | 242.5±28.7 °C |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±1.3 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.733 |
| LogP | 0.77 |
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count | 2 |
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count | 5 |
| Rotatable Bond Count | 0 |
| Heavy Atom Count | 21 |
| Complexity | 481 |
| Defined Atom Stereocenter Count | 4 |
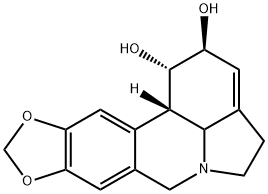
| SMILES | C1CN2CC3=CC4=C(C=C3[C@H]5[C@H]2C1=C[C@@H]([C@H]5O)O)OCO4 |
| InChi Key | XGVJWXAYKUHDOO-DANNLKNASA-N |
| InChi Code | InChI=1S/C16H17NO4/c18-11-3-8-1-2-17-6-9-4-12-13(21-7-20-12)5-10(9)14(15(8)17)16(11)19/h3-5,11,14-16,18-19H,1-2,6-7H2/t11-,14-,15+,16+/m0/s1 |
| Chemical Name | (1S,17S,18S,19S)-5,7-dioxa-12-azapentacyclo[10.6.1.02,10.04,8.015,19]nonadeca-2,4(8),9,15-tetraene-17,18-diol |
| HS Tariff Code | 2934.99.9001 |
| Storage |
Powder-20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
| Shipping Condition | Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs) |
Biological Activity
| ln Vitro | Lycorine has a minor effect on PNT1A cell proliferation, as well as a cyclic inhibitory effect on cell proliferation on the four PCa cell lines mentioned above, with an IC50 range of 5 μM to 10 μM [1]. In order to control or safeguard SREBF in the endoplasmic reticulum, SCAP (SREBF molecular chaperone), an endoplasmic reticulum-to-Golgi transporter, transforms structurally by creating a complex with INSIG1 (insulin-inducible gene) 1)[2]. In a dose- and time-dependent way, Lycorine (5-40 μM; 16) considerably reduces SREBF activity (up to -70%) without having overt effects in cells. Lycorine (10-20 μM; 2-16 hours). Cytotoxicity [2]. decreases in HL-7702 cells the amounts of mature SREBF1 and SREBF2 proteins [2]. ABCG5 and ABCG8 are two NR1H3 target genes that are not affected by lycorine (20 μM; 16 hours) or NR1H3 transcription activation. Sterol Forwarding activity for NR1H3 is activated [1]. Treatment with lycorine (0-25 μM; 48 hours) markedly and dose-dependently suppressed the expression of vascular endothelial (VE)-cadherin and marginally decreased the expression of Sema4D in C8161 cells. The VE-cadherin protein level in C8161 cells was dramatically lowered by the expression of the other 6 genes after 48 hours of treatment with Lycorine (0-25 μM) [3]. |
| ln Vivo | Lycorine (facial; 15 mg/kg, 30 mg/kg; once daily) attenuates fat coupling and depletion therapy and enhances fat stratification and oxidation of grafts and precursor and mature SREBF in mice [2]. |
| Cell Assay |
Cell viability assay [2] Cell Types: HL-7702/SRE- Luc. Cell Tested Concentrations: 16 hrs (hours) Incubation Duration: 5 μM; 10 μM; 20 μM; 40 μM Experimental Results: No cytotoxicity to HL-7702 cells. Western Blot Analysis[2] Cell Types: HL-7702/SRE-Luc Cell Tested Concentrations: 2 hour, 4 hrs (hours), 8 hrs (hours), 12 hrs (hours), 16 hrs (hours) Incubation Duration: 10 μM; 20 μM Experimental Results: p-SREBF1, m-SREBF1, p-SREBF2 and p-SREBF1 protein expression diminished. RT-PCR[3] Cell Types:C8161 Cell Tested Concentrations: 0 μM, 1.56 μM, 3.13 μM, 6.25 μM, 12.5 μM, 25 μM Incubation Duration: 48 hrs (hours) Experimental Results: Dramatically inhibited the expression of VE-cadherin in a dose-dependent manner, and also slightly diminished C8161 Expression of Sema4D in cells. |
| Animal Protocol |
Animal/Disease Models: C57BL/6J mice fed high-fat diet (HFD) [2] Doses: 15 mg/kg, 30 mg/kg Route of Administration: oral; one time/day Experimental Results: Improved high-fat diet-induced hypertensive disorders in mice Lipidemia, hepatic steatosis, and insulin resistance. |
| ADME/Pharmacokinetics |
Metabolism / Metabolites Paraoxonase (PON1) is a key enzyme in the metabolism of organophosphates. PON1 can inactivate some organophosphates through hydrolysis. PON1 hydrolyzes the active metabolites in several organophosphates insecticides as well as, nerve agents such as soman, sarin, and VX. The presence of PON1 polymorphisms causes there to be different enzyme levels and catalytic efficiency of this esterase, which in turn suggests that different individuals may be more susceptible to the toxic effect of OP exposure. |
| Toxicity/Toxicokinetics |
