Physicochemical Properties
| Exact Mass | 891.4391578 |
| CAS # | 2858812-91-4 |
| PubChem CID | 162624810 |
| Appearance | Light yellow to yellow solid powder |
| LogP | 2.7 |
| InChi Key | ZYUOWVKGQBMNGW-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| InChi Code | InChI=1S/C46H57N11O8/c1-5-19-56-44(61)36-31-48-45(51-43(36)57(56)38-9-7-8-37(50-38)46(3,4)62)49-33-10-12-34(13-11-33)53-22-20-52(21-23-53)26-28-64-30-29-63-27-18-47-39(58)16-14-35-15-17-42(65-35)55-25-24-54(32-41(55)60)40(59)6-2/h5-13,15,17,31,62H,1-2,14,16,18-30,32H2,3-4H3,(H,47,58)(H,48,49,51) |
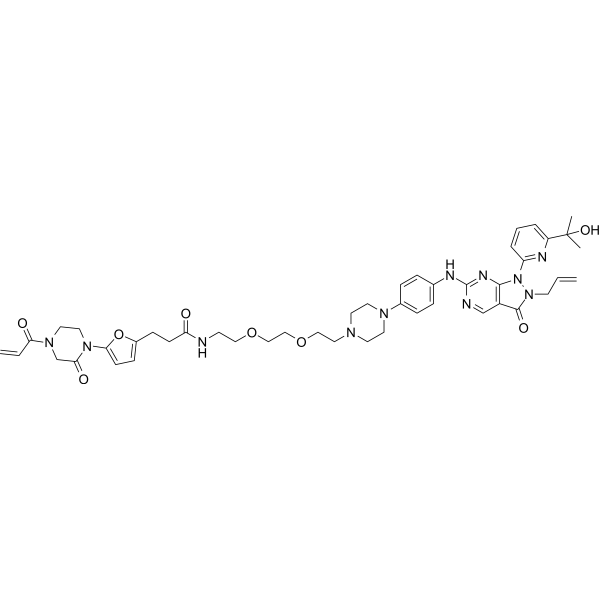
| Chemical Name | N-[2-[2-[2-[4-[4-[[1-[6-(2-hydroxypropan-2-yl)pyridin-2-yl]-3-oxo-2-prop-2-enylpyrazolo[3,4-d]pyrimidin-6-yl]amino]phenyl]piperazin-1-yl]ethoxy]ethoxy]ethyl]-3-[5-(2-oxo-4-prop-2-enoylpiperazin-1-yl)furan-2-yl]propanamide |
| HS Tariff Code | 2934.99.9001 |
| Storage |
Powder-20°C 3 years 4°C 2 years In solvent -80°C 6 months -20°C 1 month |
| Shipping Condition | Room temperature (This product is stable at ambient temperature for a few days during ordinary shipping and time spent in Customs) |
Biological Activity
| Targets | WEE1 |
| ln Vitro | In this study, we discovered a covalent small-molecule recruiter EN523 for the K48-ubiquitin chain-specific DUB OTUB1. We demonstrated that this recruiter can be used incorporated into fully synthetic heterobifunctional DUBTACs by linking a DUB recruiter to protein targeting ligands to enable TPS of actively degraded target proteins in cells. We showed two successful examples of TPS with ΔF508-CFTR and WEE1. For ΔF508-CFTR, we also demonstrated that we not only heightened the levels of the mutant protein, but also improved cell surface chloride channel conductance of CFTR with our DUBTAC in combination with the potentiator ivacaftor, compared to lumacaftor and ivacaftor treatments. While we showed early validation of the DUBTAC platform here, there are many avenues for future exploration. These include further optimization of DUB recruiters against OTUB1 to improve their potency and proteome-wide selectivity, as well as the discovery of new recruiters against other candidate DUBs. For exploring optimization of CFTR DUBTACs, further improvement of the linker between lumacaftor and the DUB recruiter could improve potency and degree of CFTR stabilization. In addition, elucidating the mechanism, structural underpinnings, and kinetics in the formation of the ternary complex formed between CFTR and OTUB1 and understanding how CFTR is deubiquitinated by the DUBTAC will be important. Furthermore, better understanding of whether we are disrupting endogenous OTUB1 function would be important to understanding the mechanism and safety of DUBTACs[1]. |
| References |
[1]. Deubiquitinase-targeting chimeras for targeted protein stabilization. Nat Chem Biol. 2022 Apr;18(4):412-421. |
| Additional Infomation | Many diseases are driven by proteins that are aberrantly ubiquitinated and degraded. These diseases would be therapeutically benefited by targeted protein stabilization (TPS). Here we present deubiquitinase-targeting chimeras (DUBTACs), heterobifunctional small molecules consisting of a deubiquitinase recruiter linked to a protein-targeting ligand, to stabilize the levels of specific proteins degraded in a ubiquitin-dependent manner. Using chemoproteomic approaches, we discovered the covalent ligand EN523 that targets a non-catalytic allosteric cysteine C23 in the K48-ubiquitin-specific deubiquitinase OTUB1. We showed that a DUBTAC consisting of our EN523 OTUB1 recruiter linked to lumacaftor, a drug used to treat cystic fibrosis that binds ΔF508-cystic fibrosis transmembrane conductance regulator (CFTR), robustly stabilized ΔF508-CFTR protein levels, leading to improved chloride channel conductance in human cystic fibrosis bronchial epithelial cells. We also demonstrated stabilization of the tumor suppressor kinase WEE1 in hepatoma cells. Our study showcases covalent chemoproteomic approaches to develop new induced proximity-based therapeutic modalities and introduces the DUBTAC platform for TPS.[1] |
Solubility Data
| Solubility (In Vitro) | May dissolve in DMSO (in most cases), if not, try other solvents such as H2O, Ethanol, or DMF with a minute amount of products to avoid loss of samples |
| Solubility (In Vivo) |
Note: Listed below are some common formulations that may be used to formulate products with low water solubility (e.g. < 1 mg/mL), you may test these formulations using a minute amount of products to avoid loss of samples. Injection Formulations (e.g. IP/IV/IM/SC) Injection Formulation 1: DMSO : Tween 80: Saline = 10 : 5 : 85 (i.e. 100 μL DMSO stock solution → 50 μL Tween 80 → 850 μL Saline) *Preparation of saline: Dissolve 0.9 g of sodium chloride in 100 mL ddH ₂ O to obtain a clear solution. Injection Formulation 2: DMSO : PEG300 :Tween 80 : Saline = 10 : 40 : 5 : 45 (i.e. 100 μL DMSO → 400 μLPEG300 → 50 μL Tween 80 → 450 μL Saline) Injection Formulation 3: DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90 (i.e. 100 μL DMSO → 900 μL Corn oil) Example: Take the Injection Formulation 3 (DMSO : Corn oil = 10 : 90) as an example, if 1 mL of 2.5 mg/mL working solution is to be prepared, you can take 100 μL 25 mg/mL DMSO stock solution and add to 900 μL corn oil, mix well to obtain a clear or suspension solution (2.5 mg/mL, ready for use in animals). Injection Formulation 4: DMSO : 20% SBE-β-CD in saline = 10 : 90 [i.e. 100 μL DMSO → 900 μL (20% SBE-β-CD in saline)] *Preparation of 20% SBE-β-CD in Saline (4°C,1 week): Dissolve 2 g SBE-β-CD in 10 mL saline to obtain a clear solution. Injection Formulation 5: 2-Hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin : Saline = 50 : 50 (i.e. 500 μL 2-Hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin → 500 μL Saline) Injection Formulation 6: DMSO : PEG300 : castor oil : Saline = 5 : 10 : 20 : 65 (i.e. 50 μL DMSO → 100 μLPEG300 → 200 μL castor oil → 650 μL Saline) Injection Formulation 7: Ethanol : Cremophor : Saline = 10: 10 : 80 (i.e. 100 μL Ethanol → 100 μL Cremophor → 800 μL Saline) Injection Formulation 8: Dissolve in Cremophor/Ethanol (50 : 50), then diluted by Saline Injection Formulation 9: EtOH : Corn oil = 10 : 90 (i.e. 100 μL EtOH → 900 μL Corn oil) Injection Formulation 10: EtOH : PEG300:Tween 80 : Saline = 10 : 40 : 5 : 45 (i.e. 100 μL EtOH → 400 μLPEG300 → 50 μL Tween 80 → 450 μL Saline) Oral Formulations Oral Formulation 1: Suspend in 0.5% CMC Na (carboxymethylcellulose sodium) Oral Formulation 2: Suspend in 0.5% Carboxymethyl cellulose Example: Take the Oral Formulation 1 (Suspend in 0.5% CMC Na) as an example, if 100 mL of 2.5 mg/mL working solution is to be prepared, you can first prepare 0.5% CMC Na solution by measuring 0.5 g CMC Na and dissolve it in 100 mL ddH2O to obtain a clear solution; then add 250 mg of the product to 100 mL 0.5% CMC Na solution, to make the suspension solution (2.5 mg/mL, ready for use in animals). Oral Formulation 3: Dissolved in PEG400 Oral Formulation 4: Suspend in 0.2% Carboxymethyl cellulose Oral Formulation 5: Dissolve in 0.25% Tween 80 and 0.5% Carboxymethyl cellulose Oral Formulation 6: Mixing with food powders Note: Please be aware that the above formulations are for reference only. InvivoChem strongly recommends customers to read literature methods/protocols carefully before determining which formulation you should use for in vivo studies, as different compounds have different solubility properties and have to be formulated differently. (Please use freshly prepared in vivo formulations for optimal results.) |