Toxicity Summary Lycorine is a cholinesterase or acetylcholinesterase (AChE) inhibitor. A cholinesterase inhibitor (or 'anticholinesterase') suppresses the action of acetylcholinesterase. Because of its essential function, chemicals that interfere with the action of acetylcholinesterase are potent neurotoxins, causing excessive salivation and eye-watering in low doses, followed by muscle spasms and ultimately death. Nerve gases and many substances used in insecticides have been shown to act by binding a serine in the active site of acetylcholine esterase, inhibiting the enzyme completely. Acetylcholine esterase breaks down the neurotransmitter acetylcholine, which is released at nerve and muscle junctions, in order to allow the muscle or organ to relax. The result of acetylcholine esterase inhibition is that acetylcholine builds up and continues to act so that any nerve impulses are continually transmitted and muscle contractions do not stop. Among the most common acetylcholinesterase inhibitors are phosphorus-based compounds, which are designed to bind to the active site of the enzyme. The structural requirements are a phosphorus atom bearing two lipophilic groups, a leaving group (such as a halide or thiocyanate), and a terminal oxygen. |
| References |
[1]. Lycorine is a novel inhibitor of the growth and metastasis of hormone-refractory prostate cancer.Oncotarget. 2015 Jun 20;6(17):15348-61. [2]. Discovery of a Potent SCAP Degrader That Ameliorates HFD-induced Obesity, Hyperlipidemia and Insulin Resistance via an Autophagy-Independent Lysosomal Pathway. Autophagy. 2020 May 20;1-22. [3]. Lycorine hydrochloride inhibits metastatic melanoma cell-dominant vasculogenic mimicry. Pigment cell & melanoma research 25, 630-638, doi:10.1111/j.1755-148X.2012.01036.x (2012). |
| Additional Infomation |
Lycorine is an indolizidine alkaloid that is 3,12-didehydrogalanthan substituted by hydroxy groups at positions and 2 and a methylenedioxy group across positions 9 and 10. Isolated from Crinum asiaticum, it has been shown to exhibit antimalarial activity. It has a role as a protein synthesis inhibitor, an antimalarial, a plant metabolite and an anticoronaviral agent. It derives from a hydride of a galanthan. Lycorine has been reported in Crinum moorei, Clivia nobilis, and other organisms with data available. Lycorine is a toxic crystalline alkaloid found in various Amaryllidaceae species, such as the cultivated bush lily (Clivia miniata), surprise lilies (Lycoris), and daffodils (Narcissus). It may be highly poisonous, or even lethal, when ingested in certain quantities. Symptoms of lycorine toxicity are vomiting, diarrhea, and convulsions. Lycorine, definition at mercksource.com Regardless, it is sometimes used medicinally, a reason why some groups may harvest the very popular Clivia miniata. See also: Lycorine hydrochloride (annotation moved to). |
Solubility Data
| Solubility (In Vitro) | DMSO : ~25 mg/mL (~87.01 mM) |
| Solubility (In Vivo) |
Solubility in Formulation 1: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (8.70 mM) (saturation unknown) in 10% DMSO + 40% PEG300 + 5% Tween80 + 45% Saline (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), clear solution. For example, if 1 mL of working solution is to be prepared, you can add 100 μL of 25.0 mg/mL clear DMSO stock solution to 400 μL PEG300 and mix evenly; then add 50 μL Tween-80 to the above solution and mix evenly; then add 450 μL normal saline to adjust the volume to 1 mL. Preparation of saline: Dissolve 0.9 g of sodium chloride in 100 mL ddH₂ O to obtain a clear solution. Solubility in Formulation 2: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (8.70 mM) (saturation unknown) in 10% DMSO + 90% (20% SBE-β-CD in Saline) (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), clear solution. For example, if 1 mL of working solution is to be prepared, you can add 100 μL of 25.0 mg/mL clear DMSO stock solution to 900 μL of 20% SBE-β-CD physiological saline solution and mix evenly. Preparation of 20% SBE-β-CD in Saline (4°C,1 week): Dissolve 2 g SBE-β-CD in 10 mL saline to obtain a clear solution. Solubility in Formulation 3: ≥ 2.5 mg/mL (8.70 mM) (saturation unknown) in 10% DMSO + 90% Corn Oil (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), clear solution. For example, if 1 mL of working solution is to be prepared, you can add 100 μL of 25.0 mg/mL clear DMSO stock solution to 900 μL of corn oil and mix evenly. Solubility in Formulation 4: 25 mg/mL (87.01 mM) in 50% PEG300 50% Saline (add these co-solvents sequentially from left to right, and one by one), suspension solution; with ultrasonication. Preparation of saline: Dissolve 0.9 g of sodium chloride in 100 mL ddH₂ O to obtain a clear solution. (Please use freshly prepared in vivo formulations for optimal results.) |
| Preparing Stock Solutions | 1 mg | 5 mg | 10 mg | |
| 1 mM | 3.4806 mL | 17.4028 mL | 34.8056 mL | |
| 5 mM | 0.6961 mL | 3.4806 mL | 6.9611 mL | |
| 10 mM | 0.3481 mL | 1.7403 mL | 3.4806 mL |